Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1559. Detect Cycles in 2D Grid
Description
Given a 2D array of characters grid of size m x n, you need to find if there exists any cycle consisting of the same value in grid.
A cycle is a path of length 4 or more in the grid that starts and ends at the same cell. From a given cell, you can move to one of the cells adjacent to it - in one of the four directions (up, down, left, or right), if it has the same value of the current cell.
Also, you cannot move to the cell that you visited in your last move. For example, the cycle (1, 1) -> (1, 2) -> (1, 1) is invalid because from (1, 2) we visited (1, 1) which was the last visited cell.
Return true if any cycle of the same value exists in grid, otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
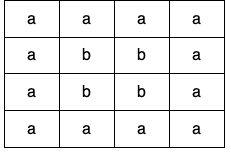
Input: grid = [["a","a","a","a"],["a","b","b","a"],["a","b","b","a"],["a","a","a","a"]] Output: true Explanation: There are two valid cycles shown in different colors in the image below: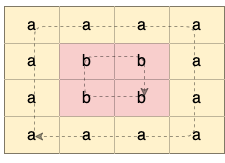
Example 2:
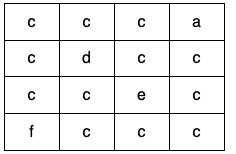
Input: grid = [["c","c","c","a"],["c","d","c","c"],["c","c","e","c"],["f","c","c","c"]] Output: true Explanation: There is only one valid cycle highlighted in the image below: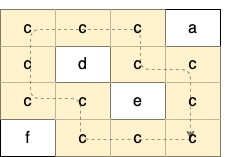
Example 3:
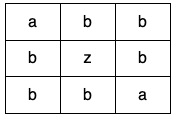
Input: grid = [["a","b","b"],["b","z","b"],["b","b","a"]] Output: false
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500gridconsists only of lowercase English letters.
Solutions
Union find.
-
class Solution { private int[] p; public boolean containsCycle(char[][] grid) { int m = grid.length; int n = grid[0].length; p = new int[m * n]; for (int i = 0; i < p.length; ++i) { p[i] = i; } int[] dirs = {0, 1, 0}; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { for (int k = 0; k < 2; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k]; int y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x < m && y < n && grid[i][j] == grid[x][y]) { if (find(x * n + y) == find(i * n + j)) { return true; } p[find(x * n + y)] = find(i * n + j); } } } } return false; } private int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<int> p; bool containsCycle(vector<vector<char>>& grid) { int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(); p.resize(m * n); for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); ++i) p[i] = i; vector<int> dirs = {0, 1, 0}; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { for (int k = 0; k < 2; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x < m && y < n && grid[x][y] == grid[i][j]) { if (find(x * n + y) == find(i * n + j)) return 1; p[find(x * n + y)] = find(i * n + j); } } } } return 0; } int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]); return p[x]; } }; -
class Solution: def containsCycle(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> bool: def find(x): if p[x] != x: p[x] = find(p[x]) return p[x] m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0]) p = list(range(m * n)) for i in range(m): for j in range(n): for a, b in [[0, 1], [1, 0]]: x, y = i + a, j + b if x < m and y < n and grid[x][y] == grid[i][j]: if find(x * n + y) == find(i * n + j): return True p[find(x * n + y)] = find(i * n + j) return False -
func containsCycle(grid [][]byte) bool { m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0]) p := make([]int, m*n) for i := range p { p[i] = i } var find func(x int) int find = func(x int) int { if p[x] != x { p[x] = find(p[x]) } return p[x] } dirs := []int{1, 0, 1} for i := 0; i < m; i++ { for j := 0; j < n; j++ { for k := 0; k < 2; k++ { x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1] if x < m && y < n && grid[x][y] == grid[i][j] { if find(x*n+y) == find(i*n+j) { return true } p[find(x*n+y)] = find(i*n + j) } } } } return false } -
/** * @param {character[][]} grid * @return {boolean} */ var containsCycle = function (grid) { const m = grid.length; const n = grid[0].length; let p = Array.from({ length: m * n }, (_, i) => i); function find(x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } const dirs = [0, 1, 0]; for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { for (let k = 0; k < 2; ++k) { const x = i + dirs[k]; const y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x < m && y < n && grid[x][y] == grid[i][j]) { if (find(x * n + y) == find(i * n + j)) { return true; } p[find(x * n + y)] = find(i * n + j); } } } } return false; }; -
impl Solution { #[allow(dead_code)] pub fn contains_cycle(grid: Vec<Vec<char>>) -> bool { let n = grid.len(); let m = grid[0].len(); let mut d_set: Vec<usize> = vec![0; n * m]; // Initialize the disjoint set for i in 0..n * m { d_set[i] = i; } // Traverse the grid for i in 0..n { for j in 0..m { if i + 1 < n && grid[i + 1][j] == grid[i][j] { // Check the below cell let p_curr = Self::find(i * m + j, &mut d_set); let p_below = Self::find((i + 1) * m + j, &mut d_set); if p_curr == p_below { return true; } // Otherwise, union the two cells Self::union(p_curr, p_below, &mut d_set); } // Same to the right cell if j + 1 < m && grid[i][j + 1] == grid[i][j] { let p_curr = Self::find(i * m + j, &mut d_set); let p_right = Self::find(i * m + (j + 1), &mut d_set); if p_curr == p_right { return true; } // Otherwise, union the two cells Self::union(p_curr, p_right, &mut d_set); } } } false } #[allow(dead_code)] fn find(x: usize, d_set: &mut Vec<usize>) -> usize { if d_set[x] != x { d_set[x] = Self::find(d_set[x], d_set); } d_set[x] } #[allow(dead_code)] fn union(x: usize, y: usize, d_set: &mut Vec<usize>) { let p_x = Self::find(x, d_set); let p_y = Self::find(y, d_set); d_set[p_x] = p_y; } } -
function containsCycle(grid: string[][]): boolean { const [m, n] = [grid.length, grid[0].length]; const vis: boolean[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(false)); const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1]; for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (!vis[i][j]) { const q: [number, number, number, number][] = [[i, j, -1, -1]]; vis[i][j] = true; for (const [x, y, px, py] of q) { for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) { const [nx, ny] = [x + dirs[k], y + dirs[k + 1]]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n) { if (grid[nx][ny] !== grid[x][y] || (nx === px && ny === py)) { continue; } if (vis[nx][ny]) { return true; } q.push([nx, ny, x, y]); vis[nx][ny] = true; } } } } } } return false; }