Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
687. Longest Univalue Path
Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the longest path, where each node in the path has the same value. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of the path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
Example 1:
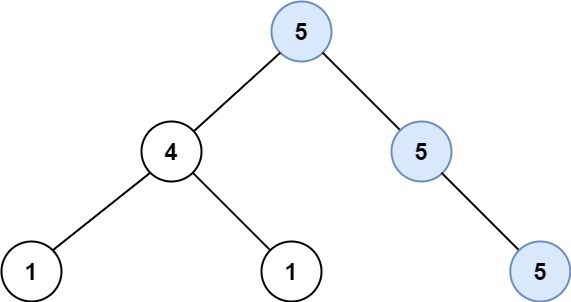
Input: root = [5,4,5,1,1,null,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The shown image shows that the longest path of the same value (i.e. 5).
Example 2:
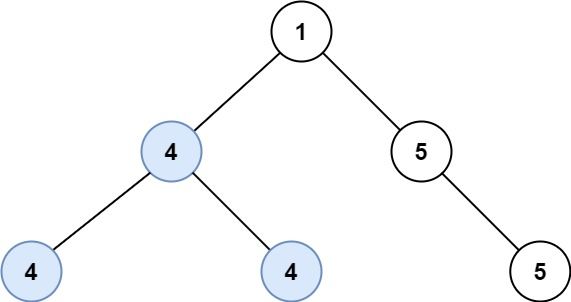
Input: root = [1,4,5,4,4,null,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The shown image shows that the longest path of the same value (i.e. 4).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000- The depth of the tree will not exceed
1000.
Solutions
Similar to problem 543. Diameter of Binary Tree.
-
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { private int ans; public int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode root) { ans = 0; dfs(root); return ans; } private int dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int left = dfs(root.left); int right = dfs(root.right); left = root.left != null && root.left.val == root.val ? left + 1 : 0; right = root.right != null && root.right.val == root.val ? right + 1 : 0; ans = Math.max(ans, left + right); return Math.max(left, right); } } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int ans; int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root) { ans = 0; dfs(root); return ans; } int dfs(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return 0; int left = dfs(root->left), right = dfs(root->right); left = root->left && root->left->val == root->val ? left + 1 : 0; right = root->right && root->right->val == root->val ? right + 1 : 0; ans = max(ans, left + right); return max(left, right); } }; -
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def longestUnivaluePath(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: def dfs(root): if root is None: return 0 left, right = dfs(root.left), dfs(root.right) left = left + 1 if root.left and root.left.val == root.val else 0 right = right + 1 if root.right and root.right.val == root.val else 0 nonlocal ans ans = max(ans, left + right) return max(left, right) ans = 0 dfs(root) return ans -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func longestUnivaluePath(root *TreeNode) int { ans := 0 var dfs func(root *TreeNode) int dfs = func(root *TreeNode) int { if root == nil { return 0 } left, right := dfs(root.Left), dfs(root.Right) if root.Left != nil && root.Left.Val == root.Val { left++ } else { left = 0 } if root.Right != nil && root.Right.Val == root.Val { right++ } else { right = 0 } ans = max(ans, left+right) return max(left, right) } dfs(root) return ans } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */ function longestUnivaluePath(root: TreeNode | null): number { if (root == null) { return 0; } let res = 0; const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null, target: number) => { if (root == null) { return 0; } const { val, left, right } = root; let l = dfs(left, val); let r = dfs(right, val); res = Math.max(res, l + r); if (val === target) { return Math.max(l, r) + 1; } return 0; }; dfs(root, root.val); return res; } -
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val, left, right) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } */ /** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {number} */ var longestUnivaluePath = function (root) { let ans = 0; let dfs = function (root) { if (!root) { return 0; } let left = dfs(root.left), right = dfs(root.right); left = root.left?.val == root.val ? left + 1 : 0; right = root.right?.val == root.val ? right + 1 : 0; ans = Math.max(ans, left + right); return Math.max(left, right); }; dfs(root); return ans; }; -
// Definition for a binary tree node. // #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)] // pub struct TreeNode { // pub val: i32, // pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // } // // impl TreeNode { // #[inline] // pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // TreeNode { // val, // left: None, // right: None // } // } // } use std::rc::Rc; use std::cell::RefCell; impl Solution { fn dfs(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target: i32, res: &mut i32) -> i32 { if root.is_none() { return 0; } let root = root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow(); let left = Self::dfs(&root.left, root.val, res); let right = Self::dfs(&root.right, root.val, res); *res = (*res).max(left + right); if root.val == target { return left.max(right) + 1; } 0 } pub fn longest_univalue_path(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 { if root.is_none() { return 0; } let mut res = 0; Self::dfs(&root, root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow().val, &mut res); res } }