Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
323. Number of Connected Components in an Undirected Graph
Description
You have a graph of n nodes. You are given an integer n and an array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between ai and bi in the graph.
Return the number of connected components in the graph.
Example 1:
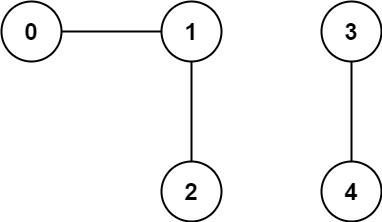
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[3,4]] Output: 2
Example 2:
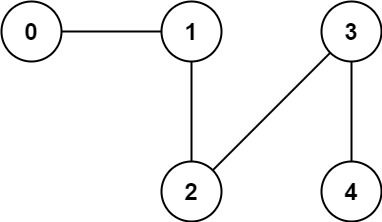
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]] Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 20001 <= edges.length <= 5000edges[i].length == 20 <= ai <= bi < nai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
Solutions
DFS
One solution is to use DFS. The idea is to give each node a flag to mark whether it has been visited. For an unvisited node, we will increment the result by 1, because this must be a new connected region. , And then we traverse the neighboring nodes through the adjacency list and mark them as visited.
After traversing all connected nodes, we continue to look for the next unvisited node, and so on until all nodes have been visited, then the number of connected regions is also calculated at this time
Union Find
Create a root array with the same subscript and node value. At this time, root[i] indicates that node i belongs to group i. We initialized n parts (res = n), assuming that each node belongs to a separate interval at the beginning .
Then we start to traverse all the edges. For two points of an edge, their values in the root at the beginning are not the same. At this time, we reduce the result by 1, which means one interval is missing. Then update the root of one of the nodes Value to make the root value of the two nodes the same.
Then we can mark the root values of all nodes in the connected interval as the same value, and the root values of different connected intervals are different, so that we can also find the number of connected intervals.
-
class Solution { private int[] p; public int countComponents(int n, int[][] edges) { p = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; } for (int[] e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; p[find(a)] = find(b); } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (i == find(i)) { ++ans; } } return ans; } private int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } } -
class Solution { public: int countComponents(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) { vector<int> p(n); iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) p[i] = i; function<int(int)> find = [&](int x) -> int { if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]); return p[x]; }; for (auto& e : edges) { int a = e[0], b = e[1]; p[find(a)] = find(b); } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans += i == find(i); return ans; } }; -
''' example-2: [[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4]] for loop [0, 1] 0 parent set to 1 1 parent set to 1 [1, 2] 1 parent set to 2 2 parent set to 2 [2, 3] 2 parent set to 3 3 parent set to 3 final: 0 parent set to 1 1 parent set to 2 2 parent set to 3 3 parent set to 3 ===> so filter for 'i == find(i)' ''' class Solution: def countComponents(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int: def find(x): if p[x] != x: p[x] = find(p[x]) return p[x] p = list(range(n)) for a, b in edges: p[find(a)] = find(b) return sum(i == find(i) for i in range(n)) # or len(set(parents)) ############ class Solution: # more literal def countComponents(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int: # Initialize parent array for union-find parent = [i for i in range(n)] # Perform union-find on each edge for u, v in edges: self.union(u, v, parent) # Count the number of distinct parents (connected components) count = len(set(self.find(x, parent) for x in range(n))) return count def union(self, x: int, y: int, parent: List[int]) -> None: rootX = self.find(x, parent) rootY = self.find(y, parent) if rootX != rootY: parent[rootX] = rootY def find(self, x: int, parent: List[int]) -> int: if parent[x] != x: parent[x] = self.find(parent[x], parent) return parent[x] -
func countComponents(n int, edges [][]int) (ans int) { p := make([]int, n) for i := range p { p[i] = i } var find func(int) int find = func(x int) int { if p[x] != x { p[x] = find(p[x]) } return p[x] } for _, e := range edges { a, b := e[0], e[1] p[find(a)] = find(b) } for i := 0; i < n; i++ { if i == find(i) { ans++ } } return } -
/** * @param {number} n * @param {number[][]} edges * @return {number} */ var countComponents = function (n, edges) { let p = new Array(n); for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { p[i] = i; } function find(x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } for (const [a, b] of edges) { p[find(a)] = find(b); } let ans = 0; for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (i == find(i)) { ++ans; } } return ans; }; -
function countComponents(n: number, edges: number[][]): number { const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []); for (const [a, b] of edges) { g[a].push(b); g[b].push(a); } const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false); const dfs = (i: number): number => { if (vis[i]) { return 0; } vis[i] = true; for (const j of g[i]) { dfs(j); } return 1; }; return g.reduce((acc, _, i) => acc + dfs(i), 0); }