Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
1008. Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal
Description
Given an array of integers preorder, which represents the preorder traversal of a BST (i.e., binary search tree), construct the tree and return its root.
It is guaranteed that there is always possible to find a binary search tree with the given requirements for the given test cases.
A binary search tree is a binary tree where for every node, any descendant of Node.left has a value strictly less than Node.val, and any descendant of Node.right has a value strictly greater than Node.val.
A preorder traversal of a binary tree displays the value of the node first, then traverses Node.left, then traverses Node.right.
Example 1:
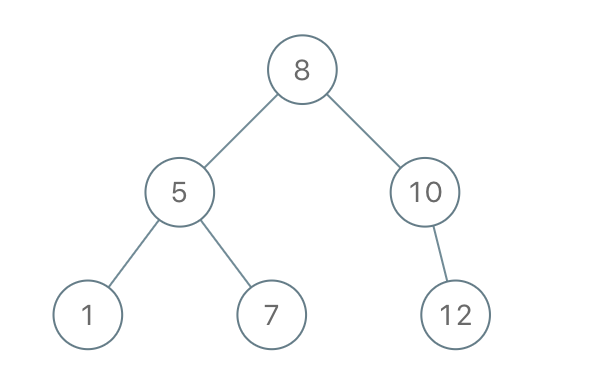
Input: preorder = [8,5,1,7,10,12] Output: [8,5,10,1,7,null,12]
Example 2:
Input: preorder = [1,3] Output: [1,null,3]
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 1001 <= preorder[i] <= 1000- All the values of
preorderare unique.
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder) { return dfs(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1); } private TreeNode dfs(int[] preorder, int i, int j) { if (i > j || i >= preorder.length) { return null; } TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[i]); int left = i + 1, right = j + 1; while (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) >> 1; if (preorder[mid] > preorder[i]) { right = mid; } else { left = mid + 1; } } root.left = dfs(preorder, i + 1, left - 1); root.right = dfs(preorder, left, j); return root; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* bstFromPreorder(vector<int>& preorder) { return dfs(preorder, 0, preorder.size() - 1); } TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>& preorder, int i, int j) { if (i > j || i >= preorder.size()) return nullptr; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[i]); int left = i + 1, right = j + 1; while (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) >> 1; if (preorder[mid] > preorder[i]) right = mid; else left = mid + 1; } root->left = dfs(preorder, i + 1, left - 1); root->right = dfs(preorder, left, j); return root; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def bstFromPreorder(self, preorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]: def dfs(preorder): if not preorder: return None root = TreeNode(preorder[0]) left, right = 1, len(preorder) while left < right: mid = (left + right) >> 1 if preorder[mid] > preorder[0]: right = mid else: left = mid + 1 root.left = dfs(preorder[1:left]) root.right = dfs(preorder[left:]) return root return dfs(preorder) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func bstFromPreorder(preorder []int) *TreeNode { var dfs func(i, j int) *TreeNode dfs = func(i, j int) *TreeNode { if i > j || i >= len(preorder) { return nil } root := &TreeNode{Val: preorder[i]} left, right := i+1, len(preorder) for left < right { mid := (left + right) >> 1 if preorder[mid] > preorder[i] { right = mid } else { left = mid + 1 } } root.Left = dfs(i+1, left-1) root.Right = dfs(left, j) return root } return dfs(0, len(preorder)-1) } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function bstFromPreorder(preorder: number[]): TreeNode | null { const n = preorder.length; const next = new Array(n); const stack = []; for (let i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) { while (stack.length !== 0 && preorder[stack[stack.length - 1]] < preorder[i]) { stack.pop(); } next[i] = stack[stack.length - 1] ?? n; stack.push(i); } const dfs = (left: number, right: number) => { if (left >= right) { return null; } return new TreeNode(preorder[left], dfs(left + 1, next[left]), dfs(next[left], right)); }; return dfs(0, n); } -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; impl Solution { fn dfs( preorder: &Vec<i32>, next: &Vec<usize>, left: usize, right: usize ) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { if left >= right { return None; } Some( Rc::new( RefCell::new(TreeNode { val: preorder[left], left: Self::dfs(preorder, next, left + 1, next[left]), right: Self::dfs(preorder, next, next[left], right), }) ) ) } pub fn bst_from_preorder(preorder: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> { let n = preorder.len(); let mut stack = Vec::new(); let mut next = vec![n; n]; for i in (0..n).rev() { while !stack.is_empty() && preorder[*stack.last().unwrap()] < preorder[i] { stack.pop(); } if !stack.is_empty() { next[i] = *stack.last().unwrap(); } stack.push(i); } Self::dfs(&preorder, &next, 0, n) } }