Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix
Description
Given an n x n binary matrix grid, return the length of the shortest clear path in the matrix. If there is no clear path, return -1.
A clear path in a binary matrix is a path from the top-left cell (i.e., (0, 0)) to the bottom-right cell (i.e., (n - 1, n - 1)) such that:
- All the visited cells of the path are
0. - All the adjacent cells of the path are 8-directionally connected (i.e., they are different and they share an edge or a corner).
The length of a clear path is the number of visited cells of this path.
Example 1:
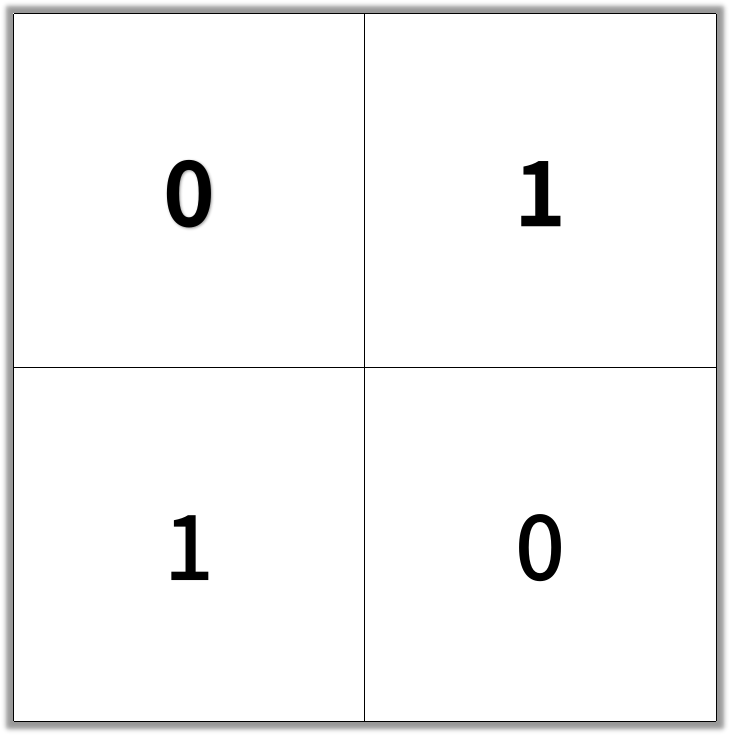
Input: grid = [[0,1],[1,0]] Output: 2
Example 2:
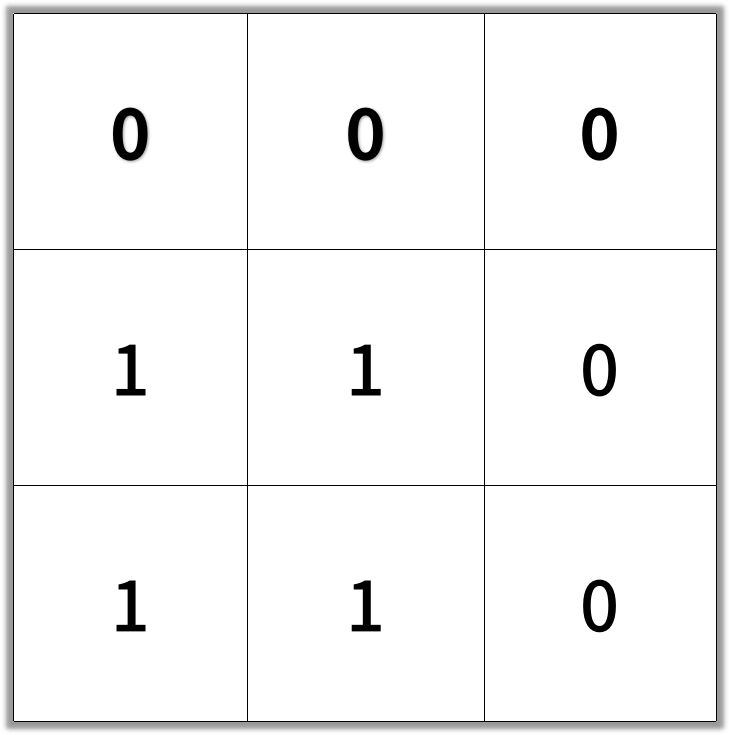
Input: grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]] Output: 4
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]] Output: -1
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 100grid[i][j] is 0 or 1
Solutions
BFS.
-
class Solution { public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) { if (grid[0][0] == 1) { return -1; } int n = grid.length; grid[0][0] = 1; Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.offer(new int[] {0, 0}); for (int ans = 1; !q.isEmpty(); ++ans) { for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) { var p = q.poll(); int i = p[0], j = p[1]; if (i == n - 1 && j == n - 1) { return ans; } for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) { for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) { if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 0) { grid[x][y] = 1; q.offer(new int[] {x, y}); } } } } } return -1; } } -
class Solution { public: int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { if (grid[0][0]) { return -1; } int n = grid.size(); grid[0][0] = 1; queue<pair<int, int>> q; q.emplace(0, 0); for (int ans = 1; !q.empty(); ++ans) { for (int k = q.size(); k; --k) { auto [i, j] = q.front(); q.pop(); if (i == n - 1 && j == n - 1) { return ans; } for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) { for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) { if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && !grid[x][y]) { grid[x][y] = 1; q.emplace(x, y); } } } } } return -1; } }; -
class Solution: def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int: if grid[0][0]: return -1 n = len(grid) grid[0][0] = 1 q = deque([(0, 0)]) ans = 1 while q: for _ in range(len(q)): i, j = q.popleft() if i == j == n - 1: return ans for x in range(i - 1, i + 2): for y in range(j - 1, j + 2): if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y] == 0: grid[x][y] = 1 q.append((x, y)) ans += 1 return -1 -
func shortestPathBinaryMatrix(grid [][]int) int { if grid[0][0] == 1 { return -1 } n := len(grid) grid[0][0] = 1 q := [][2]int{ {0, 0} } for ans := 1; len(q) > 0; ans++ { for k := len(q); k > 0; k-- { p := q[0] i, j := p[0], p[1] q = q[1:] if i == n-1 && j == n-1 { return ans } for x := i - 1; x <= i+1; x++ { for y := j - 1; y <= j+1; y++ { if x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 0 { grid[x][y] = 1 q = append(q, [2]int{x, y}) } } } } } return -1 } -
function shortestPathBinaryMatrix(grid: number[][]): number { if (grid[0][0]) { return -1; } const n = grid.length; grid[0][0] = 1; let q: number[][] = [[0, 0]]; for (let ans = 1; q.length > 0; ++ans) { const nq: number[][] = []; for (const [i, j] of q) { if (i === n - 1 && j === n - 1) { return ans; } for (let x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) { for (let y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) { if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && !grid[x][y]) { grid[x][y] = 1; nq.push([x, y]); } } } } q = nq; } return -1; } -
use std::collections::VecDeque; impl Solution { pub fn shortest_path_binary_matrix(mut grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 { let n = grid.len(); let mut queue = VecDeque::new(); queue.push_back([0, 0]); let mut res = 0; while !queue.is_empty() { res += 1; for _ in 0..queue.len() { let [i, j] = queue.pop_front().unwrap(); if grid[i][j] == 1 { continue; } if i == n - 1 && j == n - 1 { return res; } grid[i][j] = 1; for x in -1..=1 { for y in -1..=1 { let x = x + (i as i32); let y = y + (j as i32); if x < 0 || x == (n as i32) || y < 0 || y == (n as i32) { continue; } queue.push_back([x as usize, y as usize]); } } } } -1 } }