Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Question
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/218.html
218. The Skyline Problem
Level
Hard
Description
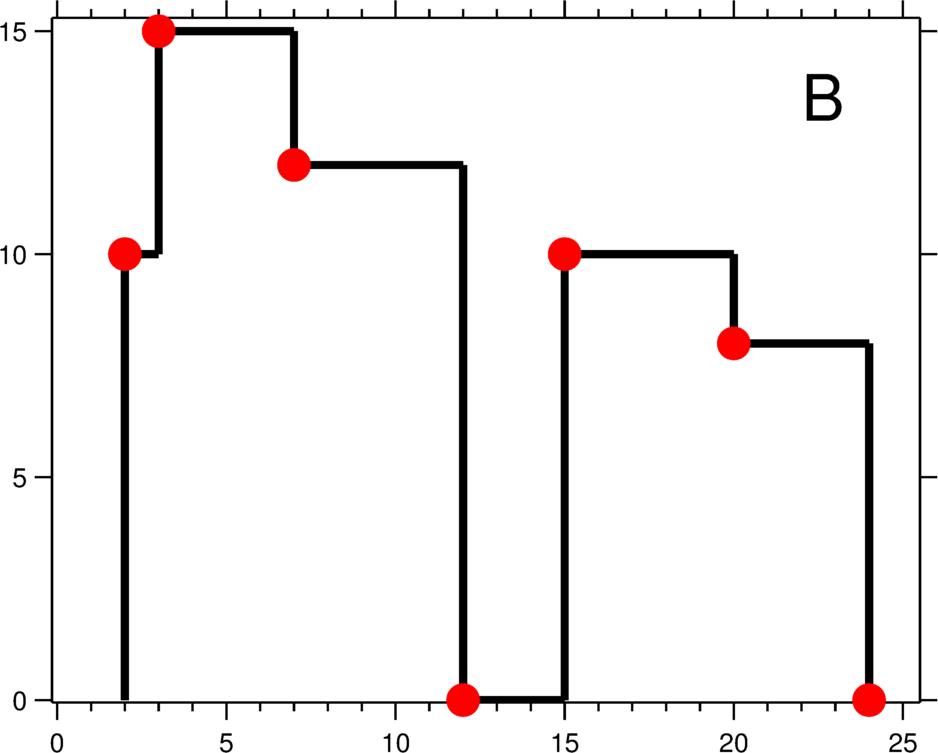
A city’s skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Now suppose you are given the locations and height of all the buildings as shown on a cityscape photo (Figure A), write a program to output the skyline formed by these buildings collectively (Figure B).
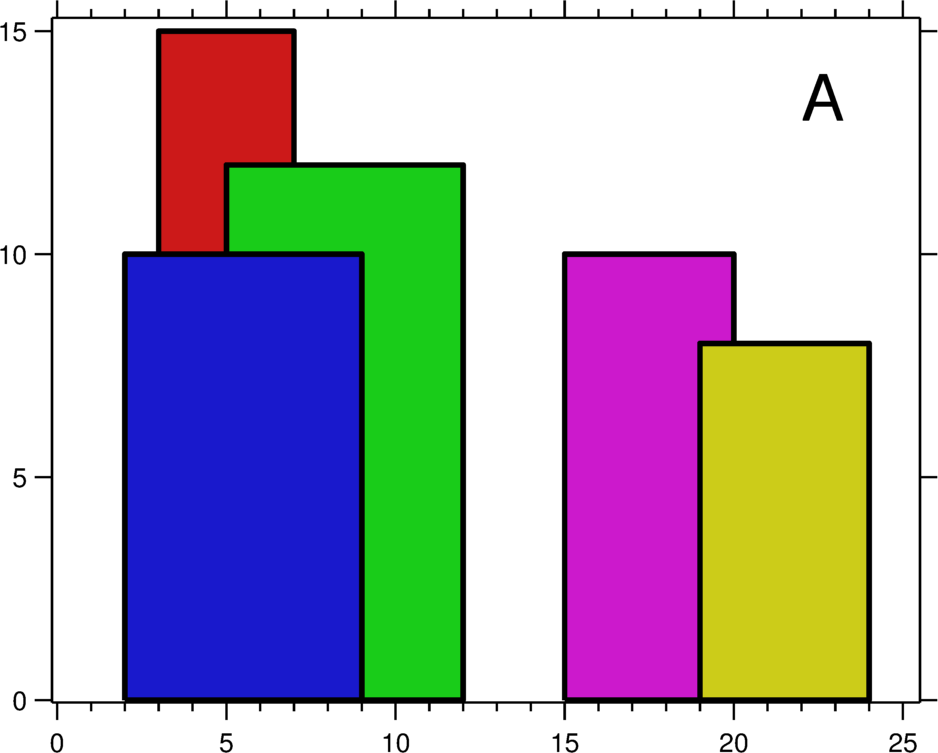
The geometric information of each building is represented by a triplet of integers [Li, Ri, Hi], where Li and Ri are the x coordinates of the left and right edge of the ith building, respectively, and Hi is its height. It is guaranteed that 0 ≤ Li, Ri ≤ INT_MAX, 0 < Hi ≤ INT_MAX, and Ri - Li > 0. You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
For instance, the dimensions of all buildings in Figure A are recorded as: [ [2 9 10], [3 7 15], [5 12 12], [15 20 10], [19 24 8] ].
The output is a list of “key points” (red dots in Figure B) in the format of [ [x1,y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], ... ] that uniquely defines a skyline. A key point is the left endpoint of a horizontal line segment. Note that the last key point, where the rightmost building ends, is merely used to mark the termination of the skyline, and always has zero height. Also, the ground in between any two adjacent buildings should be considered part of the skyline contour.
For instance, the skyline in Figure B should be represented as: [ [2 10], [3 15], [7 12], [12 0], [15 10], [20 8], [24, 0] ].
Notes:
- The number of buildings in any input list is guaranteed to be in the range
[0, 10000]. - The input list is already sorted in ascending order by the left x position
Li. - The output list must be sorted by the x position.
- There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance,
[...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...]is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
