Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1284. Minimum Number of Flips to Convert Binary Matrix to Zero Matrix
Description
Given a m x n binary matrix mat. In one step, you can choose one cell and flip it and all the four neighbors of it if they exist (Flip is changing 1 to 0 and 0 to 1). A pair of cells are called neighbors if they share one edge.
Return the minimum number of steps required to convert mat to a zero matrix or -1 if you cannot.
A binary matrix is a matrix with all cells equal to 0 or 1 only.
A zero matrix is a matrix with all cells equal to 0.
Example 1:
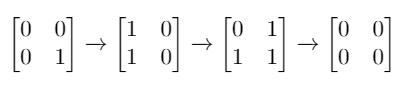
Input: mat = [[0,0],[0,1]] Output: 3 Explanation: One possible solution is to flip (1, 0) then (0, 1) and finally (1, 1) as shown.
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[0]] Output: 0 Explanation: Given matrix is a zero matrix. We do not need to change it.
Example 3:
Input: mat = [[1,0,0],[1,0,0]] Output: -1 Explanation: Given matrix cannot be a zero matrix.
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 3mat[i][j]is either0or1.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int minFlips(int[][] mat) { int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; int state = 0; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (mat[i][j] == 1) { state |= 1 << (i * n + j); } } } Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.offer(state); Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>(); vis.add(state); int ans = 0; int[] dirs = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 0}; while (!q.isEmpty()) { for (int t = q.size(); t > 0; --t) { state = q.poll(); if (state == 0) { return ans; } for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int nxt = state; for (int k = 0; k < 5; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n) { continue; } if ((nxt & (1 << (x * n + y))) != 0) { nxt -= 1 << (x * n + y); } else { nxt |= 1 << (x * n + y); } } if (!vis.contains(nxt)) { vis.add(nxt); q.offer(nxt); } } } } ++ans; } return -1; } } -
class Solution { public: int minFlips(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size(); int state = 0; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) if (mat[i][j]) state |= (1 << (i * n + j)); queue<int> q{ {state} }; unordered_set<int> vis{ {state} }; int ans = 0; vector<int> dirs = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 0}; while (!q.empty()) { for (int t = q.size(); t; --t) { state = q.front(); if (state == 0) return ans; q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int nxt = state; for (int k = 0; k < 5; ++k) { int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1]; if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n) continue; if ((nxt & (1 << (x * n + y))) != 0) nxt -= 1 << (x * n + y); else nxt |= 1 << (x * n + y); } if (!vis.count(nxt)) { vis.insert(nxt); q.push(nxt); } } } } ++ans; } return -1; } }; -
class Solution: def minFlips(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> int: m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0]) state = sum(1 << (i * n + j) for i in range(m) for j in range(n) if mat[i][j]) q = deque([state]) vis = {state} ans = 0 dirs = [0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 0] while q: for _ in range(len(q)): state = q.popleft() if state == 0: return ans for i in range(m): for j in range(n): nxt = state for k in range(5): x, y = i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1] if not 0 <= x < m or not 0 <= y < n: continue if nxt & (1 << (x * n + y)): nxt -= 1 << (x * n + y) else: nxt |= 1 << (x * n + y) if nxt not in vis: vis.add(nxt) q.append(nxt) ans += 1 return -1 -
func minFlips(mat [][]int) int { m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0]) state := 0 for i, row := range mat { for j, v := range row { if v == 1 { state |= 1 << (i*n + j) } } } q := []int{state} vis := map[int]bool{state: true} ans := 0 dirs := []int{0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 0} for len(q) > 0 { for t := len(q); t > 0; t-- { state = q[0] if state == 0 { return ans } q = q[1:] for i := 0; i < m; i++ { for j := 0; j < n; j++ { nxt := state for k := 0; k < 5; k++ { x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1] if x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n { continue } if (nxt & (1 << (x*n + y))) != 0 { nxt -= 1 << (x*n + y) } else { nxt |= 1 << (x*n + y) } } if !vis[nxt] { vis[nxt] = true q = append(q, nxt) } } } } ans++ } return -1 }