Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
505. The Maze II
Description
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces (represented as 0) and walls (represented as 1). The ball can go through the empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the m x n maze, the ball's start position and the destination, where start = [startrow, startcol] and destination = [destinationrow, destinationcol], return the shortest distance for the ball to stop at the destination. If the ball cannot stop at destination, return -1.
The distance is the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the destination (included).
You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls (see examples).
Example 1:
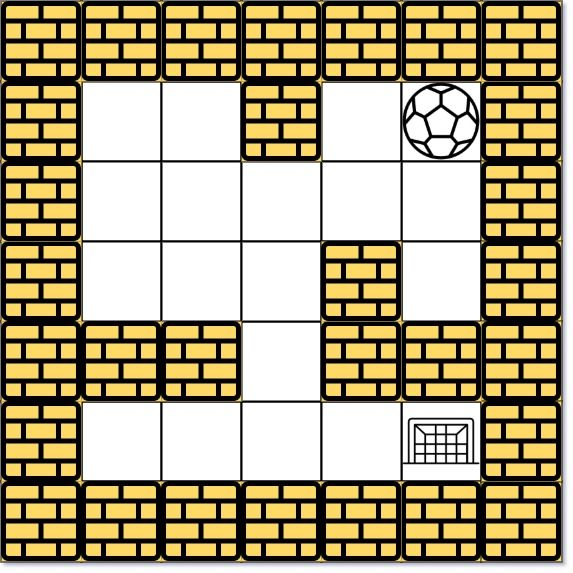
Input: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [4,4] Output: 12 Explanation: One possible way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right. The length of the path is 1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12.
Example 2:
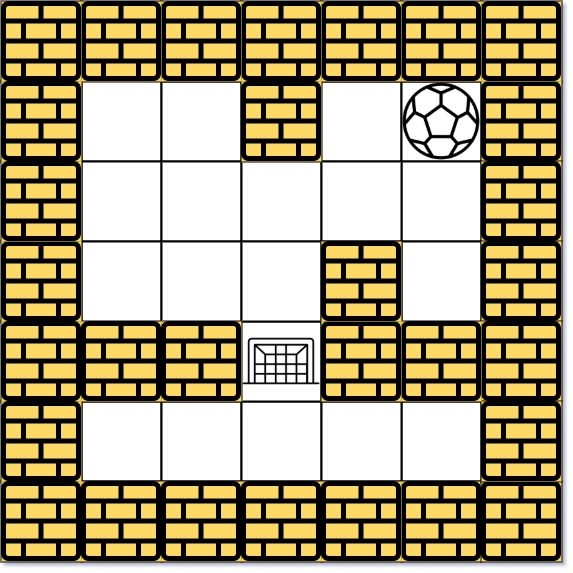
Input: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [3,2] Output: -1 Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination. Notice that you can pass through the destination but you cannot stop there.
Example 3:
Input: maze = [[0,0,0,0,0],[1,1,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1],[0,1,0,0,0]], start = [4,3], destination = [0,1] Output: -1
Constraints:
m == maze.lengthn == maze[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100maze[i][j]is0or1.start.length == 2destination.length == 20 <= startrow, destinationrow < m0 <= startcol, destinationcol < n- Both the ball and the destination exist in an empty space, and they will not be in the same position initially.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces.
Solutions
BFS.
-
class Solution { public int shortestDistance(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) { int m = maze.length, n = maze[0].length; final int inf = 1 << 30; int[][] dist = new int[m][n]; for (var row : dist) { Arrays.fill(row, inf); } int si = start[0], sj = start[1]; int di = destination[0], dj = destination[1]; dist[si][sj] = 0; Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.offer(new int[] {si, sj}); int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; while (!q.isEmpty()) { var p = q.poll(); int i = p[0], j = p[1]; for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { int x = i, y = j, k = dist[i][j]; int a = dirs[d], b = dirs[d + 1]; while ( x + a >= 0 && x + a < m && y + b >= 0 && y + b < n && maze[x + a][y + b] == 0) { x += a; y += b; ++k; } if (k < dist[x][y]) { dist[x][y] = k; q.offer(new int[] {x, y}); } } } return dist[di][dj] == inf ? -1 : dist[di][dj]; } } -
class Solution { public: int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) { int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size(); int dist[m][n]; memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist)); int si = start[0], sj = start[1]; int di = destination[0], dj = destination[1]; dist[si][sj] = 0; queue<pair<int, int>> q; q.emplace(si, sj); int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}; while (!q.empty()) { auto [i, j] = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { int x = i, y = j, k = dist[i][j]; int a = dirs[d], b = dirs[d + 1]; while (x + a >= 0 && x + a < m && y + b >= 0 && y + b < n && maze[x + a][y + b] == 0) { x += a; y += b; ++k; } if (k < dist[x][y]) { dist[x][y] = k; q.emplace(x, y); } } } return dist[di][dj] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : dist[di][dj]; } }; -
class Solution: def shortestDistance( self, maze: List[List[int]], start: List[int], destination: List[int] ) -> int: m, n = len(maze), len(maze[0]) dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1) si, sj = start di, dj = destination q = deque([(si, sj)]) dist = [[inf] * n for _ in range(m)] dist[si][sj] = 0 while q: i, j = q.popleft() for a, b in pairwise(dirs): x, y, k = i, j, dist[i][j] while 0 <= x + a < m and 0 <= y + b < n and maze[x + a][y + b] == 0: x, y, k = x + a, y + b, k + 1 if k < dist[x][y]: dist[x][y] = k q.append((x, y)) return -1 if dist[di][dj] == inf else dist[di][dj] -
func shortestDistance(maze [][]int, start []int, destination []int) int { m, n := len(maze), len(maze[0]) dist := make([][]int, m) const inf = 1 << 30 for i := range dist { dist[i] = make([]int, n) for j := range dist[i] { dist[i][j] = inf } } dist[start[0]][start[1]] = 0 q := [][]int{start} dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1} for len(q) > 0 { p := q[0] q = q[1:] i, j := p[0], p[1] for d := 0; d < 4; d++ { x, y, k := i, j, dist[i][j] a, b := dirs[d], dirs[d+1] for x+a >= 0 && x+a < m && y+b >= 0 && y+b < n && maze[x+a][y+b] == 0 { x, y, k = x+a, y+b, k+1 } if k < dist[x][y] { dist[x][y] = k q = append(q, []int{x, y}) } } } di, dj := destination[0], destination[1] if dist[di][dj] == inf { return -1 } return dist[di][dj] } -
function shortestDistance(maze: number[][], start: number[], destination: number[]): number { const m = maze.length; const n = maze[0].length; const dist: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array.from({ length: n }, () => Infinity), ); const [si, sj] = start; const [di, dj] = destination; dist[si][sj] = 0; const q: number[][] = [[si, sj]]; const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1]; while (q.length) { const [i, j] = q.shift()!; for (let d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { let [x, y, k] = [i, j, dist[i][j]]; const [a, b] = [dirs[d], dirs[d + 1]]; while (x + a >= 0 && x + a < m && y + b >= 0 && y + b < n && maze[x + a][y + b] === 0) { x += a; y += b; ++k; } if (k < dist[x][y]) { dist[x][y] = k; q.push([x, y]); } } } return dist[di][dj] === Infinity ? -1 : dist[di][dj]; }