Algorithm
The skyline is defined as the outer contour of the rectangles formed by the buildings when viewed from a distance. The problem input is a list of buildings, each represented by a list [left, right, height], and the output is a list of key points defining the skyline, where each key point is a list [x, height] representing a vertical line at x with a height change.
Preparation
-
Initialization: The solution initializes an empty list
ansfor the skyline key points, a listlinesfor all unique building edgexcoordinates (both left and right edges), and aPriorityQueuepqto maintain active buildings by height in descending order (negative heights are used since Python’sPriorityQueueis a min-heap). -
Collecting Edges: It iterates through all buildings and adds both the left and right edge
xcoordinates tolines. -
Sorting Edges: The
lineslist is sorted to process edge coordinates in ascending order.
Processing Each Edge
-
Iterating Through Edges: For each edge
lineinlines, the algorithm performs two main tasks:-
Adding Buildings to the Queue: It adds to
pqall buildings that start before or at the currentline(i.e., buildings whose left edge is<= line). Each entry inpqis a list[-height, left, right], whereheightis negated to simulate a max-heap behavior, allowing buildings with the greatest height to be processed first. -
Removing Expired Buildings: It removes from
pqall buildings that end before or atline(i.e., buildings whose right edge is<= line), as they are no longer part of the skyline past this point.
-
-
Determining the Highest Building: After adding new buildings and removing expired ones, the highest remaining building (if any) influences the skyline at
line. The height of this building is determined frompq.queue[0][0](negated back to positive). -
Updating the Skyline: If the current
highis different from the height of the last added key point inans, a new key point[line, high]is added toans. This step skips redundant key points where the height does not change.
