Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1424. Diagonal Traverse II
Description
Given a 2D integer array nums, return all elements of nums in diagonal order as shown in the below images.
Example 1:
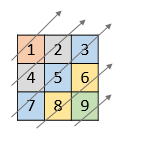
Input: nums = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: [1,4,2,7,5,3,8,6,9]
Example 2:
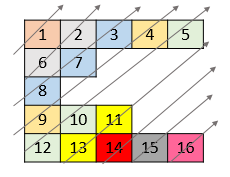
Input: nums = [[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7],[8],[9,10,11],[12,13,14,15,16]] Output: [1,6,2,8,7,3,9,4,12,10,5,13,11,14,15,16]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i].length <= 1051 <= sum(nums[i].length) <= 1051 <= nums[i][j] <= 105
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int[] findDiagonalOrder(List<List<Integer>> nums) { List<int[]> arr = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < nums.get(i).size(); ++j) { arr.add(new int[] {i + j, j, nums.get(i).get(j)}); } } arr.sort((a, b) -> a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] - b[1] : a[0] - b[0]); int[] ans = new int[arr.size()]; for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); ++i) { ans[i] = arr.get(i)[2]; } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<int> findDiagonalOrder(vector<vector<int>>& nums) { vector<tuple<int, int, int>> arr; for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].size(); ++j) { arr.push_back({i + j, j, nums[i][j]}); } } sort(arr.begin(), arr.end()); vector<int> ans; for (auto& e : arr) { ans.push_back(get<2>(e)); } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def findDiagonalOrder(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]: arr = [] for i, row in enumerate(nums): for j, v in enumerate(row): arr.append((i + j, j, v)) arr.sort() return [v[2] for v in arr] -
func findDiagonalOrder(nums [][]int) []int { arr := [][]int{} for i, row := range nums { for j, v := range row { arr = append(arr, []int{i + j, j, v}) } } sort.Slice(arr, func(i, j int) bool { if arr[i][0] == arr[j][0] { return arr[i][1] < arr[j][1] } return arr[i][0] < arr[j][0] }) ans := []int{} for _, v := range arr { ans = append(ans, v[2]) } return ans } -
public class Solution { public int[] FindDiagonalOrder(IList<IList<int>> nums) { List<int[]> arr = new List<int[]>(); for (int i = 0; i < nums.Count; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].Count; ++j) { arr.Add(new int[] { i + j, j, nums[i][j] }); } } arr.Sort((a, b) => a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] - b[1] : a[0] - b[0]); int[] ans = new int[arr.Count]; for (int i = 0; i < arr.Count; ++i) { ans[i] = arr[i][2]; } return ans; } } -
function findDiagonalOrder(nums: number[][]): number[] { const arr: number[][] = []; for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < nums[i].length; ++j) { arr.push([i + j, j, nums[i][j]]); } } arr.sort((a, b) => (a[0] === b[0] ? a[1] - b[1] : a[0] - b[0])); return arr.map(x => x[2]); }