Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1765. Map of Highest Peak
Description
You are given an integer matrix isWater of size m x n that represents a map of land and water cells.
- If
isWater[i][j] == 0, cell(i, j)is a land cell. - If
isWater[i][j] == 1, cell(i, j)is a water cell.
You must assign each cell a height in a way that follows these rules:
- The height of each cell must be non-negative.
- If the cell is a water cell, its height must be
0. - Any two adjacent cells must have an absolute height difference of at most
1. A cell is adjacent to another cell if the former is directly north, east, south, or west of the latter (i.e., their sides are touching).
Find an assignment of heights such that the maximum height in the matrix is maximized.
Return an integer matrix height of size m x n where height[i][j] is cell (i, j)'s height. If there are multiple solutions, return any of them.
Example 1:
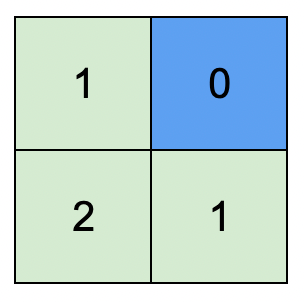
Input: isWater = [[0,1],[0,0]] Output: [[1,0],[2,1]] Explanation: The image shows the assigned heights of each cell. The blue cell is the water cell, and the green cells are the land cells.
Example 2:
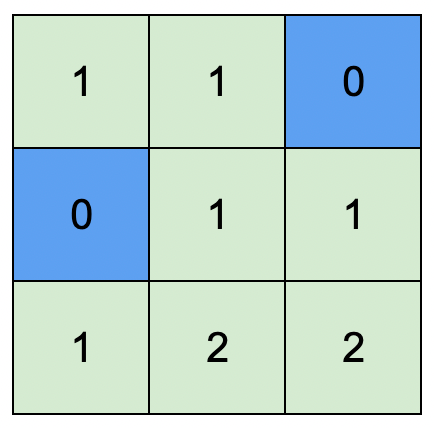
Input: isWater = [[0,0,1],[1,0,0],[0,0,0]] Output: [[1,1,0],[0,1,1],[1,2,2]] Explanation: A height of 2 is the maximum possible height of any assignment. Any height assignment that has a maximum height of 2 while still meeting the rules will also be accepted.
Constraints:
m == isWater.lengthn == isWater[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1000isWater[i][j]is0or1.- There is at least one water cell.
Solutions
Method One: Multi-Source BFS
Based on the problem description, the height of the water area must be $0$, and the height difference between any adjacent cells can be at most $1$.
Therefore, we can start from all water cells, perform BFS to search for adjacent and unvisited cells, and set their heights to the height of the current cell plus one.
Finally, return the resulting matrix.
The time complexity is $O(m \times n)$, and the space complexity is $O(m \times n)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns in the integer matrix isWater, respectively.
-
class Solution { public int[][] highestPeak(int[][] isWater) { int m = isWater.length, n = isWater[0].length; int[][] ans = new int[m][n]; Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { ans[i][j] = isWater[i][j] - 1; if (ans[i][j] == 0) { q.offer(new int[] {i, j}); } } } int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; while (!q.isEmpty()) { var p = q.poll(); int i = p[0], j = p[1]; for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) { ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1; q.offer(new int[] {x, y}); } } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: const int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; vector<vector<int>> highestPeak(vector<vector<int>>& isWater) { int m = isWater.size(), n = isWater[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> ans(m, vector<int>(n)); queue<pair<int, int>> q; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { ans[i][j] = isWater[i][j] - 1; if (ans[i][j] == 0) { q.emplace(i, j); } } } while (!q.empty()) { auto [i, j] = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) { ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1; q.emplace(x, y); } } } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def highestPeak(self, isWater: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: m, n = len(isWater), len(isWater[0]) ans = [[-1] * n for _ in range(m)] q = deque() for i, row in enumerate(isWater): for j, v in enumerate(row): if v: q.append((i, j)) ans[i][j] = 0 while q: i, j = q.popleft() for a, b in pairwise((-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)): x, y = i + a, j + b if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and ans[x][y] == -1: ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1 q.append((x, y)) return ans -
func highestPeak(isWater [][]int) [][]int { m, n := len(isWater), len(isWater[0]) ans := make([][]int, m) type pair struct{ i, j int } q := []pair{} for i, row := range isWater { ans[i] = make([]int, n) for j, v := range row { ans[i][j] = v - 1 if v == 1 { q = append(q, pair{i, j}) } } } dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1} for len(q) > 0 { p := q[0] q = q[1:] i, j := p.i, p.j for k := 0; k < 4; k++ { x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1] if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1 { ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1 q = append(q, pair{x, y}) } } } return ans } -
function highestPeak(isWater: number[][]): number[][] { const m = isWater.length; const n = isWater[0].length; let ans: number[][] = []; let q: number[][] = []; for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { ans.push(new Array(n).fill(-1)); for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (isWater[i][j]) { q.push([i, j]); ans[i][j] = 0; } } } const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1]; while (q.length) { let tq: number[][] = []; for (const [i, j] of q) { for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) { const [x, y] = [i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) { tq.push([x, y]); ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1; } } } q = tq; } return ans; } -
use std::collections::VecDeque; impl Solution { #[allow(dead_code)] pub fn highest_peak(is_water: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> { let n = is_water.len(); let m = is_water[0].len(); let mut ret_vec = vec![vec![-1; m]; n]; let mut q: VecDeque<(usize, usize)> = VecDeque::new(); let vis_pair: Vec<(i32, i32)> = vec![(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]; // Initialize the return vector for i in 0..n { for j in 0..m { if is_water[i][j] == 1 { // This cell is water, the height of which must be 0 ret_vec[i][j] = 0; q.push_back((i, j)); } } } while !q.is_empty() { // Get the front X-Y Coordinates let (x, y) = q.front().unwrap().clone(); q.pop_front(); // Traverse through the vis pair for d in &vis_pair { let (dx, dy) = *d; if Self::check_bounds((x as i32) + dx, (y as i32) + dy, n as i32, m as i32) { if ret_vec[((x as i32) + dx) as usize][((y as i32) + dy) as usize] == -1 { // This cell hasn't been visited, update its height ret_vec[((x as i32) + dx) as usize][((y as i32) + dy) as usize] = ret_vec[x][y] + 1; // Enqueue the current cell q.push_back((((x as i32) + dx) as usize, ((y as i32) + dy) as usize)); } } } } ret_vec } #[allow(dead_code)] fn check_bounds(i: i32, j: i32, n: i32, m: i32) -> bool { i >= 0 && i < n && j >= 0 && j < m } }