Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1373. Maximum Sum BST in Binary Tree
Description
Given a binary tree root, return the maximum sum of all keys of any sub-tree which is also a Binary Search Tree (BST).
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
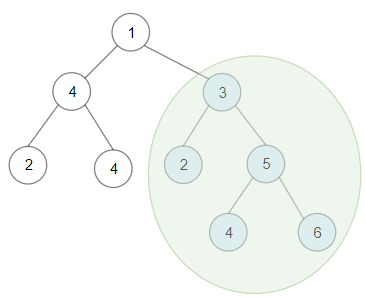
Input: root = [1,4,3,2,4,2,5,null,null,null,null,null,null,4,6] Output: 20 Explanation: Maximum sum in a valid Binary search tree is obtained in root node with key equal to 3.
Example 2:
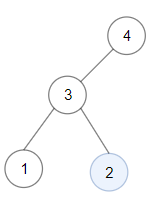
Input: root = [4,3,null,1,2] Output: 2 Explanation: Maximum sum in a valid Binary search tree is obtained in a single root node with key equal to 2.
Example 3:
Input: root = [-4,-2,-5] Output: 0 Explanation: All values are negatives. Return an empty BST.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 4 * 104]. -4 * 104 <= Node.val <= 4 * 104
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS
To determine whether a tree is a binary search tree, it needs to meet the following four conditions:
- The left subtree is a binary search tree;
- The right subtree is a binary search tree;
- The maximum value of the left subtree is less than the value of the root node;
- The minimum value of the right subtree is greater than the value of the root node.
Therefore, we design a function $dfs(root)$, the return value of the function is a quadruple $(bst, mi, mx, s)$, where:
- The number $bst$ indicates whether the tree with $root$ as the root is a binary search tree. If it is a binary search tree, then $bst = 1$; otherwise $bst = 0$;
- The number $mi$ represents the minimum value of the tree with $root$ as the root;
- The number $mx$ represents the maximum value of the tree with $root$ as the root;
- The number $s$ represents the sum of all nodes of the tree with $root$ as the root.
The execution logic of the function $dfs(root)$ is as follows:
If $root$ is an empty node, return $(1, +\infty, -\infty, 0)$, indicating that the empty tree is a binary search tree, the minimum value and maximum value are positive infinity and negative infinity respectively, and the sum of nodes is $0$.
Otherwise, recursively calculate the left subtree and right subtree of $root$, and get $(lbst, lmi, lmx, ls)$ and $(rbst, rmi, rmx, rs)$ respectively, then judge whether the $root$ node meets the conditions of the binary search tree.
If $lbst = 1$ and $rbst = 1$ and $lmx < root.val < rmi$, then the tree with $root$ as the root is a binary search tree, and the sum of nodes $s= ls + rs + root.val$. We update the answer $ans = \max(ans, s)$, and return $(1, \min(lmi, root.val), \max(rmx, root.val), s)$.
Otherwise, the tree with $root$ as the root is not a binary search tree, we return $(0, 0, 0, 0)$.
We call $dfs(root)$ in the main function. After execution, the answer is $ans$.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Where $n$ is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private int ans; private final int inf = 1 << 30; public int maxSumBST(TreeNode root) { dfs(root); return ans; } private int[] dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return new int[] {1, inf, -inf, 0}; } var l = dfs(root.left); var r = dfs(root.right); int v = root.val; if (l[0] == 1 && r[0] == 1 && l[2] < v && r[1] > v) { int s = v + l[3] + r[3]; ans = Math.max(ans, s); return new int[] {1, Math.min(l[1], v), Math.max(r[2], v), s}; } return new int[4]; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int maxSumBST(TreeNode* root) { int ans = 0; const int inf = 1 << 30; function<vector<int>(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) { if (!root) { return vector<int>{1, inf, -inf, 0}; } auto l = dfs(root->left); auto r = dfs(root->right); int v = root->val; if (l[0] && r[0] && l[2] < v && v < r[1]) { int s = l[3] + r[3] + v; ans = max(ans, s); return vector<int>{1, min(l[1], v), max(r[2], v), s}; } return vector<int>(4); }; dfs(root); return ans; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def maxSumBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> tuple: if root is None: return 1, inf, -inf, 0 lbst, lmi, lmx, ls = dfs(root.left) rbst, rmi, rmx, rs = dfs(root.right) if lbst and rbst and lmx < root.val < rmi: nonlocal ans s = ls + rs + root.val ans = max(ans, s) return 1, min(lmi, root.val), max(rmx, root.val), s return 0, 0, 0, 0 ans = 0 dfs(root) return ans -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func maxSumBST(root *TreeNode) (ans int) { const inf = 1 << 30 var dfs func(root *TreeNode) [4]int dfs = func(root *TreeNode) [4]int { if root == nil { return [4]int{1, inf, -inf, 0} } l, r := dfs(root.Left), dfs(root.Right) if l[0] == 1 && r[0] == 1 && l[2] < root.Val && root.Val < r[1] { s := l[3] + r[3] + root.Val ans = max(ans, s) return [4]int{1, min(l[1], root.Val), max(r[2], root.Val), s} } return [4]int{} } dfs(root) return } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function maxSumBST(root: TreeNode | null): number { const inf = 1 << 30; let ans = 0; const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null): [boolean, number, number, number] => { if (!root) { return [true, inf, -inf, 0]; } const [lbst, lmi, lmx, ls] = dfs(root.left); const [rbst, rmi, rmx, rs] = dfs(root.right); if (lbst && rbst && lmx < root.val && root.val < rmi) { const s = ls + rs + root.val; ans = Math.max(ans, s); return [true, Math.min(lmi, root.val), Math.max(rmx, root.val), s]; } return [false, 0, 0, 0]; }; dfs(root); return ans; }