Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1203. Sort Items by Groups Respecting Dependencies
Description
There are n items each belonging to zero or one of m groups where group[i] is the group that the i-th item belongs to and it's equal to -1 if the i-th item belongs to no group. The items and the groups are zero indexed. A group can have no item belonging to it.
Return a sorted list of the items such that:
- The items that belong to the same group are next to each other in the sorted list.
- There are some relations between these items where
beforeItems[i]is a list containing all the items that should come before thei-th item in the sorted array (to the left of thei-th item).
Return any solution if there is more than one solution and return an empty list if there is no solution.
Example 1:
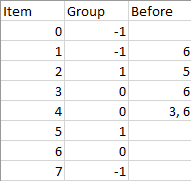
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3,6],[],[],[]] Output: [6,3,4,1,5,2,0,7]
Example 2:
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3],[],[4],[]] Output: [] Explanation: This is the same as example 1 except that 4 needs to be before 6 in the sorted list.
Constraints:
1 <= m <= n <= 3 * 104group.length == beforeItems.length == n-1 <= group[i] <= m - 10 <= beforeItems[i].length <= n - 10 <= beforeItems[i][j] <= n - 1i != beforeItems[i][j]beforeItems[i]does not contain duplicates elements.
Solutions
Solution 1: Topological Sorting
First, we traverse the array $group$. For each project, if it does not belong to any group, we create a new group for it with the ID $m$, and increment $m$. This ensures that all projects belong to some group. Then, we use an array $groupItems$ to record the projects contained in each group. The array index is the group ID, and the array value is the list of projects in the group.
Next, we need to build the graph. For each project, we need to build two types of graphs: one for the projects and one for the groups. We traverse the array $group$. For the current project $i$, its group is $group[i]$. We traverse $beforeItems[i]$, and for each project $j$ in it, if $group[i] = group[j]$, it means that $i$ and $j$ belong to the same group. We add an edge $j \to i$ in the project graph. Otherwise, it means that $i$ and $j$ belong to different groups. We add an edge $group[j] \to group[i]$ in the group graph, and update the corresponding in-degree array.
Next, we perform topological sorting on the group graph to get the sorted group list $groupOrder$. If the length of the sorted list is not equal to the total number of groups, it means that the sorting cannot be completed, so we return an empty list. Otherwise, we traverse $groupOrder$, and for each group $gi$, we perform topological sorting on the project list $groupItems[gi]$ to get the sorted project list $itemOrder$. If the length of the sorted list is not equal to the total number of projects in the group, it means that the sorting cannot be completed, so we return an empty list. Otherwise, we add the projects in $itemOrder$ to the answer array, and finally return this answer array.
The time complexity is $O(n + m)$, and the space complexity is $O(n + m)$. Here, $n$ and $m$ are the total number of projects and groups, respectively.
-
class Solution { public int[] sortItems(int n, int m, int[] group, List<List<Integer>> beforeItems) { int idx = m; List<Integer>[] groupItems = new List[n + m]; int[] itemDegree = new int[n]; int[] groupDegree = new int[n + m]; List<Integer>[] itemGraph = new List[n]; List<Integer>[] groupGraph = new List[n + m]; Arrays.setAll(groupItems, k -> new ArrayList<>()); Arrays.setAll(itemGraph, k -> new ArrayList<>()); Arrays.setAll(groupGraph, k -> new ArrayList<>()); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (group[i] == -1) { group[i] = idx++; } groupItems[group[i]].add(i); } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j : beforeItems.get(i)) { if (group[i] == group[j]) { ++itemDegree[i]; itemGraph[j].add(i); } else { ++groupDegree[group[i]]; groupGraph[group[j]].add(group[i]); } } } List<Integer> items = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n + m; ++i) { items.add(i); } var groupOrder = topoSort(groupDegree, groupGraph, items); if (groupOrder.isEmpty()) { return new int[0]; } List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (int gi : groupOrder) { items = groupItems[gi]; var itemOrder = topoSort(itemDegree, itemGraph, items); if (itemOrder.size() != items.size()) { return new int[0]; } ans.addAll(itemOrder); } return ans.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray(); } private List<Integer> topoSort(int[] degree, List<Integer>[] graph, List<Integer> items) { Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); for (int i : items) { if (degree[i] == 0) { q.offer(i); } } List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(); while (!q.isEmpty()) { int i = q.poll(); ans.add(i); for (int j : graph[i]) { if (--degree[j] == 0) { q.offer(j); } } } return ans.size() == items.size() ? ans : List.of(); } } -
