Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1293. Shortest Path in a Grid with Obstacles Elimination
Description
You are given an m x n integer matrix grid where each cell is either 0 (empty) or 1 (obstacle). You can move up, down, left, or right from and to an empty cell in one step.
Return the minimum number of steps to walk from the upper left corner (0, 0) to the lower right corner (m - 1, n - 1) given that you can eliminate at most k obstacles. If it is not possible to find such walk return -1.
Example 1:
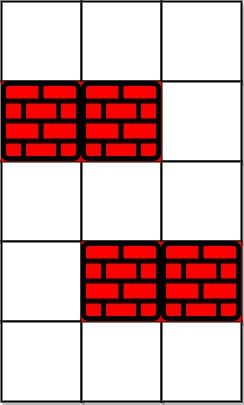
Input: grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,0],[0,1,1],[0,0,0]], k = 1 Output: 6 Explanation: The shortest path without eliminating any obstacle is 10. The shortest path with one obstacle elimination at position (3,2) is 6. Such path is (0,0) -> (0,1) -> (0,2) -> (1,2) -> (2,2) -> (3,2) -> (4,2).
Example 2:
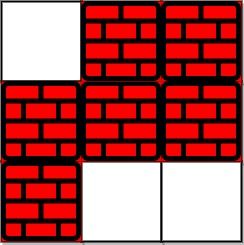
Input: grid = [[0,1,1],[1,1,1],[1,0,0]], k = 1 Output: -1 Explanation: We need to eliminate at least two obstacles to find such a walk.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 401 <= k <= m * ngrid[i][j]is either0or1.grid[0][0] == grid[m - 1][n - 1] == 0
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int shortestPath(int[][] grid, int k) { int m = grid.length; int n = grid[0].length; if (k >= m + n - 3) { return m + n - 2; } Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.offer(new int[] {0, 0, k}); boolean[][][] vis = new boolean[m][n][k + 1]; vis[0][0][k] = true; int ans = 0; int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; while (!q.isEmpty()) { ++ans; for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; --i) { int[] p = q.poll(); k = p[2]; for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) { int x = p[0] + dirs[j]; int y = p[1] + dirs[j + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) { if (x == m - 1 && y == n - 1) { return ans; } if (grid[x][y] == 0 && !vis[x][y][k]) { q.offer(new int[] {x, y, k}); vis[x][y][k] = true; } else if (grid[x][y] == 1 && k > 0 && !vis[x][y][k - 1]) { q.offer(new int[] {x, y, k - 1}); vis[x][y][k - 1] = true; } } } } } return -1; } } -
class Solution { public: int shortestPath(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int k) { int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(); if (k >= m + n - 3) return m + n - 2; queue<vector<int>> q; q.push({0, 0, k}); vector<vector<vector<bool>>> vis(m, vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(k + 1))); vis[0][0][k] = true; int ans = 0; vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; while (!q.empty()) { ++ans; for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; --i) { auto p = q.front(); k = p[2]; q.pop(); for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) { int x = p[0] + dirs[j], y = p[1] + dirs[j + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) { if (x == m - 1 && y == n - 1) return ans; if (grid[x][y] == 0 && !vis[x][y][k]) { q.push({x, y, k}); vis[x][y][k] = true; } else if (grid[x][y] == 1 && k > 0 && !vis[x][y][k - 1]) { q.push({x, y, k - 1}); vis[x][y][k - 1] = true; } } } } } return -1; } }; -
class Solution: def shortestPath(self, grid: List[List[int]], k: int) -> int: m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0]) if k >= m + n - 3: return m + n - 2 q = deque([(0, 0, k)]) vis = {(0, 0, k)} ans = 0 while q: ans += 1 for _ in range(len(q)): i, j, k = q.popleft() for a, b in [[0, -1], [0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]: x, y = i + a, j + b if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n: if x == m - 1 and y == n - 1: return ans if grid[x][y] == 0 and (x, y, k) not in vis: q.append((x, y, k)) vis.add((x, y, k)) if grid[x][y] == 1 and k > 0 and (x, y, k - 1) not in vis: q.append((x, y, k - 1)) vis.add((x, y, k - 1)) return -1 -
func shortestPath(grid [][]int, k int) int { m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0]) if k >= m+n-3 { return m + n - 2 } q := [][]int{[]int{0, 0, k} } vis := make([][][]bool, m) for i := range vis { vis[i] = make([][]bool, n) for j := range vis[i] { vis[i][j] = make([]bool, k+1) } } vis[0][0][k] = true dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1} ans := 0 for len(q) > 0 { ans++ for i := len(q); i > 0; i-- { p := q[0] q = q[1:] k = p[2] for j := 0; j < 4; j++ { x, y := p[0]+dirs[j], p[1]+dirs[j+1] if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n { if x == m-1 && y == n-1 { return ans } if grid[x][y] == 0 && !vis[x][y][k] { q = append(q, []int{x, y, k}) vis[x][y][k] = true } else if grid[x][y] == 1 && k > 0 && !vis[x][y][k-1] { q = append(q, []int{x, y, k - 1}) vis[x][y][k-1] = true } } } } } return -1 } -
function shortestPath(grid: number[][], k: number): number { const m = grid.length; const n = grid[0].length; if (k >= m + n - 3) { return m + n - 2; } let q: Point[] = [[0, 0, k]]; const vis = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array.from({ length: k + 1 }, () => false)), ); vis[0][0][k] = true; const dirs = [0, 1, 0, -1, 0]; let ans = 0; while (q.length) { const nextQ: Point[] = []; ++ans; for (const [i, j, k] of q) { for (let d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { const [x, y] = [i + dirs[d], j + dirs[d + 1]]; if (x === m - 1 && y === n - 1) { return ans; } const v = grid[x]?.[y]; if (v === 0 && !vis[x][y][k]) { nextQ.push([x, y, k]); vis[x][y][k] = true; } else if (v === 1 && k > 0 && !vis[x][y][k - 1]) { nextQ.push([x, y, k - 1]); vis[x][y][k - 1] = true; } } } q = nextQ; } return -1; } type Point = [number, number, number];