Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1572. Matrix Diagonal Sum
Description
Given a square matrix mat, return the sum of the matrix diagonals.
Only include the sum of all the elements on the primary diagonal and all the elements on the secondary diagonal that are not part of the primary diagonal.
Example 1:
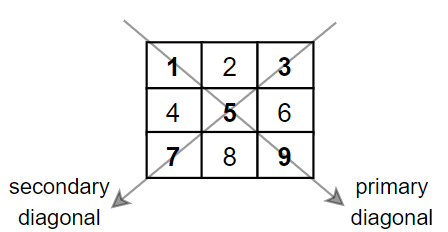
Input: mat = [[1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9]] Output: 25 Explanation: Diagonals sum: 1 + 5 + 9 + 3 + 7 = 25 Notice that element mat[1][1] = 5 is counted only once.
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[1,1,1,1], [1,1,1,1], [1,1,1,1], [1,1,1,1]] Output: 8
Example 3:
Input: mat = [[5]] Output: 5
Constraints:
n == mat.length == mat[i].length1 <= n <= 1001 <= mat[i][j] <= 100
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int diagonalSum(int[][] mat) { int ans = 0; int n = mat.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int j = n - i - 1; ans += mat[i][i] + (i == j ? 0 : mat[i][j]); } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: int diagonalSum(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int ans = 0; int n = mat.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int j = n - i - 1; ans += mat[i][i] + (i == j ? 0 : mat[i][j]); } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def diagonalSum(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> int: ans = 0 n = len(mat) for i, row in enumerate(mat): j = n - i - 1 ans += row[i] + (0 if j == i else row[j]) return ans -
func diagonalSum(mat [][]int) (ans int) { n := len(mat) for i, row := range mat { ans += row[i] if j := n - i - 1; j != i { ans += row[j] } } return } -
function diagonalSum(mat: number[][]): number { let ans = 0; const n = mat.length; for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { const j = n - i - 1; ans += mat[i][i] + (i === j ? 0 : mat[i][j]); } return ans; } -
impl Solution { pub fn diagonal_sum(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 { let n = mat.len(); let mut ans = 0; for i in 0..n { ans += mat[i][i] + mat[n - 1 - i][i]; } if (n & 1) == 1 { ans -= mat[n >> 1][n >> 1]; } ans } }