Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1536. Minimum Swaps to Arrange a Binary Grid
Description
Given an n x n binary grid, in one step you can choose two adjacent rows of the grid and swap them.
A grid is said to be valid if all the cells above the main diagonal are zeros.
Return the minimum number of steps needed to make the grid valid, or -1 if the grid cannot be valid.
The main diagonal of a grid is the diagonal that starts at cell (1, 1) and ends at cell (n, n).
Example 1:
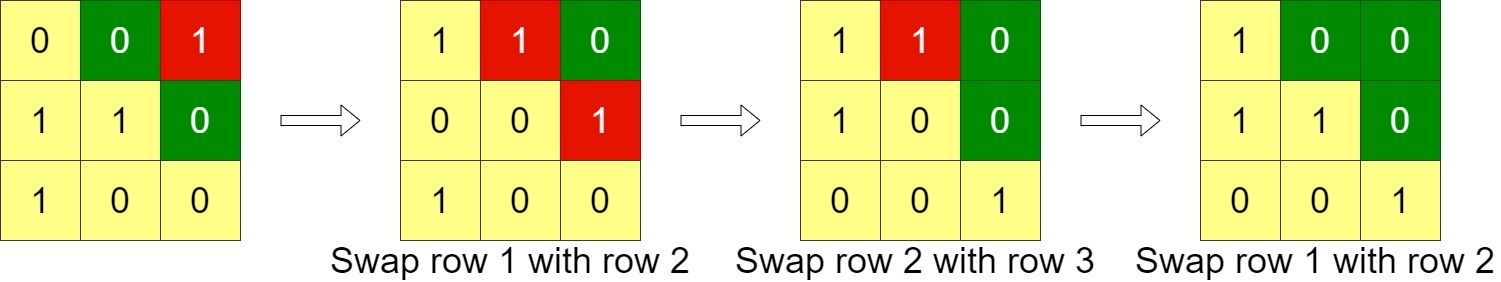
Input: grid = [[0,0,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,0]] Output: 3
Example 2:
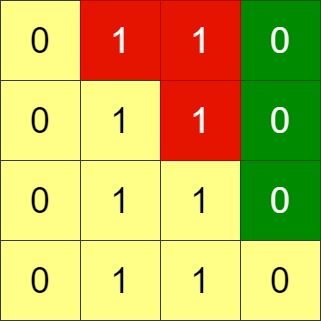
Input: grid = [[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0]] Output: -1 Explanation: All rows are similar, swaps have no effect on the grid.
Example 3:
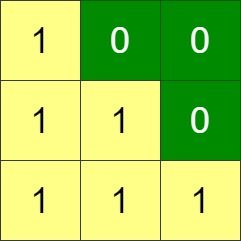
Input: grid = [[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,1]] Output: 0
Constraints:
n == grid.length== grid[i].length1 <= n <= 200grid[i][j]is either0or1
Solutions
Solution 1: Greedy
We process row by row. For the $i$-th row, the position of the last ‘1’ must be less than or equal to $i$. We find the first row that meets the condition in $[i, n)$, denoted as $k$. Then, starting from the $k$-th row, we swap the adjacent two rows upwards until the $i$-th row.
The time complexity is $O(n^2)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the side length of the grid.
-
class Solution { public int minSwaps(int[][] grid) { int n = grid.length; int[] pos = new int[n]; Arrays.fill(pos, -1); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; --j) { if (grid[i][j] == 1) { pos[i] = j; break; } } } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int k = -1; for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) { if (pos[j] <= i) { ans += j - i; k = j; break; } } if (k == -1) { return -1; } for (; k > i; --k) { int t = pos[k]; pos[k] = pos[k - 1]; pos[k - 1] = t; } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: int minSwaps(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int n = grid.size(); vector<int> pos(n, -1); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; --j) { if (grid[i][j] == 1) { pos[i] = j; break; } } } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int k = -1; for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) { if (pos[j] <= i) { ans += j - i; k = j; break; } } if (k == -1) { return -1; } for (; k > i; --k) { swap(pos[k], pos[k - 1]); } } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def minSwaps(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int: n = len(grid) pos = [-1] * n for i in range(n): for j in range(n - 1, -1, -1): if grid[i][j] == 1: pos[i] = j break ans = 0 for i in range(n): k = -1 for j in range(i, n): if pos[j] <= i: ans += j - i k = j break if k == -1: return -1 while k > i: pos[k], pos[k - 1] = pos[k - 1], pos[k] k -= 1 return ans -
func minSwaps(grid [][]int) (ans int) { n := len(grid) pos := make([]int, n) for i := range pos { pos[i] = -1 } for i := 0; i < n; i++ { for j := n - 1; j >= 0; j-- { if grid[i][j] == 1 { pos[i] = j break } } } for i := 0; i < n; i++ { k := -1 for j := i; j < n; j++ { if pos[j] <= i { ans += j - i k = j break } } if k == -1 { return -1 } for ; k > i; k-- { pos[k], pos[k-1] = pos[k-1], pos[k] } } return } -
function minSwaps(grid: number[][]): number { const n = grid.length; const pos: number[] = Array(n).fill(-1); for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (let j = n - 1; ~j; --j) { if (grid[i][j] === 1) { pos[i] = j; break; } } } let ans = 0; for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { let k = -1; for (let j = i; j < n; ++j) { if (pos[j] <= i) { ans += j - i; k = j; break; } } if (k === -1) { return -1; } for (; k > i; --k) { [pos[k], pos[k - 1]] = [pos[k - 1], pos[k]]; } } return ans; }