Output
- Returning the Result: Finally, after processing all edges, the
anslist, which now contains the skyline key points, is returned.
Example Illustration
Suppose the input is buildings = [[2,9,10], [3,7,15], [5,12,12]]. The key steps would involve:
- Sorting the edges:
lines = [2, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12]. - Iterating through each edge, updating
pqwith active buildings, and determining the highest building at each edge. - Constructing
ansbased on height changes at each processed edge, resulting in the skyline.
This solution efficiently computes the skyline by leveraging a priority queue to keep track of active buildings and their heights, ensuring that the highest buildings at each edge are accurately reflected in the output.
Code
-
import java.util.*; public class The_Skyline_Problem { public static void main(String[] args) { The_Skyline_Problem out = new The_Skyline_Problem(); Solution_Heap s = out.new Solution_Heap(); // output: [ [2 10], [3 15], [7 12], [12 0], [15 10], [20 8], [24, 0] ] s.getSkyline( new int[][]{ {2,9,10}, {3,7,15}, {5,12,12}, {15,20,10}, {19,24,8} } ) .stream().forEach(System.out::println); } class Solution_Heap { public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); if (buildings == null || buildings.length == 0 || buildings[0].length == 0) { return result; } List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<Edge>(); // add all left/right edges for (int[] each: buildings) { edges.add(new Edge(each[0], each[2], true)); edges.add(new Edge(each[1], each[2], false)); } // sort edges, NlogN Collections.sort(edges, (a, b) -> { if (a.x != b.x) { return Integer.compare(a.x, b.x); } if (a.isStart && b.isStart) { return Integer.compare(b.height, a.height); // higher edge at front } if (!a.isStart && !b.isStart) { return Integer.compare(a.height, b.height); // lower edge at front } return a.isStart ? -1 : 1; // lower edge at front }); // process edges, comparator is reverseOrder() PriorityQueue<Integer> heightHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(Collections.reverseOrder()); for (Edge edge : edges) { if (edge.isStart) { if (heightHeap.isEmpty() || edge.height > heightHeap.peek()) { result.add(Arrays.asList( edge.x, edge.height )); } heightHeap.add(edge.height); } else { heightHeap.remove(edge.height); if (heightHeap.isEmpty()){ result.add( Arrays.asList(edge.x, 0) ); // last point } else if (edge.height > heightHeap.peek()){ // @note: intersect result.add( Arrays.asList(edge.x, heightHeap.peek()) ); } } } return result; } class Edge { int x; // x坐标 int height; boolean isStart; public Edge(int x, int height, boolean isStart) { this.x = x; this.height = height; this.isStart = isStart; } } } // merge sort example public class Solution_mergeSort { public List<int[]> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) { if(buildings == null || buildings.length == 0) { return new LinkedList<int[]>(); } return getSkyline(buildings, 0, buildings.length - 1); } // NlogN private LinkedList<int[]> getSkyline(int[][] buildings, int lo, int hi) { if (lo < hi) { int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; return mergeSkylines(getSkyline(buildings, lo, mid), getSkyline(buildings, mid + 1, hi)); } else { // lo == hi, base case, add the final already-merged building to skyline LinkedList<int[]> skyline = new LinkedList<int[]>(); skyline.add(new int[]{buildings[lo][0], buildings[lo][2]}); // only care about [left-index, height] skyline.add(new int[]{buildings[lo][1], 0}); // right-index is just for last right edge return skyline; } } // merge two Skylines private LinkedList<int[]> mergeSkylines(LinkedList<int[]> skyline1, LinkedList<int[]> skyline2) { LinkedList<int[]> skyline = new LinkedList<int[]>(); int height1 = 0, height2 = 0; while(skyline1.size() > 0 && skyline2.size() > 