Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
872. Leaf-Similar Trees
Description
Consider all the leaves of a binary tree, from left to right order, the values of those leaves form a leaf value sequence.
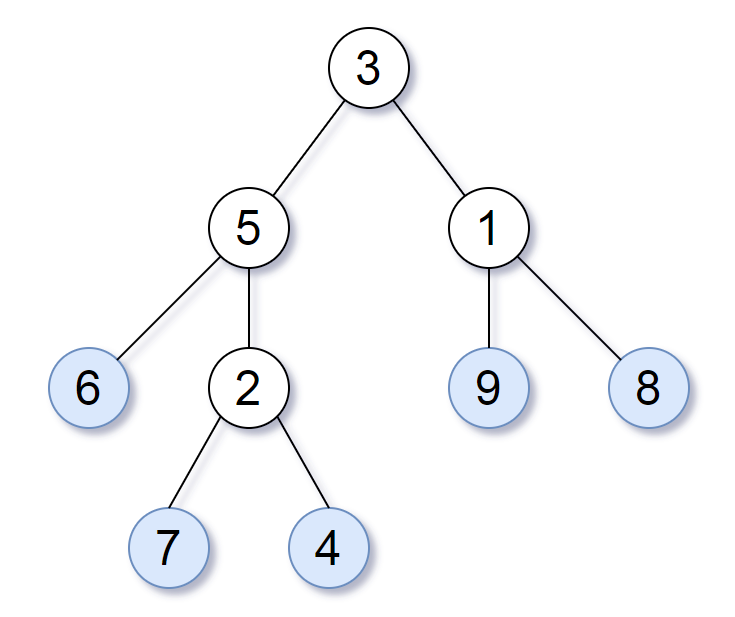
For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is (6, 7, 4, 9, 8).
Two binary trees are considered leaf-similar if their leaf value sequence is the same.
Return true if and only if the two given trees with head nodes root1 and root2 are leaf-similar.
Example 1:
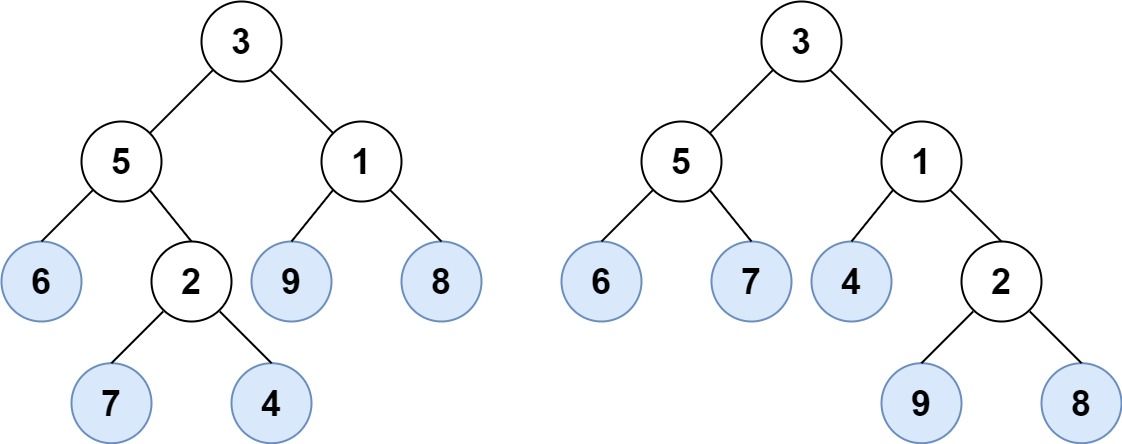
Input: root1 = [3,5,1,6,2,9,8,null,null,7,4], root2 = [3,5,1,6,7,4,2,null,null,null,null,null,null,9,8] Output: true
Example 2:
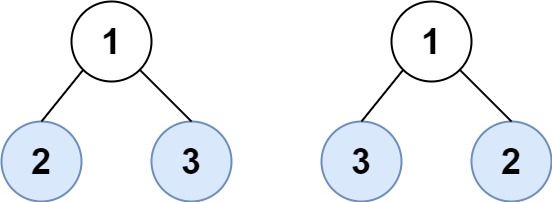
Input: root1 = [1,2,3], root2 = [1,3,2] Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree will be in the range
[1, 200]. - Both of the given trees will have values in the range
[0, 200].
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { List<Integer> l1 = dfs(root1); List<Integer> l2 = dfs(root2); return l1.equals(l2); } private List<Integer> dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return new ArrayList<>(); } List<Integer> ans = dfs(root.left); ans.addAll(dfs(root.right)); if (ans.isEmpty()) { ans.add(root.val); } return ans; } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool leafSimilar(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) { return dfs(root1) == dfs(root2); } vector<int> dfs(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return {}; auto ans = dfs(root->left); auto right = dfs(root->right); ans.insert(ans.end(), right.begin(), right.end()); if (ans.empty()) ans.push_back(root->val); return ans; } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def leafSimilar(self, root1: Optional[TreeNode], root2: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool: def dfs(root): if root is None: return [] ans = dfs(root.left) + dfs(root.right) return ans or [root.val] return dfs(root1) == dfs(root2) -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func leafSimilar(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode) bool { var dfs func(*TreeNode) []int dfs = func(root *TreeNode) []int { if root == nil { return []int{} } ans := dfs(root.Left) ans = append(ans, dfs(root.Right)...) if len(ans) == 0 { ans = append(ans, root.Val) } return ans } return reflect.DeepEqual(dfs(root1), dfs(root2)) } -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; impl Solution { #[allow(dead_code)] pub fn leaf_similar( root1: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, root2: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> ) -> bool { let mut one_vec: Vec<i32> = Vec::new(); let mut two_vec: Vec<i32> = Vec::new(); // Initialize the two vector Self::traverse(&mut one_vec, root1); Self::traverse(&mut two_vec, root2); one_vec == two_vec } #[allow(dead_code)] fn traverse(v: &mut Vec<i32>, root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) { if root.is_none() { return; } if Self::is_leaf_node(&root) { v.push(root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().val); } let left = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().left.clone(); let right = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().right.clone(); Self::traverse(v, left); Self::traverse(v, right); } #[allow(dead_code)] fn is_leaf_node(node: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool { node.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().left.is_none() && node.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().right.is_none() } } -
var leafSimilar = function (root1, root2) { const dfs = root => { if (!root) { return []; } let ans = [...dfs(root.left), ...dfs(root.right)]; if (!ans.length) { ans = [root.val]; } return ans; }; const l1 = dfs(root1); const l2 = dfs(root2); return l1.toString() === l2.toString(); };