Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1443. Minimum Time to Collect All Apples in a Tree
Description
Given an undirected tree consisting of n vertices numbered from 0 to n-1, which has some apples in their vertices. You spend 1 second to walk over one edge of the tree. Return the minimum time in seconds you have to spend to collect all apples in the tree, starting at vertex 0 and coming back to this vertex.
The edges of the undirected tree are given in the array edges, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] means that exists an edge connecting the vertices ai and bi. Additionally, there is a boolean array hasApple, where hasApple[i] = true means that vertex i has an apple; otherwise, it does not have any apple.
Example 1:
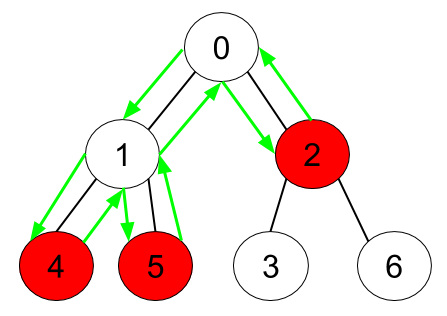
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], hasApple = [false,false,true,false,true,true,false] Output: 8 Explanation: The figure above represents the given tree where red vertices have an apple. One optimal path to collect all apples is shown by the green arrows.
Example 2:
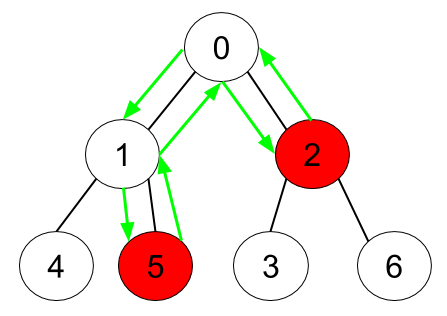
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], hasApple = [false,false,true,false,false,true,false] Output: 6 Explanation: The figure above represents the given tree where red vertices have an apple. One optimal path to collect all apples is shown by the green arrows.
Example 3:
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], hasApple = [false,false,false,false,false,false,false] Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai < bi <= n - 1hasApple.length == n
Solutions
DFS.
-
class Solution { public int minTime(int n, int[][] edges, List<Boolean> hasApple) { boolean[] vis = new boolean[n]; List<Integer>[] g = new List[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int[] e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1]; g[u].add(v); g[v].add(u); } return dfs(0, 0, g, hasApple, vis); } private int dfs(int u, int cost, List<Integer>[] g, List<Boolean> hasApple, boolean[] vis) { if (vis[u]) { return 0; } vis[u] = true; int nxtCost = 0; for (int v : g[u]) { nxtCost += dfs(v, 2, g, hasApple, vis); } if (!hasApple.get(u) && nxtCost == 0) { return 0; } return cost + nxtCost; } } -
class Solution { public: int minTime(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<bool>& hasApple) { vector<bool> vis(n); vector<vector<int>> g(n); for (auto& e : edges) { int u = e[0], v = e[1]; g[u].push_back(v); g[v].push_back(u); } return dfs(0, 0, g, hasApple, vis); } int dfs(int u, int cost, vector<vector<int>>& g, vector<bool>& hasApple, vector<bool>& vis) { if (vis[u]) return 0; vis[u] = true; int nxt = 0; for (int& v : g[u]) nxt += dfs(v, 2, g, hasApple, vis); if (!hasApple[u] && !nxt) return 0; return cost + nxt; } }; -
class Solution: def minTime(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], hasApple: List[bool]) -> int: def dfs(u, cost): if vis[u]: return 0 vis[u] = True nxt_cost = 0 for v in g[u]: nxt_cost += dfs(v, 2) if not hasApple[u] and nxt_cost == 0: return 0 return cost + nxt_cost g = defaultdict(list) for u, v in edges: g[u].append(v) g[v].append(u) vis = [False] * n return dfs(0, 0) -
func minTime(n int, edges [][]int, hasApple []bool) int { vis := make([]bool, n) g := make([][]int, n) for _, e := range edges { u, v := e[0], e[1] g[u] = append(g[u], v) g[v] = append(g[v], u) } var dfs func(int, int) int dfs = func(u, cost int) int { if vis[u] { return 0 } vis[u] = true nxt := 0 for _, v := range g[u] { nxt += dfs(v, 2) } if !hasApple[u] && nxt == 0 { return 0 } return cost + nxt } return dfs(0, 0) }