Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1485. Clone Binary Tree With Random Pointer
Description
A binary tree is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the tree or null.
Return a deep copy of the tree.
The tree is represented in the same input/output way as normal binary trees where each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (in the input) where the random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
You will be given the tree in class Node and you should return the cloned tree in class NodeCopy. NodeCopy class is just a clone of Node class with the same attributes and constructors.
Example 1:
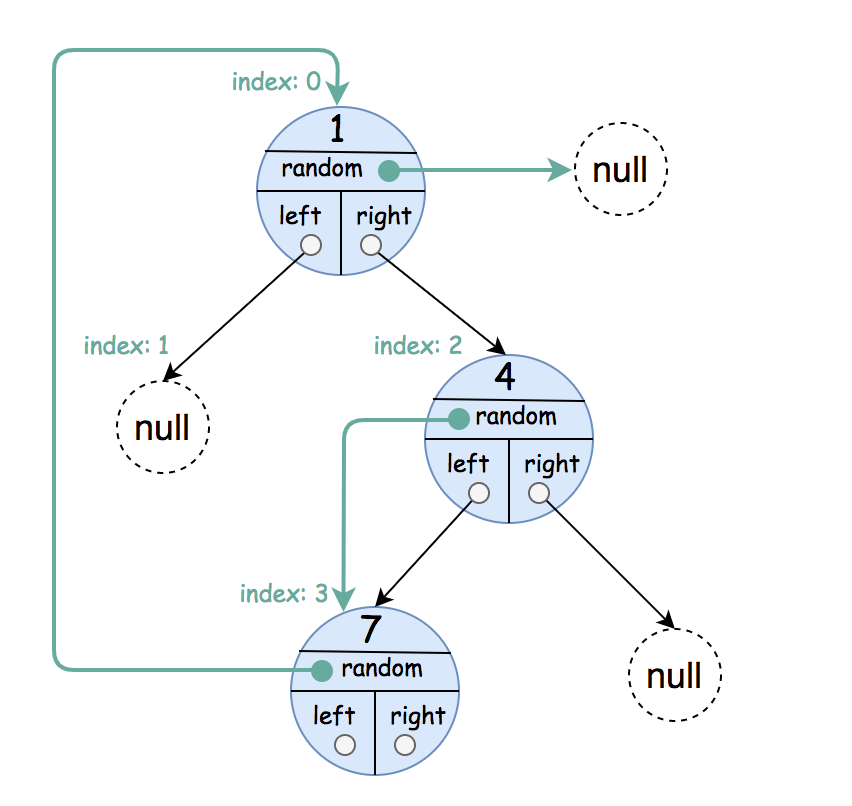
Input: root = [[1,null],null,[4,3],[7,0]] Output: [[1,null],null,[4,3],[7,0]] Explanation: The original binary tree is [1,null,4,7]. The random pointer of node one is null, so it is represented as [1, null]. The random pointer of node 4 is node 7, so it is represented as [4, 3] where 3 is the index of node 7 in the array representing the tree. The random pointer of node 7 is node 1, so it is represented as [7, 0] where 0 is the index of node 1 in the array representing the tree.
