Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
958. Check Completeness of a Binary Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is a complete binary tree.
In a complete binary tree, every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between 1 and 2h nodes inclusive at the last level h.
Example 1:
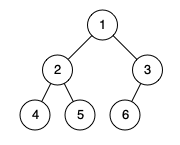
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: true
Explanation: Every level before the last is full (ie. levels with node-values {1} and {2, 3}), and all nodes in the last level ({4, 5, 6}) are as far left as possible.
Example 2:
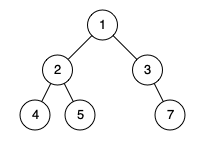
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7] Output: false Explanation: The node with value 7 isn't as far left as possible.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) { Deque<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.offer(root); while (q.peek() != null) { TreeNode node = q.poll(); q.offer(node.left); q.offer(node.right); } while (!q.isEmpty() && q.peek() == null) { q.poll(); } return q.isEmpty(); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isCompleteTree(TreeNode* root) { queue<TreeNode*> q{ {root} }; while (q.front()) { root = q.front(); q.pop(); q.push(root->left); q.push(root->right); } while (!q.empty() && !q.front()) q.pop(); return q.empty(); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def isCompleteTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: q = deque([root]) while q: node = q.popleft() if node is None: break q.append(node.left) q.append(node.right) return all(node is None for node in q) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func isCompleteTree(root *TreeNode) bool { q := []*TreeNode{root} for q[0] != nil { root = q[0] q = q[1:] q = append(q, root.Left) q = append(q, root.Right) } for len(q) > 0 && q[0] == nil { q = q[1:] } return len(q) == 0 }