--- layout: post title: "339 - Nested List Weight Sum" date: "2016-11-03" --- ##### Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube <script src="https://apis.google.com/js/platform.js"></script>
339. Nested List Weight Sum
Description
You are given a nested list of integers nestedList. Each element is either an integer or a list whose elements may also be integers or other lists.
The depth of an integer is the number of lists that it is inside of. For example, the nested list [1,[2,2],[[3],2],1] has each integer's value set to its depth.
Return the sum of each integer in nestedList multiplied by its depth.
Example 1:
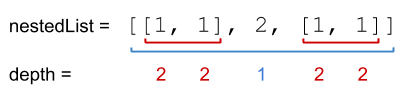
Input: nestedList = [[1,1],2,[1,1]] Output: 10 Explanation: Four 1's at depth 2, one 2 at depth 1. 1*2 + 1*2 + 2*1 + 1*2 + 1*2 = 10.
Example 2:
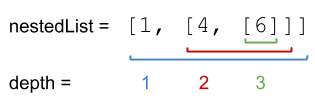
Input: nestedList = [1,[4,[6]]] Output: 27 Explanation: One 1 at depth 1, one 4 at depth 2, and one 6 at depth 3. 1*1 + 4*2 + 6*3 = 27.
Example 3:
Input: nestedList = [0] Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= nestedList.length <= 50- The values of the integers in the nested list is in the range
[-100, 100]. - The maximum depth of any integer is less than or equal to
50.
Solutions
Traverse the given nested linked list array, for each nested linked list object, call the dfs function, assign a depth value of 1, and add up and return.
In the dfs function, first determine whether it is an integer,
- If yes, it returns the current depth multiplied by an integer
- If not, then we traverse the nested array again, call the recursive function for each nested linked list, and add up the return value to return
-
/** * // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists. * // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation * public interface NestedInteger { * // Constructor initializes an empty nested list. * public NestedInteger(); * * // Constructor initializes a single integer. * public NestedInteger(int value); * * // @return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list. * public boolean isInteger(); * * // @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer * // Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list * public Integer getInteger(); * * // Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer. * public void setInteger(int value); * * // Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer to it. * public void add(NestedInteger ni); * * // @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list * // Return empty list if this NestedInteger holds a single integer * public List<NestedInteger> getList(); * } */ class Solution { public int depthSum(List<NestedInteger> nestedList) { return dfs(nestedList, 1); } private int dfs(List<NestedInteger> nestedList, int depth) { int depthSum = 0; for (NestedInteger item : nestedList) { if (item.isInteger()) { depthSum += item.getInteger() * depth; } else { depthSum += dfs(item.getList(), depth + 1); } } return depthSum; } } -
# """ # This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists. # You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation # """ # class NestedInteger: # def __init__(self, value=None): # """ # If value is not specified, initializes an empty list. # Otherwise initializes a single integer equal to value. # """ # # def isInteger(self): # """ # @return True if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list. # :rtype bool # """ # # def add(self, elem): # """ # Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer elem to it. # :rtype void # """ # # def setInteger(self, value): # """ # Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer equal to value. # :rtype void # """ # # def getInteger(self): # """ # @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer # Return None if this NestedInteger holds a nested list # :rtype int # """ # # def getList(self): # """ # @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list # Return None if this NestedInteger holds a single integer # :rtype List[NestedInteger] # """ class Solution: def depthSum(self, nestedList: List[NestedInteger]) -> int: def dfs(nestedList, depth): depth_sum = 0 for item in nestedList: if item.isInteger(): depth_sum += item.getInteger() * depth else: depth_sum += dfs(item.getList(), depth + 1) return depth_sum return dfs(nestedList, 1) ################ class Solution: # iterative def depthSum(self, nestedList): stack = [] for nestedInteger in nestedList: stack.append((1, nestedInteger)) ans = 0 while stack: depth, current = stack.pop() if current.isInteger(): ans += depth * current.getInteger() else: lst = current.getList() for nestedInteger in lst: stack.append((depth+1, nestedInteger)) return ans ############ class Solution(object): def depthSum(self, nestedList): """ :type nestedList: List[NestedInteger] :rtype: int """ def helper(root, depth): res = 0 for nested in root: if nested.isInteger(): res += depth * nested.getInteger() else: res += helper(nested.getList(), depth + 1) return res return helper(nestedList, 1) -
/** * // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists. * // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation * function NestedInteger() { * * Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list. * @return {boolean} * this.isInteger = function() { * ... * }; * * Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer * Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list * @return {integer} * this.getInteger = function() { * ... * }; * * Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer equal to value. * @return {void} * this.setInteger = function(value) { * ... * }; * * Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer elem to it. * @return {void} * this.add = function(elem) { * ... * }; * * Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list * Return null if this NestedInteger holds a single integer * @return {NestedInteger[]} * this.getList = function() { * ... * }; * }; */ /** * @param {NestedInteger[]} nestedList * @return {number} */ var depthSum = function (nestedList) { const dfs = (nestedList, depth) => { let depthSum = 0; for (const item of nestedList) { if (item.isInteger()) { depthSum += item.getInteger() * depth; } else { depthSum += dfs(item.getList(), depth + 1); } } return depthSum; }; return dfs(nestedList, 1); };