Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1105. Filling Bookcase Shelves
Description
You are given an array books where books[i] = [thicknessi, heighti] indicates the thickness and height of the ith book. You are also given an integer shelfWidth.
We want to place these books in order onto bookcase shelves that have a total width shelfWidth.
We choose some of the books to place on this shelf such that the sum of their thickness is less than or equal to shelfWidth, then build another level of the shelf of the bookcase so that the total height of the bookcase has increased by the maximum height of the books we just put down. We repeat this process until there are no more books to place.
Note that at each step of the above process, the order of the books we place is the same order as the given sequence of books.
- For example, if we have an ordered list of
5books, we might place the first and second book onto the first shelf, the third book on the second shelf, and the fourth and fifth book on the last shelf.
Return the minimum possible height that the total bookshelf can be after placing shelves in this manner.
Example 1:
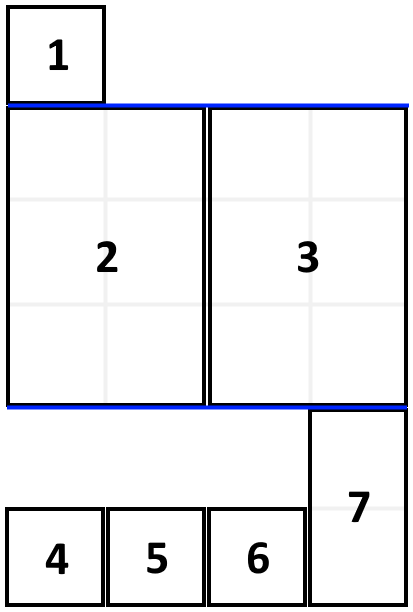
Input: books = [[1,1],[2,3],[2,3],[1,1],[1,1],[1,1],[1,2]], shelfWidth = 4 Output: 6 Explanation: The sum of the heights of the 3 shelves is 1 + 3 + 2 = 6. Notice that book number 2 does not have to be on the first shelf.
Example 2:
Input: books = [[1,3],[2,4],[3,2]], shelfWidth = 6 Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= books.length <= 10001 <= thicknessi <= shelfWidth <= 10001 <= heighti <= 1000
Solutions
Solution 1: Dynamic Programming
We define $f[i]$ as the minimum height for placing the first $i$ books, initially $f[0] = 0$, and the answer is $f[n]$.
Consider $f[i]$, the last book is $books[i - 1]$, its thickness is $w$, and its height is $h$.
- If this book is placed on a new layer alone, then $f[i] = f[i - 1] + h$;
- If this book can be placed on the same layer with the last few books in front, we enumerate the first book $books[j-1]$ on the same layer from back to front, where $j \in [1, i - 1]$, accumulate the thickness of the book to $w$, if $w > shelfWidth$, it means that $books[j-1]$ can no longer be placed on the same layer with $books[i-1]$, stop enumeration; otherwise, we update the maximum height $h = \max(h, books[j-1][1])$ of the current layer, then $f[i] = \min(f[i], f[j - 1] + h)$.
The final answer is $f[n]$.
The time complexity is $O(n^2)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the length of the array $books$.
-
class Solution { public int minHeightShelves(int[][] books, int shelfWidth) { int n = books.length; int[] f = new int[n + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { int w = books[i - 1][0], h = books[i - 1][1]; f[i] = f[i - 1] + h; for (int j = i - 1; j > 0; --j) { w += books[j - 1][0]; if (w > shelfWidth) { break; } h = Math.max(h, books[j - 1][1]); f[i] = Math.min(f[i], f[j - 1] + h); } } return f[n]; } } -
class Solution { public: int minHeightShelves(vector<vector<int>>& books, int shelfWidth) { int n = books.size(); int f[n + 1]; f[0] = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { int w = books[i - 1][0], h = books[i - 1][1]; f[i] = f[i - 1] + h; for (int j = i - 1; j > 0; --j) { w += books[j - 1][0]; if (w > shelfWidth) { break; } h = max(h, books[j - 1][1]); f[i] = min(f[i], f[j - 1] + h); } } return f[n]; } }; -
class Solution: def minHeightShelves(self, books: List[List[int]], shelfWidth: int) -> int: n = len(books) f = [0] * (n + 1) for i, (w, h) in enumerate(books, 1): f[i] = f[i - 1] + h for j in range(i - 1, 0, -1): w += books[j - 1][0] if w > shelfWidth: break h = max(h, books[j - 1][1]) f[i] = min(f[i], f[j - 1] + h) return f[n] -
func minHeightShelves(books [][]int, shelfWidth int) int { n := len(books) f := make([]int, n+1) for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { w, h := books[i-1][0], books[i-1][1] f[i] = f[i-1] + h for j := i - 1; j > 0; j-- { w += books[j-1][0] if w > shelfWidth { break } h = max(h, books[j-1][1]) f[i] = min(f[i], f[j-1]+h) } } return f[n] } -
function minHeightShelves(books: number[][], shelfWidth: number): number { const n = books.length; const f = new Array(n + 1).fill(0); for (let i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { let [w, h] = books[i - 1]; f[i] = f[i - 1] + h; for (let j = i - 1; j > 0; --j) { w += books[j - 1][0]; if (w > shelfWidth) { break; } h = Math.max(h, books[j - 1][1]); f[i] = Math.min(f[i], f[j - 1] + h); } } return f[n]; } -
public class Solution { public int MinHeightShelves(int[][] books, int shelfWidth) { int n = books.Length; int[] f = new int[n + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { int w = books[i - 1][0], h = books[i - 1][1]; f[i] = f[i - 1] + h; for (int j = i - 1; j > 0; --j) { w += books[j - 1][0]; if (w > shelfWidth) { break; } h = Math.Max(h, books[j - 1][1]); f[i] = Math.Min(f[i], f[j - 1] + h); } } return f[n]; } }