Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1272. Remove Interval
Description
A set of real numbers can be represented as the union of several disjoint intervals, where each interval is in the form [a, b). A real number x is in the set if one of its intervals [a, b) contains x (i.e. a <= x < b).
You are given a sorted list of disjoint intervals intervals representing a set of real numbers as described above, where intervals[i] = [ai, bi] represents the interval [ai, bi). You are also given another interval toBeRemoved.
Return the set of real numbers with the interval toBeRemoved removed from intervals. In other words, return the set of real numbers such that every x in the set is in intervals but not in toBeRemoved. Your answer should be a sorted list of disjoint intervals as described above.
Example 1:
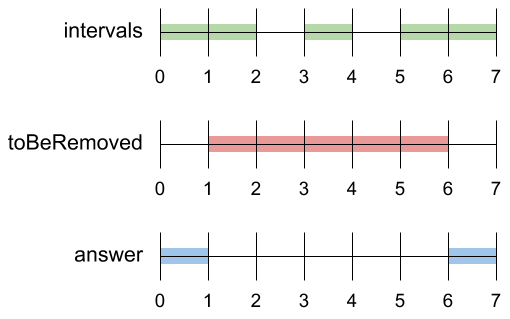
Input: intervals = [[0,2],[3,4],[5,7]], toBeRemoved = [1,6] Output: [[0,1],[6,7]]
Example 2:
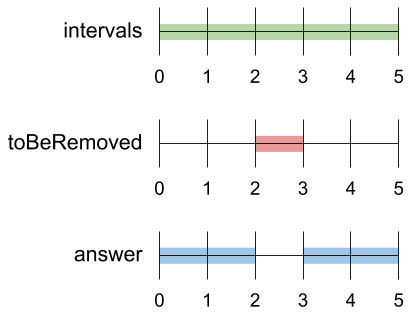
Input: intervals = [[0,5]], toBeRemoved = [2,3] Output: [[0,2],[3,5]]
Example 3:
Input: intervals = [[-5,-4],[-3,-2],[1,2],[3,5],[8,9]], toBeRemoved = [-1,4] Output: [[-5,-4],[-3,-2],[4,5],[8,9]]
Constraints:
1 <= intervals.length <= 104-109 <= ai < bi <= 109
Solutions
Solution 1: Case Discussion
We denote the interval to be removed as $[x, y)$. We traverse the interval list, and for each interval $[a, b)$, there are three cases:
- $a \geq y$ or $b \leq x$, which means that this interval does not intersect with the interval to be removed. We directly add this interval to the answer.
- $a \lt x$, $b \gt y$, which means that this interval intersects with the interval to be removed. We split this interval into two intervals and add them to the answer.
- $a \geq x$, $b \leq y$, which means that this interval is completely covered by the interval to be removed. We do not add it to the answer.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the length of the interval list. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
-
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> removeInterval(int[][] intervals, int[] toBeRemoved) { int x = toBeRemoved[0], y = toBeRemoved[1]; List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (var e : intervals) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; if (a >= y || b <= x) { ans.add(Arrays.asList(a, b)); } else { if (a < x) { ans.add(Arrays.asList(a, x)); } if (b > y) { ans.add(Arrays.asList(y, b)); } } } return ans; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> removeInterval(vector<vector<int>>& intervals, vector<int>& toBeRemoved) { int x = toBeRemoved[0], y = toBeRemoved[1]; vector<vector<int>> ans; for (auto& e : intervals) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; if (a >= y || b <= x) { ans.push_back(e); } else { if (a < x) { ans.push_back({a, x}); } if (b > y) { ans.push_back({y, b}); } } } return ans; } }; -
''' >>> a [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] >>> >>> x, y = a Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> ValueError: too many values to unpack >>> x,y,z,p,q = a >>> x 1 >>> y 2 >>> z 3 ''' class Solution: def removeInterval( self, intervals: List[List[int]], toBeRemoved: List[int] ) -> List[List[int]]: x, y = toBeRemoved ans = [] for a, b in intervals: if a >= y or b <= x: ans.append([a, b]) else: if a < x: ans.append([a, x]) # in this else block, meaning b>x, so no need to append [a,min(b,x)] if b > y: ans.append([y, b]) # if x < a < b < y, then delete (a,b), do nothing and skip here return ans ############ class Solution: def removeInterval( self, intervals: List[List[int]], toBeRemoved: List[int] ) -> List[List[int]]: result = [] for ind, intv in enumerate(intervals): if intv[1] < toBeRemoved[0] or toBeRemoved[1] < intv[0]: result.append(intv) else: if intv[0] < toBeRemoved[0]: result.append([intv[0], min(intv[1], toBeRemoved[0])]) # min() is not needed if intv[1] > toBeRemoved[1]: result.append([max(intv[0], toBeRemoved[1]), intv[1]]) return result -
func removeInterval(intervals [][]int, toBeRemoved []int) (ans [][]int) { x, y := toBeRemoved[0], toBeRemoved[1] for _, e := range intervals { a, b := e[0], e[1] if a >= y || b <= x { ans = append(ans, e) } else { if a < x { ans = append(ans, []int{a, x}) } if b > y { ans = append(ans, []int{y, b}) } } } return }