Example 2:
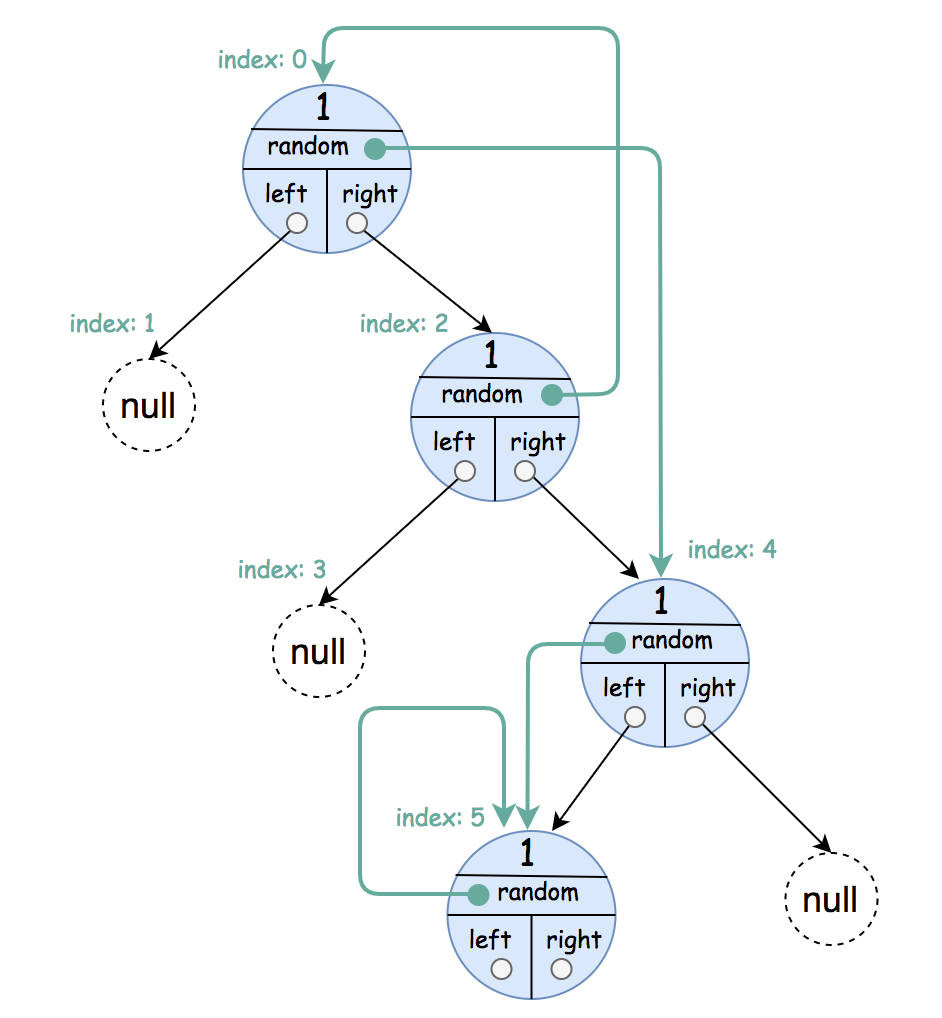
Input: root = [[1,4],null,[1,0],null,[1,5],[1,5]] Output: [[1,4],null,[1,0],null,[1,5],[1,5]] Explanation: The random pointer of a node can be the node itself.
Example 3:
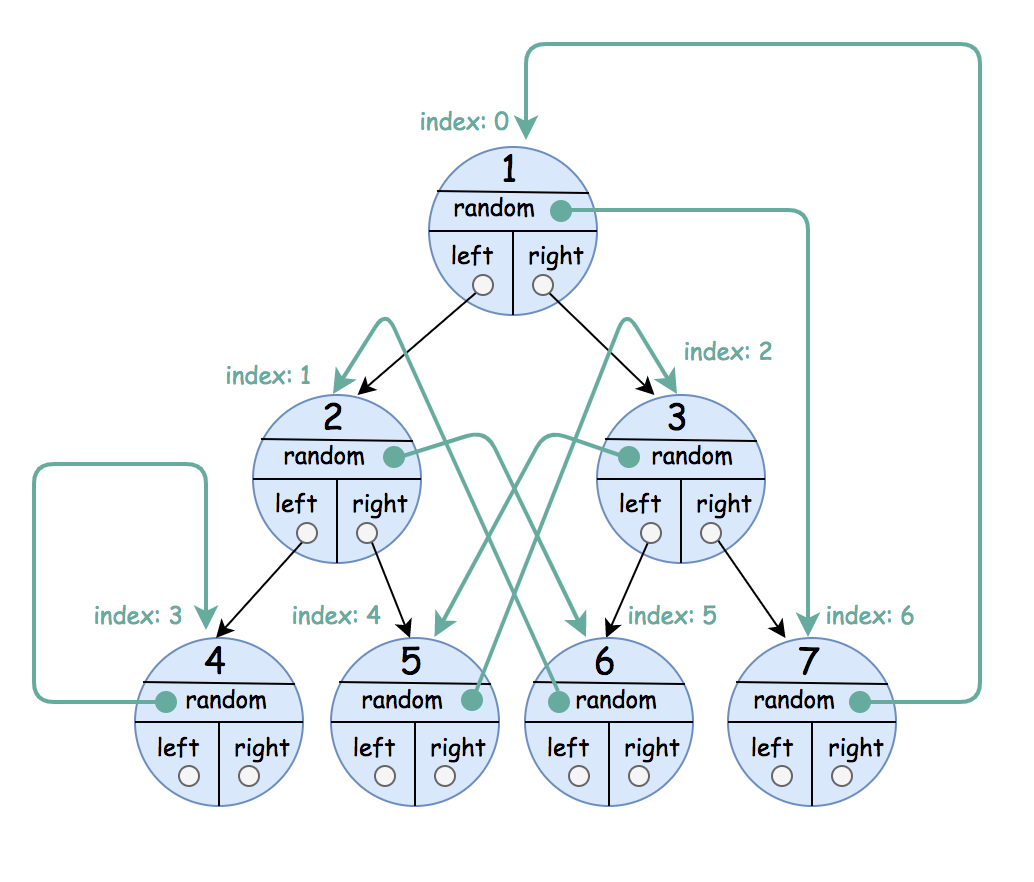
Input: root = [[1,6],[2,5],[3,4],[4,3],[5,2],[6,1],[7,0]] Output: [[1,6],[2,5],[3,4],[4,3],[5,2],[6,1],[7,0]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the
treeis in the range[0, 1000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 106
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for Node. * public class Node { * int val; * Node left; * Node right; * Node random; * Node() {} * Node(int val) { this.val = val; } * Node(int val, Node left, Node right, Node random) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * this.random = random; * } * } */ class Solution { private Map<Node, NodeCopy> mp; public NodeCopy copyRandomBinaryTree(Node root) { mp = new HashMap<>(); return dfs(root); } private NodeCopy dfs(Node root) { if (root == null) { return null; } if (mp.containsKey(root)) { return mp.get(root); } NodeCopy copy = new NodeCopy(root.val); mp.put(root, copy); copy.left = dfs(root.left); copy.right = dfs(root.right); copy.random = dfs(root.random); return copy; } } -
/** * Definition for a Node. * struct Node { * int val; * Node *left; * Node *right; * Node *random; * Node() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr), random(nullptr) {} * Node(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr), random(nullptr) {} * Node(int x, Node *left, Node *right, Node *random) : val(x), left(left), right(right), random(random) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: NodeCopy* copyRandomBinaryTree(Node* root) { unordered_map<Node*, NodeCopy*> mp; return dfs(root, mp); } NodeCopy* dfs(Node* root, unordered_map<Node*, NodeCopy*>& mp) { if (!root) return nullptr; if (mp.count(root)) return mp[root]; NodeCopy* copy = new NodeCopy(root->val); mp[root] = copy; copy->left = dfs(root->left, mp); copy->right = dfs(root->right, mp); copy->random = dfs(root->random, mp); return copy; } }; -
# Definition for Node. # class Node: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None, random=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right # self.random = random class Solution: def copyRandomBinaryTree(self, root: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[NodeCopy]': def dfs(root): if root is None: return None if root in mp: return mp[root] copy = NodeCopy(root.val) mp[root] = copy copy.left = dfs(root.left) copy.right = dfs(root.right) copy.random = dfs(root.random) return copy mp = {} return dfs(root) -
/** * Definition for a Node. * type Node struct { * Val int * Left *Node * Right *Node * Random *Node * } */ func copyRandomBinaryTree(root *Node) *NodeCopy { mp := make(map[*Node]*NodeCopy) var dfs func(root *Node) *NodeCopy dfs = func(root *Node) *NodeCopy { if root == nil { return nil } if v, ok := mp[root]; ok { return v } copy := &NodeCopy{Val: root.Val} mp[root] = copy copy.Left = dfs(root.Left) copy.Right = dfs(root.Right) copy.Random = dfs(root.Random) return copy } return dfs(root) }