0) { int index = 0, height = 0; // @note: always remove the smaller index first, so order is guaranteed if (skyline1.getFirst()[0] < skyline2.getFirst()[0]) { index = skyline1.getFirst()[0]; height1 = skyline1.getFirst()[1]; height = Math.max(height1, height2); skyline1.removeFirst(); } else if (skyline1.getFirst()[0] > skyline2.getFirst()[0]) { index = skyline2.getFirst()[0]; height2 = skyline2.getFirst()[1]; height = Math.max(height1, height2); skyline2.removeFirst(); } else { index = skyline1.getFirst()[0]; height1 = skyline1.getFirst()[1]; height2 = skyline2.getFirst()[1]; height = Math.max(height1, height2); skyline1.removeFirst(); skyline2.removeFirst(); } if (skyline.size() == 0 || height != skyline.getLast()[1]) { skyline.add(new int[]{index, height}); } } // final check skyline.addAll(skyline1); skyline.addAll(skyline2); return skyline; } } } -
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/the-skyline-problem/ // Time: O(NlogN) // Space: O(N) // Ref: https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/14939/my-c-code-using-one-priority-queue-812-ms bool cmp(vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b) { return a[0] < b[0]; } class Solution { public: vector<pair<int, int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) { vector<pair<int, int>> ans; sort(buildings.begin(), buildings.end(), cmp); int i = 0, x = 0, y = 0, N = buildings.size(); priority_queue<pair<int, int>> live;// first: height, second: right while (i < N || !live.empty()) { if (i < N && (live.empty() || live.top().second >= buildings[i][0])) { x = buildings[i][0]; while (i < N && buildings[i][0] == x) { live.push(make_pair(buildings[i][2], buildings[i][1])); ++i; } } else { x = live.top().second; while (!live.empty() && live.top().second <= x) live.pop(); } y = live.empty() ? 0 : live.top().first; if (ans.empty() || ans.back().second != y) ans.push_back(make_pair(x, y)); } return ans; } }; -
''' >>> a = [] >>> a.append((3, 5)) >>> a.append((3, -5)) >>> a.append((2, -10)) >>> a.append((2, 10)) >>> a [(3, 5), (3, -5), (2, -10), (2, 10)] >>> a.sort() >>> a [(2, -10), (2, 10), (3, -5), (3, 5)] >>> from queue import PriorityQueue >>> pq = PriorityQueue() >>> >>> pq.put([1,2,3]) >>> pq.put([-10,20,30]) >>> pq.put([11,22,33]) >>> >>> pq <Queue.PriorityQueue instance at 0x10aec51b8> >>> pq.queue[0][0] -10 >>> pq.get() [-10, 20, 30] >>> pq.queue[0][0] 1 ''' from queue import PriorityQueue class Solution: def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: ans, lines, pq = [], [], PriorityQueue() for build in buildings: lines.extend([build[0], build[1]]) lines.sort() curbuilding, n = 0, len(buildings) for line in lines: # 对于每一个边界线 lines[i],找出所有包含 lines[i] 的建筑物 while curbuilding < n and buildings[curbuilding][0] <= line: pq.put([-buildings[curbuilding][2], buildings[curbuilding][0], buildings[curbuilding][1]]) # 建筑物的高度构建优先队列(大根堆),这里会包括line自己的building curbuilding += 1 while not pq.empty() and pq.queue[0][2] <= line: # higher at heap top after negated pq.get() # i.e. pop(), remove no-overlapping building high = 0 # 建筑物的左边界小于等于 lines[i],右边界大于 lines[i],则这些建筑物中高度最高的建筑物的高度就是该线轮廓点的高度 if not pq.empty(): high = -pq.queue[0][0] if len(ans) > 0 and ans[-1][1] == high: # 绿色建筑的左边的line,就要跳过 continue ans.append([line, high]) return ans ############ ''' The solution uses a list called points to store the critical points and heights of the buildings. Each point is represented as a tuple (x, h), where x is the x-coordinate and h is the height. The points are sorted in ascending order based on the x-coordinate. The solution also uses a heap to store the heights in descending order. The heap is initialized with a height of 0. For each point, if the height is negative, it means it is the start of a building, so the negative height is added to the heap. If the