Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1329. Sort the Matrix Diagonally
Description
A matrix diagonal is a diagonal line of cells starting from some cell in either the topmost row or leftmost column and going in the bottom-right direction until reaching the matrix's end. For example, the matrix diagonal starting from mat[2][0], where mat is a 6 x 3 matrix, includes cells mat[2][0], mat[3][1], and mat[4][2].
Given an m x n matrix mat of integers, sort each matrix diagonal in ascending order and return the resulting matrix.
Example 1:
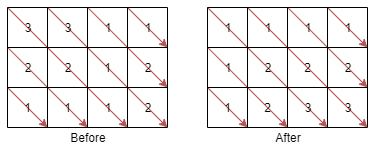
Input: mat = [[3,3,1,1],[2,2,1,2],[1,1,1,2]] Output: [[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2],[1,2,3,3]]
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[11,25,66,1,69,7],[23,55,17,45,15,52],[75,31,36,44,58,8],[22,27,33,25,68,4],[84,28,14,11,5,50]] Output: [[5,17,4,1,52,7],[11,11,25,45,8,69],[14,23,25,44,58,15],[22,27,31,36,50,66],[84,28,75,33,55,68]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1001 <= mat[i][j] <= 100
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int[][] diagonalSort(int[][] mat) { int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; for (int k = 0; k < Math.min(m, n) - 1; ++k) { for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; ++j) { if (mat[i][j] > mat[i + 1][j + 1]) { int t = mat[i][j]; mat[i][j] = mat[i + 1][j + 1]; mat[i + 1][j + 1] = t; } } } } return mat; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> diagonalSort(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size(); for (int k = 0; k < min(m, n) - 1; ++k) for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; ++j) if (mat[i][j] > mat[i + 1][j + 1]) swap(mat[i][j], mat[i + 1][j + 1]); return mat; } }; -
class Solution: def diagonalSort(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0]) for k in range(min(m, n) - 1): for i in range(m - 1): for j in range(n - 1): if mat[i][j] > mat[i + 1][j + 1]: mat[i][j], mat[i + 1][j + 1] = mat[i + 1][j + 1], mat[i][j] return mat -
func diagonalSort(mat [][]int) [][]int { m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0]) for k := 0; k < m-1 && k < n-1; k++ { for i := 0; i < m-1; i++ { for j := 0; j < n-1; j++ { if mat[i][j] > mat[i+1][j+1] { mat[i][j], mat[i+1][j+1] = mat[i+1][j+1], mat[i][j] } } } } return mat } -
function diagonalSort(mat: number[][]): number[][] { const [m, n] = [mat.length, mat[0].length]; const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m + n }, () => []); for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { g[m - i + j].push(mat[i][j]); } } for (const e of g) { e.sort((a, b) => b - a); } for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { mat[i][j] = g[m - i + j].pop()!; } } return mat; } -
public class Solution { public int[][] DiagonalSort(int[][] mat) { int m = mat.Length; int n = mat[0].Length; List<List<int>> g = new List<List<int>>(); for (int i = 0; i < m + n; i++) { g.Add(new List<int>()); } for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { g[m - i + j].Add(mat[i][j]); } } foreach (var e in g) { e.Sort((a, b) => b.CompareTo(a)); } for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { int val = g[m - i + j][g[m - i + j].Count - 1]; g[m - i + j].RemoveAt(g[m - i + j].Count - 1); mat[i][j] = val; } } return mat; } } -
impl Solution { pub fn diagonal_sort(mut mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> { let m = mat.len(); let n = mat[0].len(); let mut g: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![vec![]; m + n]; for i in 0..m { for j in 0..n { g[m - i + j].push(mat[i][j]); } } for e in &mut g { e.sort_by(|a, b| b.cmp(a)); } for i in 0..m { for j in 0..n { mat[i][j] = g[m - i + j].pop().unwrap(); } } mat } }