Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
725. Split Linked List in Parts
Description
Given the head of a singly linked list and an integer k, split the linked list into k consecutive linked list parts.
The length of each part should be as equal as possible: no two parts should have a size differing by more than one. This may lead to some parts being null.
The parts should be in the order of occurrence in the input list, and parts occurring earlier should always have a size greater than or equal to parts occurring later.
Return an array of the k parts.
Example 1:
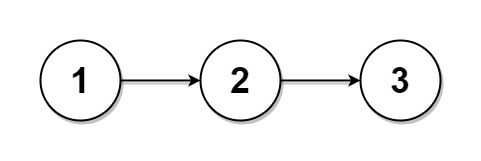
Input: head = [1,2,3], k = 5 Output: [[1],[2],[3],[],[]] Explanation: The first element output[0] has output[0].val = 1, output[0].next = null. The last element output[4] is null, but its string representation as a ListNode is [].
Example 2:
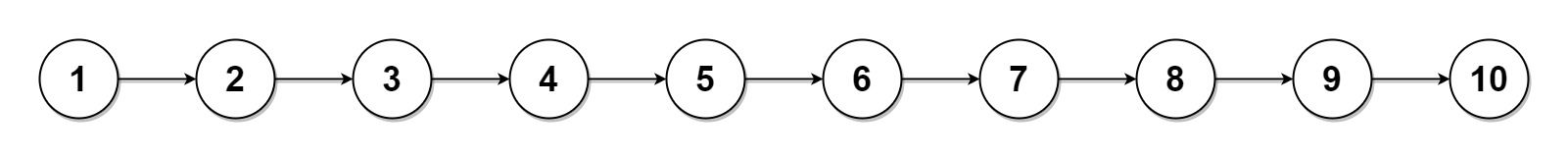
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], k = 3 Output: [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7],[8,9,10]] Explanation: The input has been split into consecutive parts with size difference at most 1, and earlier parts are a larger size than the later parts.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 10001 <= k <= 50
Solutions
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode[] splitListToParts(ListNode root, int k) { int n = 0; ListNode cur = root; while (cur != null) { ++n; cur = cur.next; } // width 表示每一部分至少含有的结点个数 // remainder 表示前 remainder 部分,每一部分多出一个数 int width = n / k, remainder = n % k; ListNode[] res = new ListNode[k]; cur = root; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { ListNode head = cur; for (int j = 0; j < width + ((i < remainder) ? 1 : 0) - 1; ++j) { if (cur != null) { cur = cur.next; } } if (cur != null) { ListNode t = cur.next; cur.next = null; cur = t; } res[i] = head; } return res; } } -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def splitListToParts(self, root: ListNode, k: int) -> List[ListNode]: n, cur = 0, root while cur: n += 1 cur = cur.next cur = root width, remainder = divmod(n, k) res = [None for _ in range(k)] for i in range(k): head = cur for j in range(width + (i < remainder) - 1): if cur: cur = cur.next if cur: cur.next, cur = None, cur.next res[i] = head return res -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<ListNode*> splitListToParts(ListNode* head, int k) { int n = 0; for (ListNode* cur = head; cur != nullptr; cur = cur->next) { ++n; } int cnt = n / k, mod = n % k; vector<ListNode*> ans(k, nullptr); ListNode* cur = head; for (int i = 0; i < k && cur != nullptr; ++i) { ans[i] = cur; int m = cnt + (i < mod ? 1 : 0); for (int j = 1; j < m; ++j) { cur = cur->next; } ListNode* nxt = cur->next; cur->next = nullptr; cur = nxt; } return ans; } }; -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func splitListToParts(head *ListNode, k int) []*ListNode { n := 0 for cur := head; cur != nil; cur = cur.Next { n++ } cnt := n / k mod := n % k ans := make([]*ListNode, k) cur := head for i := 0; i < k && cur != nil; i++ { ans[i] = cur m := cnt if i < mod { m++ } for j := 1; j < m; j++ { cur = cur.Next } next := cur.Next cur.Next = nil cur = next } return ans } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function splitListToParts(head: ListNode | null, k: number): Array<ListNode | null> { let n = 0; for (let cur = head; cur !== null; cur = cur.next) { n++; } const cnt = (n / k) | 0; const mod = n % k; const ans: Array<ListNode | null> = Array(k).fill(null); let cur = head; for (let i = 0; i < k && cur !== null; i++) { ans[i] = cur; let m = cnt + (i < mod ? 1 : 0); for (let j = 1; j < m; j++) { cur = cur.next!; } let next = cur.next; cur.next = null; cur = next; } return ans; }