height is positive, it means it is the end of a building, so the corresponding negative height is removed from the heap. After processing each point, the maximum height is obtained from the heap, and if it is different from the previous maximum height, the current point is added to the skyline. Finally, the skyline is returned, excluding the initial point (0, 0) that was added as a starting point. Note: The solution assumes that the input buildings is a list of tuples (left, right, height), where left and right represent the x-coordinates of the building's left and right edges, and height represents the height of the building. ''' import heapq class Solution: def getSkyline(self, buildings): # Create a list to store the critical points and heights points = [] for left, right, height in buildings: points.append((left, -height)) # Start of building, negative height points.append((right, height)) # End of building, positive height # Sort the points in ascending order based on x-coordinate # If two points have the same x-coordinate, the one with larger height comes first points.sort() # Create a heap to store the heights in descending order heights = [0] # Initialize the heap with a height of 0 skyline = [(0, 0)] # Initialize the skyline with a point (0, 0) for x, h in points: if h < 0: heapq.heappush(heights, h) # Add the negative height to the heap else: heights.remove(-h) # Remove the corresponding negative height from the heap heapq.heapify(heights) # Reorganize the heap # The current maximum height is the first element in the heap max_height = -heights[0] # If the maximum height has changed, add the current point to the skyline if max_height != skyline[-1][1]: skyline.append((x, max_height)) return skyline[1:] # Exclude the initial point (0, 0) -
type Matrix struct{ left, right, height int } type Queue []Matrix func (q Queue) Len() int { return len(q) } func (q Queue) Top() Matrix { return q[0] } func (q Queue) Swap(i, j int) { q[i], q[j] = q[j], q[i] } func (q Queue) Less(i, j int) bool { return q[i].height > q[j].height } func (q *Queue) Push(x interface{}) { *q = append(*q, x.(Matrix)) } func (q *Queue) Pop() interface{} { old, x := *q, (*q)[len(*q)-1] *q = old[:len(old)-1] return x } func getSkyline(buildings [][]int) [][]int { skys, lines, pq := make([][]int, 0), make([]int, 0), &Queue{} heap.Init(pq) for _, v := range buildings { lines = append(lines, v[0], v[1]) } sort.Ints(lines) city, n := 0, len(buildings) for _, line := range lines { // 将所有符合条件的矩形加入队列 for ; city < n && buildings[city][0] <= line && buildings[city][1] > line; city++ { v := Matrix{left: buildings[city][0], right: buildings[city][1], height: buildings[city][2]} heap.Push(pq, v) } // 从队列移除不符合条件的矩形 for pq.Len() > 0 && pq.Top().right <= line { heap.Pop(pq) } high := 0 // 队列为空说明是最右侧建筑物的终点,其轮廓点为 (line, 0) if pq.Len() != 0 { high = pq.Top().height } // 如果该点高度和前一个轮廓点一样的话,直接忽略 if len(skys) > 0 && skys[len(skys)-1][1] == high { continue } skys = append(skys, []int{line, high}) } return skys } -
impl Solution { pub fn get_skyline(buildings: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> { let mut skys: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![]; let mut lines = vec![]; for building in buildings.iter() { lines.push(building[0]); lines.push(building[1]); } lines.sort_unstable(); let mut pq = std::collections::BinaryHeap::new(); let (mut city, n) = (0, buildings.len()); for line in lines { while city < n && buildings[city][0] <= line && buildings[city][1] > line { pq.push((buildings[city][2], buildings[city][1])); city += 1; } while !pq.is_empty() && pq.peek().unwrap().1 <= line { pq.pop(); } let mut high = 0; if !pq.is_empty() { high = pq.peek().unwrap().0; } if !skys.is_empty() && skys.last().unwrap()[1] == high { continue; } skys.push(vec![line, high]); } skys } }