Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1353. Maximum Number of Events That Can Be Attended
Description
You are given an array of events where events[i] = [startDayi, endDayi]. Every event i starts at startDayi and ends at endDayi.
You can attend an event i at any day d where startTimei <= d <= endTimei. You can only attend one event at any time d.
Return the maximum number of events you can attend.
Example 1:
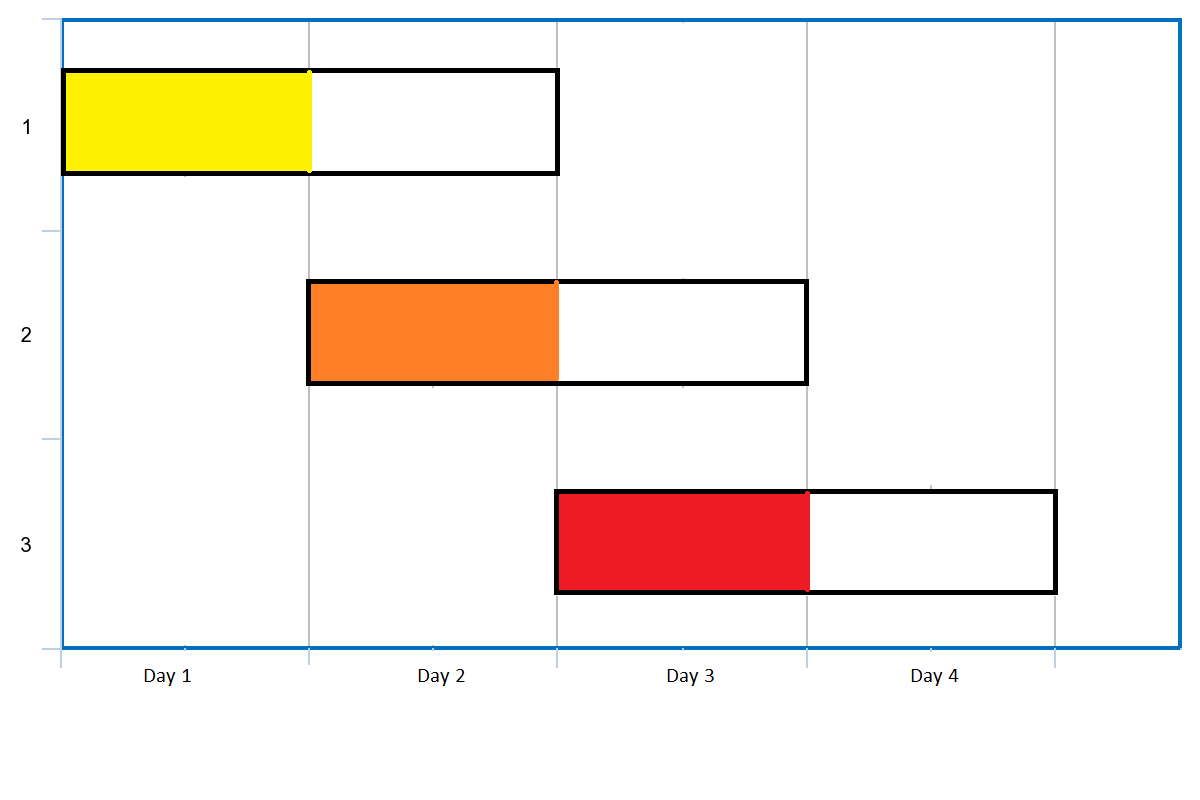
Input: events = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]] Output: 3 Explanation: You can attend all the three events. One way to attend them all is as shown. Attend the first event on day 1. Attend the second event on day 2. Attend the third event on day 3.
Example 2:
Input: events= [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,2]] Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= events.length <= 105events[i].length == 21 <= startDayi <= endDayi <= 105
Solutions
Solution 1: Hash Table + Greedy + Priority Queue
Define a hash table to record the start and end times of each meeting, where the key is the start time of the meeting, and the value is a list of end times.
Enumerate the current time $s$, find all meetings that start at the current time, and add their end times to the priority queue (min heap). At the same time, the priority queue needs to remove all meetings that end before the current time.
Then, take out the meeting with the smallest end time from the priority queue, which is the meeting that can be attended at the current time, and accumulate the answer count. If the priority queue is empty, it means that there are no meetings that can be attended at the current time.
The time complexity is $O(m \times \log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Where $m$ and $n$ represent the maximum end time of the meetings and the number of meetings, respectively.
-
class Solution { public int maxEvents(int[][] events) { Map<Integer, List<Integer>> d = new HashMap<>(); int i = Integer.MAX_VALUE, j = 0; for (var v : events) { int s = v[0], e = v[1]; d.computeIfAbsent(s, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(e); i = Math.min(i, s); j = Math.max(j, e); } PriorityQueue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>(); int ans = 0; for (int s = i; s <= j; ++s) { while (!q.isEmpty() && q.peek() < s) { q.poll(); } for (int e : d.getOrDefault(s, Collections.emptyList())) { q.offer(e); } if (!q.isEmpty()) { q.poll(); ++ans; } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: int maxEvents(vector<vector<int>>& events) { unordered_map<int, vector<int>> d; int i = INT_MAX, j = 0; for (auto& v : events) { int s = v[0], e = v[1]; d[s].push_back(e); i = min(i, s); j = max(j, e); } priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q; int ans = 0; for (int s = i; s <= j; ++s) { while (q.size() && q.top() < s) { q.pop(); } for (int e : d[s]) { q.push(e); } if (q.size()) { ++ans; q.pop(); } } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def maxEvents(self, events: List[List[int]]) -> int: d = defaultdict(list) i, j = inf, 0 for s, e in events: d[s].append(e) i = min(i, s) j = max(j, e) h = [] ans = 0 for s in range(i, j + 1): while h and h[0] < s: heappop(h) for e in d[s]: heappush(h, e) if h: ans += 1 heappop(h) return ans -
func maxEvents(events [][]int) int { d := map[int][]int{} i, j := math.MaxInt32, 0 for _, v := range events { s, e := v[0], v[1] d[s] = append(d[s], e) i = min(i, s) j = max(j, e) } q := hp{} ans := 0 for s := i; s <= j; s++ { for q.Len() > 0 && q.IntSlice[0] < s { heap.Pop(&q) } for _, e := range d[s] { heap.Push(&q, e) } if q.Len() > 0 { heap.Pop(&q) ans++ } } return ans } type hp struct{ sort.IntSlice } func (h *hp) Push(v any) { h.IntSlice = append(h.IntSlice, v.(int)) } func (h *hp) Pop() any { a := h.IntSlice v := a[len(a)-1] h.IntSlice = a[:len(a)-1] return v } func (h *hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h.IntSlice[i] < h.IntSlice[j] }