Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1035. Uncrossed Lines
Description
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2. We write the integers of nums1 and nums2 (in the order they are given) on two separate horizontal lines.
We may draw connecting lines: a straight line connecting two numbers nums1[i] and nums2[j] such that:
nums1[i] == nums2[j], and- the line we draw does not intersect any other connecting (non-horizontal) line.
Note that a connecting line cannot intersect even at the endpoints (i.e., each number can only belong to one connecting line).
Return the maximum number of connecting lines we can draw in this way.
Example 1:
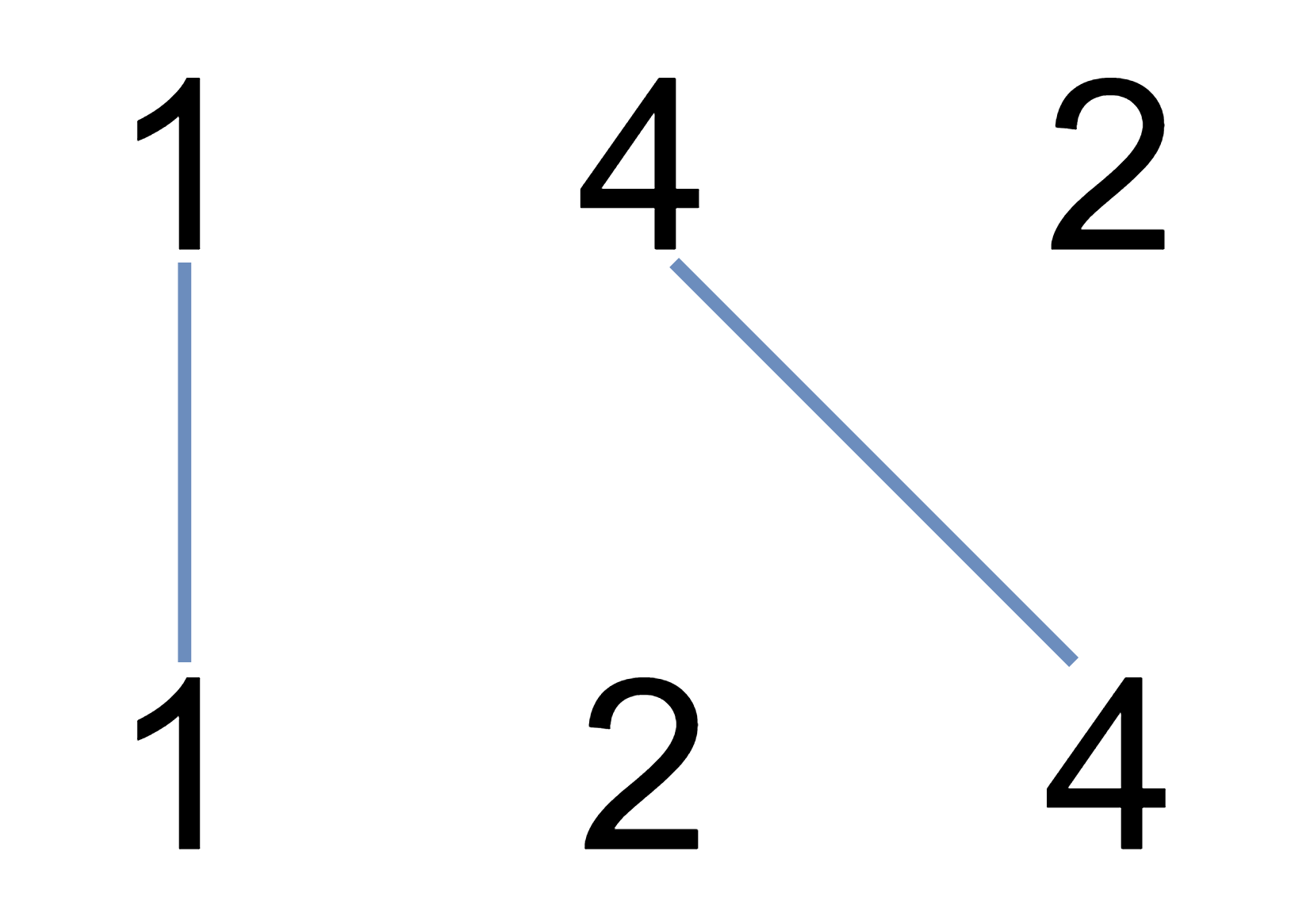
Input: nums1 = [1,4,2], nums2 = [1,2,4] Output: 2 Explanation: We can draw 2 uncrossed lines as in the diagram. We cannot draw 3 uncrossed lines, because the line from nums1[1] = 4 to nums2[2] = 4 will intersect the line from nums1[2]=2 to nums2[1]=2.
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [2,5,1,2,5], nums2 = [10,5,2,1,5,2] Output: 3
Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [1,3,7,1,7,5], nums2 = [1,9,2,5,1] Output: 2
Constraints:
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 5001 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 2000
Solutions
Longest common sub-sequences
\[dp[i][j]= \begin{cases} dp[i-1][j-1]+1, & nums1[i-1]=nums2[j-1] \\ \max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]), & nums1[i-1]\neq nums2[j-1] \end{cases}\]-
class Solution { public int maxUncrossedLines(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) { int m = nums1.length; int n = nums2.length; int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; } else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]); } } } return dp[m][n]; } } -
class Solution { public: int maxUncrossedLines(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { int m = nums1.size(), n = nums2.size(); vector<vector<int>> dp(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1)); for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; } else { dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]); } } } return dp[m][n]; } }; -
class Solution: def maxUncrossedLines(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int: m, n = len(nums1), len(nums2) dp = [[0] * (n + 1) for i in range(m + 1)] for i in range(1, m + 1): for j in range(1, n + 1): if nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]: dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1 else: dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) return dp[m][n] -
func maxUncrossedLines(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) int { m, n := len(nums1), len(nums2) dp := make([][]int, m+1) for i := range dp { dp[i] = make([]int, n+1) } for i := 1; i <= m; i++ { for j := 1; j <= n; j++ { if nums1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] { dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 } else { dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]) } } } return dp[m][n] } -
function maxUncrossedLines(nums1: number[], nums2: number[]): number { const m = nums1.length; const n = nums2.length; const dp = Array.from({ length: m + 1 }, () => new Array(n + 1).fill(0)); for (let i = 1; i <= m; ++i) { for (let j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]); if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; } } } return dp[m][n]; }