Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Question
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/255.html
Given an array of unique integers preorder, return true if it is the correct preorder traversal sequence of a binary search tree.
Example 1:
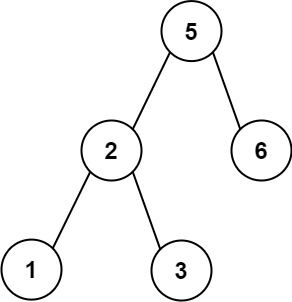
Input: preorder = [5,2,1,3,6] Output: true
Example 2:
Input: preorder = [5,2,6,1,3] Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 1041 <= preorder[i] <= 104- All the elements of
preorderare unique.
Follow up: Could you do it using only constant space complexity?
Algorithm
First, initialize a variable low with a minimum possible value, then iterate through the array. If the current value is less than low, return false.
For the root node, push it onto the stack, and then begin traversing backward.
If an encountered number is smaller than the element at the top of the stack, it indicates that this number belongs to its left subtree, and it should continue to be pushed onto the stack.
When you encounter a number greater than the stack’s top element, this number is a right child value. At this point, you need to determine the right subtree to which this node belongs.
Therefore, update the low value to the value just removed and pop the top element off the stack. Continue this process, comparing with the new top element of the stack.
If the current number is still greater, keep updating the low value and removing the top of the stack, until either the stack is empty or the current top element of the stack is greater than the current number. Then, stop and push the current number onto the stack.
Following this procedure, if the function does not return false while traversing the entire array, it should return true at the end.
Code
-
import java.util.Stack; public class Verify_Preorder_Sequence_in_Binary_Search_Tree { public static void main(String[] args) { Verify_Preorder_Sequence_in_Binary_Search_Tree out = new Verify_Preorder_Sequence_in_Binary_Search_Tree(); Solution_dfs s = out.new Solution_dfs(); System.out.println(s.verifyPreorder(new int[]{5,2,6,1,3})); System.out.println(s.verifyPreorder(new int[]{5,2,1,3,6})); Solution sss = out.new Solution(); System.out.println(sss.verifyPreorder(new int[]{5,2,6,1,3})); System.out.println(sss.verifyPreorder(new int[]{5,2,1,3,6})); } public class Solution { public boolean verifyPreorder(int[] preorder) { int lowBound = Integer.MIN_VALUE; Stack<Integer> sk = new Stack<>(); for (int each : preorder) { if (each < lowBound) { return false; } while (!sk.empty() && each > sk.peek()) { // s>peek => right value lowBound = sk.pop(); } sk.push(each); } return true; } } public class Solution_dfs { public boolean verifyPreorder(int[] preorder) { return dfs(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE); } boolean dfs(int[] preorder, int start, int end, int lower, int upper) { if (start > end) return true; int val = preorder[start]; if (val <= lower || val >= upper) return false; int i = 0; for (i = start + 1; i <= end; ++i) { if (preorder[i] >= val) break; // @note: i stops at root's first right child, same as above "if (each < lowBound) {" } return dfs(preorder, start + 1, i - 1, lower, val) && dfs(preorder, i, end, val, upper); } } } ############ class Solution { public boolean verifyPreorder(int[] preorder) { Deque<Integer> stk = new ArrayDeque<>(); int last = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int x : preorder) { if (x < last) { return false; } while (!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek() < x) { last = stk.poll(); } stk.push(x); } return true; } } -
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/verify-preorder-sequence-in-binary-search-tree/ // Time: O(N) // Space: O(N) class Solution { public: bool verifyPreorder(vector<int>& A) { stack<int> s; int mn = INT_MIN; for (int n : A) { if (n < mn) return false; while (s.size() && s.top() < n) { mn = s.top(); s.pop(); } s.push(n); } return true; } }; -
class Solution: def verifyPreorder(self, preorder: List[int]) -> bool: stk = [] last = -inf for x in preorder: if x < last: return False while stk and stk[-1] < x: last = stk.pop() stk.append(x) return True class Solution: # o(N) but modifying input list def verifyPreorder(self, preorder: List[int]) -> bool: low = -math.inf i = -1 for p in preorder: if p < low: return False while i >= 0 and preorder[i] < p: low = preorder[i] i -= 1 i += 1 preorder[i] = p return True ############ class Solution(object): # O(n) sapce complexity, **stack** def verifyPreorder(self, preorder): """ :type preorder: List[int] :rtype: bool """ if len(preorder) <= 1: return True stack, lastElem = [preorder[0]], None for i in range(1, len(preorder)): if lastElem > preorder[i]: return False while len(stack) > 0 and preorder[i] > stack[-1]: lastElem = stack.pop() stack.append(preorder[i]) return True -
func verifyPreorder(preorder []int) bool { var stk []int last := math.MinInt32 for _, x := range preorder { if x < last { return false } for len(stk) > 0 && stk[len(stk)-1] < x { last = stk[len(stk)-1] stk = stk[0 : len(stk)-1] } stk = append(stk, x) } return true }