Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
897. Increasing Order Search Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary search tree, rearrange the tree in in-order so that the leftmost node in the tree is now the root of the tree, and every node has no left child and only one right child.
Example 1:
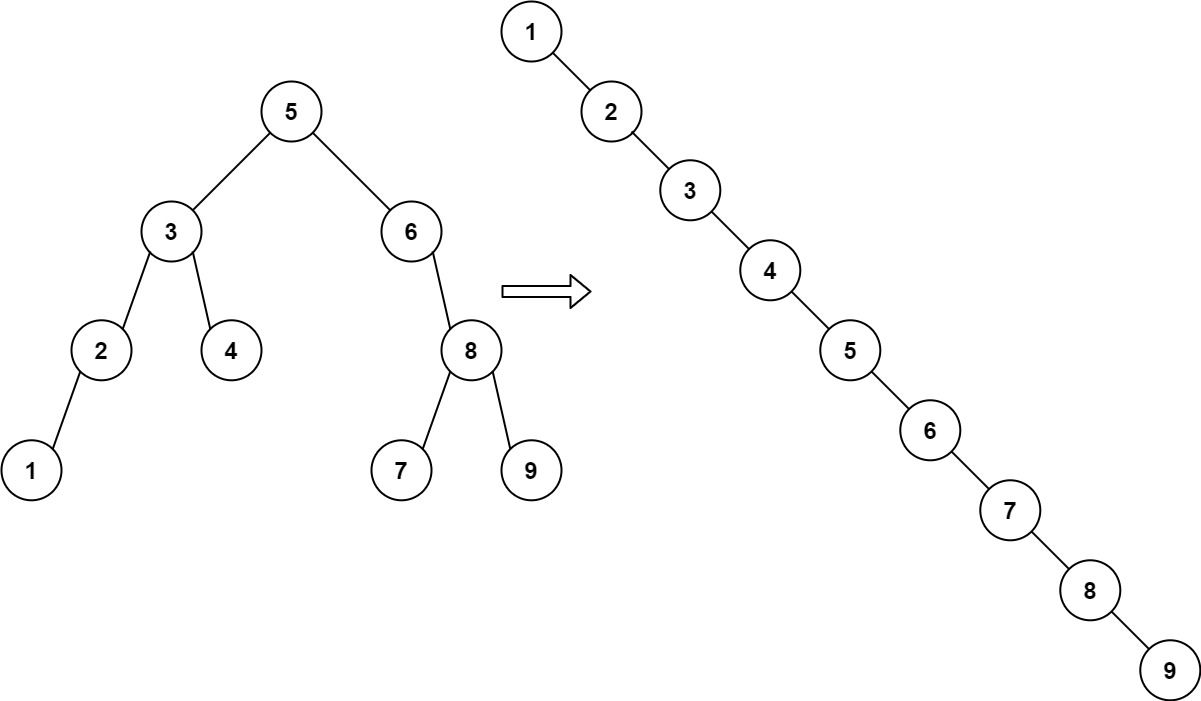
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,8,1,null,null,null,7,9] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6,null,7,null,8,null,9]
Example 2:
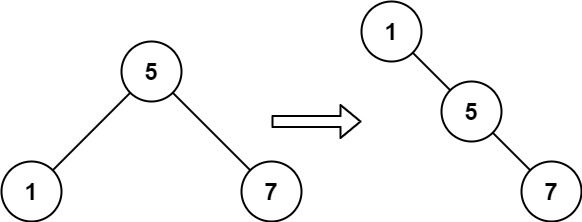
Input: root = [5,1,7] Output: [1,null,5,null,7]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS In-order Traversal
We define a virtual node $dummy$, initially the right child of $dummy$ points to the root node $root$, and a pointer $prev$ points to $dummy$.
We perform an in-order traversal on the binary search tree. During the traversal, each time we visit a node, we point the right child of $prev$ to it, then set the left child of the current node to null, and assign the current node to $prev$ for the next traversal.
After the traversal ends, the original binary search tree is modified into a singly linked list with only right child nodes. We then return the right child of the virtual node $dummy$.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the number of nodes in the binary search tree.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private TreeNode prev; public TreeNode increasingBST(TreeNode root) { TreeNode dummy = new TreeNode(0, null, root); prev = dummy; dfs(root); return dummy.right; } private void dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } dfs(root.left); prev.right = root; root.left = null; prev = root; dfs(root.right); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* increasingBST(TreeNode* root) { TreeNode* dummy = new TreeNode(0, nullptr, root); TreeNode* prev = dummy; function<void(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) { if (!root) { return; } dfs(root->left); prev->right = root; root->left = nullptr; prev = root; dfs(root->right); }; dfs(root); return dummy->right; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def increasingBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: def dfs(root): if root is None: return nonlocal prev dfs(root.left) prev.right = root root.left = None prev = root dfs(root.right) dummy = prev = TreeNode(right=root) dfs(root) return dummy.right -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func increasingBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode { dummy := &TreeNode{Val: 0, Right: root} prev := dummy var dfs func(root *TreeNode) dfs = func(root *TreeNode) { if root == nil { return } dfs(root.Left) prev.Right = root root.Left = nil prev = root dfs(root.Right) } dfs(root) return dummy.Right } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function increasingBST(root: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null { const dummy = new TreeNode((right = root)); let prev = dummy; const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null) => { if (!root) { return; } dfs(root.left); prev.right = root; root.left = null; prev = root; dfs(root.right); }; dfs(root); return dummy.right; }