Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1606. Find Servers That Handled Most Number of Requests
Description
You have k servers numbered from 0 to k-1 that are being used to handle multiple requests simultaneously. Each server has infinite computational capacity but cannot handle more than one request at a time. The requests are assigned to servers according to a specific algorithm:
- The
ith(0-indexed) request arrives. - If all servers are busy, the request is dropped (not handled at all).
- If the
(i % k)thserver is available, assign the request to that server. - Otherwise, assign the request to the next available server (wrapping around the list of servers and starting from 0 if necessary). For example, if the
ithserver is busy, try to assign the request to the(i+1)thserver, then the(i+2)thserver, and so on.
You are given a strictly increasing array arrival of positive integers, where arrival[i] represents the arrival time of the ith request, and another array load, where load[i] represents the load of the ith request (the time it takes to complete). Your goal is to find the busiest server(s). A server is considered busiest if it handled the most number of requests successfully among all the servers.
Return a list containing the IDs (0-indexed) of the busiest server(s). You may return the IDs in any order.
Example 1:
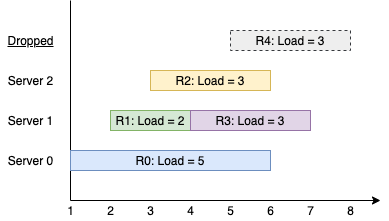
Input: k = 3, arrival = [1,2,3,4,5], load = [5,2,3,3,3] Output: [1] Explanation: All of the servers start out available. The first 3 requests are handled by the first 3 servers in order. Request 3 comes in. Server 0 is busy, so it's assigned to the next available server, which is 1. Request 4 comes in. It cannot be handled since all servers are busy, so it is dropped. Servers 0 and 2 handled one request each, while server 1 handled two requests. Hence server 1 is the busiest server.
Example 2:
Input: k = 3, arrival = [1,2,3,4], load = [1,2,1,2] Output: [0] Explanation: The first 3 requests are handled by first 3 servers. Request 3 comes in. It is handled by server 0 since the server is available. Server 0 handled two requests, while servers 1 and 2 handled one request each. Hence server 0 is the busiest server.
Example 3:
Input: k = 3, arrival = [1,2,3], load = [10,12,11] Output: [0,1,2] Explanation: Each server handles a single request, so they are all considered the busiest.
Constraints:
1 <= k <= 1051 <= arrival.length, load.length <= 105arrival.length == load.length1 <= arrival[i], load[i] <= 109arrivalis strictly increasing.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public List<Integer> busiestServers(int k, int[] arrival, int[] load) { int[] cnt = new int[k]; PriorityQueue<int[]> busy = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0])); TreeSet<Integer> free = new TreeSet<>(); for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { free.add(i); } for (int i = 0; i < arrival.length; ++i) { int start = arrival[i]; int end = start + load[i]; while (!busy.isEmpty() && busy.peek()[0] <= start) { free.add(busy.poll()[1]); } if (free.isEmpty()) { continue; } Integer server = free.ceiling(i % k); if (server == null) { server = free.first(); } ++cnt[server]; busy.offer(new int[] {end, server}); free.remove(server); } int mx = 0; for (int v : cnt) { mx = Math.max(mx, v); } List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { if (cnt[i] == mx) { ans.add(i); } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<int> busiestServers(int k, vector<int>& arrival, vector<int>& load) { set<int> free; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) free.insert(i); priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<>> busy; vector<int> cnt(k); for (int i = 0; i < arrival.size(); ++i) { int start = arrival[i], end = start + load[i]; while (!busy.empty() && busy.top().first <= start) { free.insert(busy.top().second); busy.pop(); } if (free.empty()) continue; auto p = free.lower_bound(i % k); if (p == free.end()) p = free.begin(); int server = *p; ++cnt[server]; busy.emplace(end, server); free.erase(server); } int mx = *max_element(cnt.begin(), cnt.end()); vector<int> ans; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) if (cnt[i] == mx) ans.push_back(i); return ans; } }; -
from sortedcontainers import SortedList class Solution: def busiestServers(self, k: int, arrival: List[int], load: List[int]) -> List[int]: free = SortedList(range(k)) busy = [] cnt = [0] * k for i, (start, t) in enumerate(zip(arrival, load)): while busy and busy[0][0] <= start: free.add(busy[0][1]) heappop(busy) if not free: continue j = free.bisect_left(i % k) if j == len(free): j = 0 server = free[j] cnt[server] += 1 heappush(busy, (start + t, server)) free.remove(server) mx = max(cnt) return [i for i, v in enumerate(cnt) if v == mx] -
func busiestServers(k int, arrival, load []int) (ans []int) { free := redblacktree.NewWithIntComparator() for i := 0; i < k; i++ { free.Put(i, nil) } busy := hp{} cnt := make([]int, k) for i, t := range arrival { for len(busy) > 0 && busy[0].end <= t { free.Put(busy[0].server, nil) heap.Pop(&busy) } if free.Size() == 0 { continue } p, _ := free.Ceiling(i % k) if p == nil { p = free.Left() } server := p.Key.(int) cnt[server]++ heap.Push(&busy, pair{t + load[i], server}) free.Remove(server) } mx := slices.Max(cnt) for i, v := range cnt { if v == mx { ans = append(ans, i) } } return } type pair struct{ end, server int } type hp []pair func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) } func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].end < h[j].end } func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] } func (h *hp) Push(v any) { *h = append(*h, v.(pair)) } func (h *hp) Pop() any { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }