Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
790. Domino and Tromino Tiling
Description
You have two types of tiles: a 2 x 1 domino shape and a tromino shape. You may rotate these shapes.
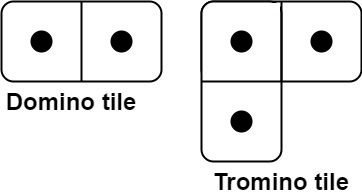
Given an integer n, return the number of ways to tile an 2 x n board. Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
In a tiling, every square must be covered by a tile. Two tilings are different if and only if there are two 4-directionally adjacent cells on the board such that exactly one of the tilings has both squares occupied by a tile.
Example 1:
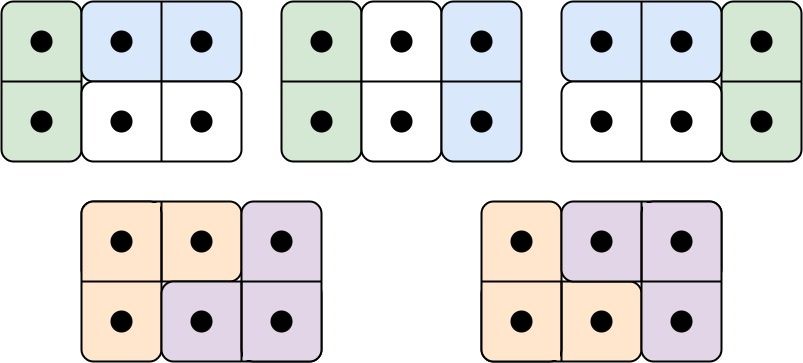
Input: n = 3 Output: 5 Explanation: The five different ways are show above.
Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000
Solutions
-
class Solution { public int numTilings(int n) { long[] f = {1, 0, 0, 0}; int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { long[] g = new long[4]; g[0] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[2] + f[3]) % mod; g[1] = (f[2] + f[3]) % mod; g[2] = (f[1] + f[3]) % mod; g[3] = f[0]; f = g; } return (int) f[0]; } } -
class Solution { public: const int mod = 1e9 + 7; int numTilings(int n) { long f[4] = {1, 0, 0, 0}; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { long g[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0}; g[0] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[2] + f[3]) % mod; g[1] = (f[2] + f[3]) % mod; g[2] = (f[1] + f[3]) % mod; g[3] = f[0]; memcpy(f, g, sizeof(g)); } return f[0]; } }; -
class Solution: def numTilings(self, n: int) -> int: @cache def dfs(i, j): if i > n or j > n: return 0 if i == n and j == n: return 1 ans = 0 if i == j: ans = ( dfs(i + 2, j + 2) + dfs(i + 1, j + 1) + dfs(i + 2, j + 1) + dfs(i + 1, j + 2) ) elif i > j: ans = dfs(i, j + 2) + dfs(i + 1, j + 2) else: ans = dfs(i + 2, j) + dfs(i + 2, j + 1) return ans % mod mod = 10**9 + 7 return dfs(0, 0) -
func numTilings(n int) int { f := [4]int{} f[0] = 1 const mod int = 1e9 + 7 for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { g := [4]int{} g[0] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[2] + f[3]) % mod g[1] = (f[2] + f[3]) % mod g[2] = (f[1] + f[3]) % mod g[3] = f[0] f = g } return f[0] } -
function numTilings(n: number): number { const mod = 1_000_000_007; let f: number[] = [1, 0, 0, 0]; for (let i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { const g: number[] = Array(4); g[0] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[2] + f[3]) % mod; g[1] = (f[2] + f[3]) % mod; g[2] = (f[1] + f[3]) % mod; g[3] = f[0] % mod; f = g; } return f[0]; } -
impl Solution { pub fn num_tilings(n: i32) -> i32 { const MOD: i64 = 1_000_000_007; let mut f: [i64; 4] = [1, 0, 0, 0]; for _ in 1..=n { let mut g = [0i64; 4]; g[0] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[2] + f[3]) % MOD; g[1] = (f[2] + f[3]) % MOD; g[2] = (f[1] + f[3]) % MOD; g[3] = f[0] % MOD; f = g; } f[0] as i32 } }