class Solution { public: vector<int> sortItems(int n, int m, vector<int>& group, vector<vector<int>>& beforeItems) { int idx = m; vector<vector<int>> groupItems(n + m); vector<int> itemDegree(n); vector<int> groupDegree(n + m); vector<vector<int>> itemGraph(n); vector<vector<int>> groupGraph(n + m); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (group[i] == -1) { group[i] = idx++; } groupItems[group[i]].push_back(i); } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j : beforeItems[i]) { if (group[i] == group[j]) { ++itemDegree[i]; itemGraph[j].push_back(i); } else { ++groupDegree[group[i]]; groupGraph[group[j]].push_back(group[i]); } } } vector<int> items(n + m); iota(items.begin(), items.end(), 0); auto topoSort = [](vector<vector<int>>& graph, vector<int>& degree, vector<int>& items) -> vector<int> { queue<int> q; for (int& i : items) { if (degree[i] == 0) { q.push(i); } } vector<int> ans; while (!q.empty()) { int i = q.front(); q.pop(); ans.push_back(i); for (int& j : graph[i]) { if (--degree[j] == 0) { q.push(j); } } } return ans.size() == items.size() ? ans : vector<int>(); }; auto groupOrder = topoSort(groupGraph, groupDegree, items); if (groupOrder.empty()) { return vector<int>(); } vector<int> ans; for (int& gi : groupOrder) { items = groupItems[gi]; auto itemOrder = topoSort(itemGraph, itemDegree, items); if (items.size() != itemOrder.size()) { return vector<int>(); } ans.insert(ans.end(), itemOrder.begin(), itemOrder.end()); } return ans; } }; -
class Solution: def sortItems( self, n: int, m: int, group: List[int], beforeItems: List[List[int]] ) -> List[int]: def topo_sort(degree, graph, items): q = deque(i for _, i in enumerate(items) if degree[i] == 0) res = [] while q: i = q.popleft() res.append(i) for j in graph[i]: degree[j] -= 1 if degree[j] == 0: q.append(j) return res if len(res) == len(items) else [] idx = m group_items = [[] for _ in range(n + m)] for i, g in enumerate(group): if g == -1: group[i] = idx idx += 1 group_items[group[i]].append(i) item_degree = [0] * n group_degree = [0] * (n + m) item_graph = [[] for _ in range(n)] group_graph = [[] for _ in range(n + m)] for i, gi in enumerate(group): for j in beforeItems[i]: gj = group[j] if gi == gj: item_degree[i] += 1 item_graph[j].append(i) else: group_degree[gi] += 1 group_graph[gj].append(gi) group_order = topo_sort(group_degree, group_graph, range(n + m)) if not group_order: return [] ans = [] for gi in group_order: items = group_items[gi] item_order = topo_sort(item_degree, item_graph, items) if len(items) != len(item_order): return [] ans.extend(item_order) return ans -
func sortItems(n int, m int, group []int, beforeItems [][]int) []int { idx := m groupItems := make([][]int, n+m) itemDegree := make([]int, n) groupDegree := make([]int, n+m) itemGraph := make([][]int, n) groupGraph := make([][]int, n+m) for i, g := range group { if g == -1 { group[i] = idx idx++ } groupItems[group[i]] = append(groupItems[group[i]], i) } for i, gi := range group { for _, j := range beforeItems[i] { gj := group[j] if gi == gj { itemDegree[i]++ itemGraph[j] = append(itemGraph[j], i) } else { groupDegree[gi]++ groupGraph[gj] = append(groupGraph[gj], gi) } } } items := make([]int, n+m) for i := range items { items[i] = i } topoSort := func(degree []int, graph [][]int, items []int) []int { q := []int{} for _, i := range items { if degree[i] == 0 { q = append(q, i) } } ans := []int{} for len(q) > 0 { i := q[0] q = q[1:] ans = append(ans, i) for _, j := range graph[i] { degree[j]-- if degree[j] == 0 { q = append(q, j) } } } return ans } groupOrder := topoSort(groupDegree, groupGraph, items) if len(groupOrder) != len(items) { return nil } ans := []int{} for _, gi := range groupOrder { items = groupItems[gi] itemOrder := topoSort(itemDegree, itemGraph, items) if len(items) != len(itemOrder) { return nil } ans = append(ans, itemOrder...) } return ans } -
function sortItems(n: number, m: number, group: number[], beforeItems: number[][]): number[] { let idx = m; const groupItems: number[][] = new Array(n + m).fill(0).map(() => []); const itemDegree: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0); const gorupDegree: number[] = new Array(n + m).fill(0); const itemGraph: number[][] = new Array(n).fill(0).map(() => []); const groupGraph: number[][] = new Array(n + m).fill(0).map(() => []); for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (group[i] === -1) { group[i] = idx++; } groupItems[group[i]].push(i); } for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (const j of beforeItems[i]) { if (group[i] === group[j]) { ++itemDegree[i]; itemGraph[j].push(i); } else { ++gorupDegree[group[i]]; groupGraph[group[j]].push(group[i]); } } } let items = new Array(n + m).fill(0).map((_, i) => i); const topoSort = (graph: number[][], degree: number[], items: number[]): number[] => { const q: number[] = []; for (const i of items) { if (degree[i] === 0) { q.push(i); } } const ans: number[] = []; while (q.length) { const i = q.pop()!; ans.push(i); for (const j of graph[i]) { if (--degree[j] === 0) { q.push(j); } } } return ans.length === items.length ? ans : []; }; const groupOrder = topoSort(groupGraph, gorupDegree, items); if (groupOrder.length === 0) { return []; } const ans: number[] = []; for (const gi of groupOrder) { items = groupItems[gi]; const itemOrder = topoSort(itemGraph, itemDegree, items); if (itemOrder.length !== items.length) { return []; } ans.push(...itemOrder); } return ans; }