Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
457. Circular Array Loop
Description
You are playing a game involving a circular array of non-zero integers nums. Each nums[i] denotes the number of indices forward/backward you must move if you are located at index i:
- If
nums[i]is positive, movenums[i]steps forward, and - If
nums[i]is negative, movenums[i]steps backward.
Since the array is circular, you may assume that moving forward from the last element puts you on the first element, and moving backwards from the first element puts you on the last element.
A cycle in the array consists of a sequence of indices seq of length k where:
- Following the movement rules above results in the repeating index sequence
seq[0] -> seq[1] -> ... -> seq[k - 1] -> seq[0] -> ... - Every
nums[seq[j]]is either all positive or all negative. k > 1
Return true if there is a cycle in nums, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
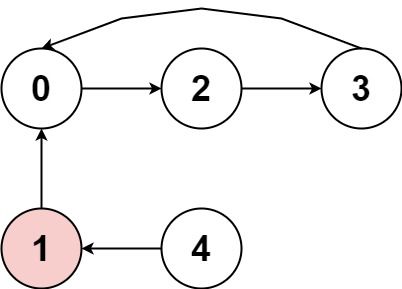
Input: nums = [2,-1,1,2,2] Output: true Explanation: The graph shows how the indices are connected. White nodes are jumping forward, while red is jumping backward. We can see the cycle 0 --> 2 --> 3 --> 0 --> ..., and all of its nodes are white (jumping in the same direction).
Example 2:
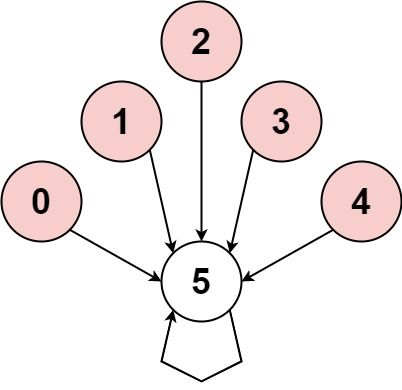
Input: nums = [-1,-2,-3,-4,-5,6] Output: false Explanation: The graph shows how the indices are connected. White nodes are jumping forward, while red is jumping backward. The only cycle is of size 1, so we return false.
Example 3:

Input: nums = [1,-1,5,1,4] Output: true Explanation: The graph shows how the indices are connected. White nodes are jumping forward, while red is jumping backward. We can see the cycle 0 --> 1 --> 0 --> ..., and while it is of size > 1, it has a node jumping forward and a node jumping backward, so it is not a cycle. We can see the cycle 3 --> 4 --> 3 --> ..., and all of its nodes are white (jumping in the same direction).
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 5000-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000nums[i] != 0
Follow up: Could you solve it in O(n) time complexity and O(1) extra space complexity?
Solutions
-
class Solution { private int n; private int[] nums; public boolean circularArrayLoop(int[] nums) { n = nums.length; this.nums = nums; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (nums[i] == 0) { continue; } int slow = i, fast = next(i); while (nums[slow] * nums[fast] > 0 && nums[slow] * nums[next(fast)] > 0) { if (slow == fast) { if (slow != next(slow)) { return true; } break; } slow = next(slow); fast = next(next(fast)); } int j = i; while (nums[j] * nums[next(j)] > 0) { nums[j] = 0; j = next(j); } } return false; } private int next(int i) { return (i + nums[i] % n + n) % n; } } -
class Solution { public: bool circularArrayLoop(vector<int>& nums) { int n = nums.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (!nums[i]) continue; int slow = i, fast = next(nums, i); while (nums[slow] * nums[fast] > 0 && nums[slow] * nums[next(nums, fast)] > 0) { if (slow == fast) { if (slow != next(nums, slow)) return true; break; } slow = next(nums, slow); fast = next(nums, next(nums, fast)); } int j = i; while (nums[j] * nums[next(nums, j)] > 0) { nums[j] = 0; j = next(nums, j); } } return false; } int next(vector<int>& nums, int i) { int n = nums.size(); return (i + nums[i] % n + n) % n; } }; -
class Solution: def circularArrayLoop(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool: n = len(nums) def next(i): return (i + nums[i] % n + n) % n for i in range(n): if nums[i] == 0: continue slow, fast = i, next(i) while nums[slow] * nums[fast] > 0 and nums[slow] * nums[next(fast)] > 0: if slow == fast: if slow != next(slow): return True break slow, fast = next(slow), next(next(fast)) j = i while nums[j] * nums[next(j)] > 0: nums[j] = 0 j = next(j) return False -
func circularArrayLoop(nums []int) bool { for i, num := range nums { if num == 0 { continue } slow, fast := i, next(nums, i) for nums[slow]*nums[fast] > 0 && nums[slow]*nums[next(nums, fast)] > 0 { if slow == fast { if slow != next(nums, slow) { return true } break } slow, fast = next(nums, slow), next(nums, next(nums, fast)) } j := i for nums[j]*nums[next(nums, j)] > 0 { nums[j] = 0 j = next(nums, j) } } return false } func next(nums []int, i int) int { n := len(nums) return (i + nums[i]%n + n) % n }