Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1214. Two Sum BSTs
Description
Given the roots of two binary search trees, root1 and root2, return true if and only if there is a node in the first tree and a node in the second tree whose values sum up to a given integer target.
Example 1:
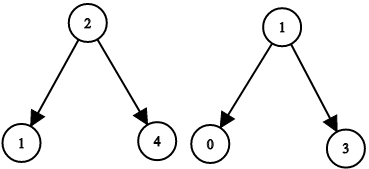
Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3], target = 5 Output: true Explanation: 2 and 3 sum up to 5.
Example 2:
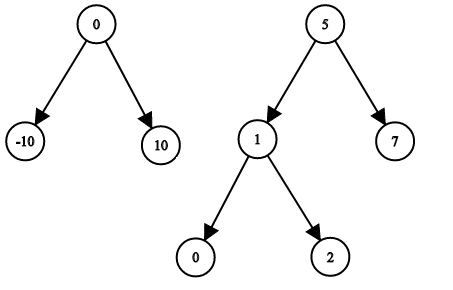
Input: root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2], target = 18 Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree is in the range
[1, 5000]. -109 <= Node.val, target <= 109
Solutions
Solution 1: In-order Traversal + Two Pointers
We perform in-order traversals on the two trees separately, obtaining two sorted arrays $nums[0]$ and $nums[1]$. Then we use a two-pointer method to determine whether there exist two numbers whose sum equals the target value. The two-pointer method is as follows:
Initialize two pointers $i$ and $j$, pointing to the left boundary of array $nums[0]$ and the right boundary of array $nums[1]$ respectively;
Each time, compare the sum $x = nums[0][i] + nums[1][j]$ with the target value. If $x = target$, return true; otherwise, if $x \lt target$, move $i$ one step to the right; otherwise, if $x \gt target$, move $j$ one step to the left.
The time complexity is $O(m + n)$, and the space complexity is $O(m + n)$. Here, $m$ and $n$ are the number of nodes in the two trees respectively.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private List<Integer>[] nums = new List[2]; public boolean twoSumBSTs(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2, int target) { Arrays.setAll(nums, k -> new ArrayList<>()); dfs(root1, 0); dfs(root2, 1); int i = 0, j = nums[1].size() - 1; while (i < nums[0].size() && j >= 0) { int x = nums[0].get(i) + nums[1].get(j); if (x == target) { return true; } if (x < target) { ++i; } else { --j; } } return false; } private void dfs(TreeNode root, int i) { if (root == null) { return; } dfs(root.left, i); nums[i].add(root.val); dfs(root.right, i); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool twoSumBSTs(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2, int target) { vector<int> nums[2]; function<void(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int i) { if (!root) { return; } dfs(root->left, i); nums[i].push_back(root->val); dfs(root->right, i); }; dfs(root1, 0); dfs(root2, 1); int i = 0, j = nums[1].size() - 1; while (i < nums[0].size() && j >= 0) { int x = nums[0][i] + nums[1][j]; if (x == target) { return true; } if (x < target) { ++i; } else { --j; } } return false; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def twoSumBSTs( self, root1: Optional[TreeNode], root2: Optional[TreeNode], target: int ) -> bool: def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode], i: int): if root is None: return dfs(root.left, i) nums[i].append(root.val) dfs(root.right, i) nums = [[], []] dfs(root1, 0) dfs(root2, 1) i, j = 0, len(nums[1]) - 1 while i < len(nums[0]) and ~j: x = nums[0][i] + nums[1][j] if x == target: return True if x < target: i += 1 else: j -= 1 return False -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func twoSumBSTs(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode, target int) bool { nums := [2][]int{} var dfs func(*TreeNode, int) dfs = func(root *TreeNode, i int) { if root == nil { return } dfs(root.Left, i) nums[i] = append(nums[i], root.Val) dfs(root.Right, i) } dfs(root1, 0) dfs(root2, 1) i, j := 0, len(nums[1])-1 for i < len(nums[0]) && j >= 0 { x := nums[0][i] + nums[1][j] if x == target { return true } if x < target { i++ } else { j-- } } return false } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function twoSumBSTs(root1: TreeNode | null, root2: TreeNode | null, target: number): boolean { const nums: number[][] = Array(2) .fill(0) .map(() => []); const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null, i: number) => { if (!root) { return; } dfs(root.left, i); nums[i].push(root.val); dfs(root.right, i); }; dfs(root1, 0); dfs(root2, 1); let i = 0; let j = nums[1].length - 1; while (i < nums[0].length && j >= 0) { const x = nums[0][i] + nums[1][j]; if (x === target) { return true; } if (x < target) { ++i; } else { --j; } } return false; }