Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
994. Rotting Oranges
Description
You are given an m x n grid where each cell can have one of three values:
0representing an empty cell,1representing a fresh orange, or2representing a rotten orange.
Every minute, any fresh orange that is 4-directionally adjacent to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Return the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange. If this is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
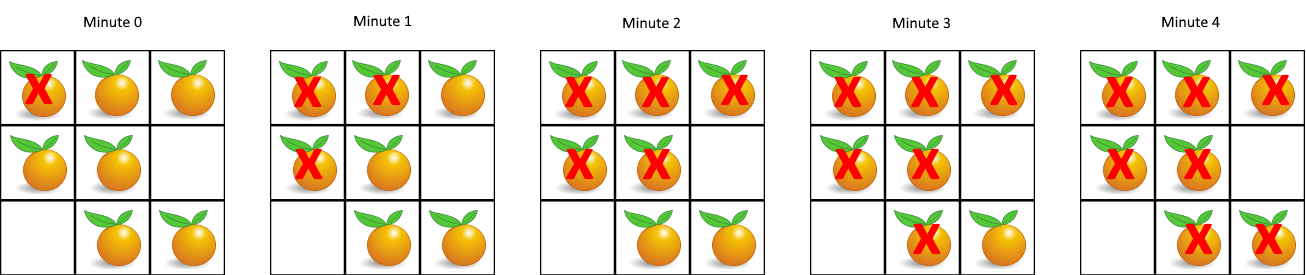
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]] Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]] Output: -1 Explanation: The orange in the bottom left corner (row 2, column 0) is never rotten, because rotting only happens 4-directionally.
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[0,2]] Output: 0 Explanation: Since there are already no fresh oranges at minute 0, the answer is just 0.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10grid[i][j]is0,1, or2.
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; int cnt = 0; Deque<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (grid[i][j] == 2) { q.offer(new int[] {i, j}); } else if (grid[i][j] == 1) { ++cnt; } } } int ans = 0; int[] dirs = {1, 0, -1, 0, 1}; while (!q.isEmpty() && cnt > 0) { ++ans; for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; --i) { int[] p = q.poll(); for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) { int x = p[0] + dirs[j]; int y = p[1] + dirs[j + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1) { grid[x][y] = 2; --cnt; q.offer(new int[] {x, y}); } } } } return cnt > 0 ? -1 : ans; } } -
class Solution { public: int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(); int cnt = 0; typedef pair<int, int> pii; queue<pii> q; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (grid[i][j] == 2) q.emplace(i, j); else if (grid[i][j] == 1) ++cnt; } } int ans = 0; vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; while (!q.empty() && cnt > 0) { ++ans; for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; --i) { auto p = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) { int x = p.first + dirs[j]; int y = p.second + dirs[j + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1) { --cnt; grid[x][y] = 2; q.emplace(x, y); } } } } return cnt > 0 ? -1 : ans; } }; -
class Solution: def orangesRotting(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int: m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0]) q = deque() cnt = 0 for i in range(m): for j in range(n): if grid[i][j] == 2: q.append((i, j)) elif grid[i][j] == 1: cnt += 1 ans = 0 while q and cnt: ans += 1 for _ in range(len(q)): i, j = q.popleft() for a, b in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]: x, y = i + a, j + b if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y] == 1: cnt -= 1 grid[x][y] = 2 q.append((x, y)) return ans if cnt == 0 else -1 -
func orangesRotting(grid [][]int) int { m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0]) cnt := 0 var q [][]int for i := 0; i < m; i++ { for j := 0; j < n; j++ { if grid[i][j] == 2 { q = append(q, []int{i, j}) } else if grid[i][j] == 1 { cnt++ } } } ans := 0 dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1} for len(q) > 0 && cnt > 0 { ans++ for i := len(q); i > 0; i-- { p := q[0] q = q[1:] for j := 0; j < 4; j++ { x, y := p[0]+dirs[j], p[1]+dirs[j+1] if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1 { cnt-- grid[x][y] = 2 q = append(q, []int{x, y}) } } } } if cnt > 0 { return -1 } return ans } -
function orangesRotting(grid: number[][]): number { const m = grid.length; const n = grid[0].length; let count = 0; const queue = []; for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (grid[i][j] === 1) { count++; } else if (grid[i][j] === 2) { queue.push([i, j]); } } } let res = 0; const dris = [1, 0, -1, 0, 1]; while (count !== 0 && queue.length !== 0) { for (let i = queue.length; i > 0; i--) { const [x, y] = queue.shift(); for (let j = 0; j < 4; j++) { const newX = x + dris[j]; const newY = y + dris[j + 1]; if (newX >= 0 && newX < m && newY >= 0 && newY <= n && grid[newX][newY] === 1) { grid[newX][newY] = 2; queue.push([newX, newY]); count--; } } } res++; } if (count != 0) { return -1; } return res; } -
use std::collections::VecDeque; impl Solution { pub fn oranges_rotting(mut grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 { let mut queue = VecDeque::new(); let m = grid.len(); let n = grid[0].len(); // 新鲜橘子数量 let mut count = 0; for i in 0..m { for j in 0..n { match grid[i][j] { 1 => { count += 1; } 2 => queue.push_back([i as i32, j as i32]), _ => (), } } } let mut res = 0; let dirs = [1, 0, -1, 0, 1]; while count != 0 && queue.len() != 0 { let mut len = queue.len(); while len != 0 { let [x, y] = queue.pop_front().unwrap(); for i in 0..4 { let new_x = x + dirs[i]; let new_y = y + dirs[i + 1]; if new_x >= 0 && new_x < (m as i32) && new_y >= 0 && new_y < (n as i32) && grid[new_x as usize][new_y as usize] == 1 { grid[new_x as usize][new_y as usize] = 2; queue.push_back([new_x, new_y]); count -= 1; } } len -= 1; } res += 1; } if count != 0 { return -1; } res } } -
/** * @param {number[][]} grid * @return {number} */ var orangesRotting = function (grid) { const m = grid.length; const n = grid[0].length; let q = []; let cnt = 0; for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if (grid[i][j] === 1) { cnt++; } else if (grid[i][j] === 2) { q.push([i, j]); } } } const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1]; for (let ans = 1; q.length && cnt; ++ans) { let t = []; for (const [i, j] of q) { for (let d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { const x = i + dirs[d]; const y = j + dirs[d + 1]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] === 1) { grid[x][y] = 2; t.push([x, y]); if (--cnt === 0) { return ans; } } } } q = [...t]; } return cnt > 0 ? -1 : 0; };