Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
Question
Formatted question description: https://leetcode.ca/all/138.html
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) that therandompointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:
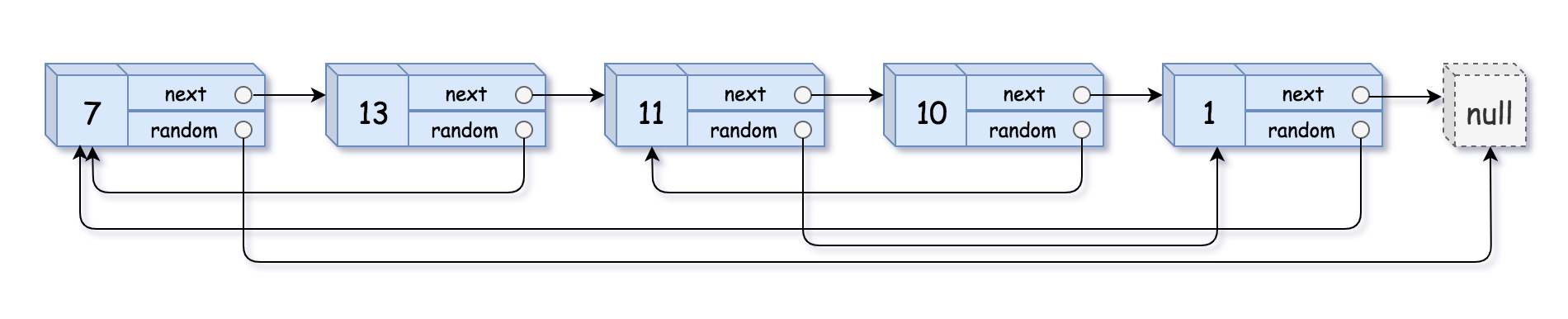
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
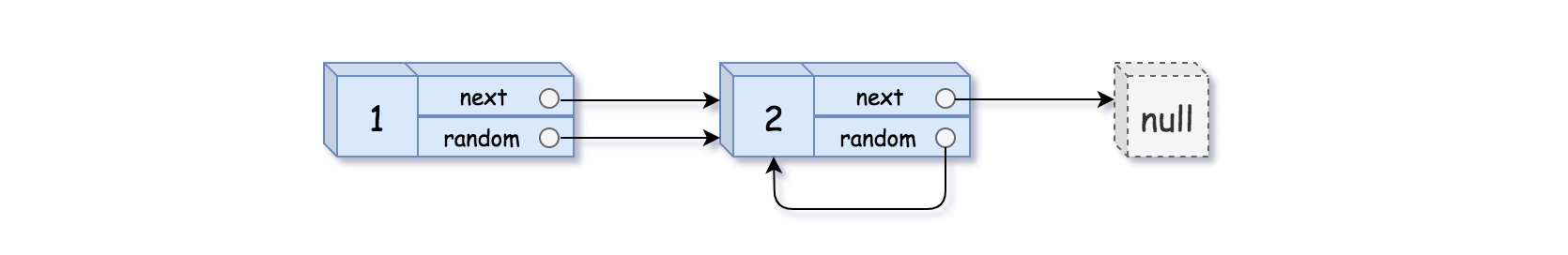
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]] Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
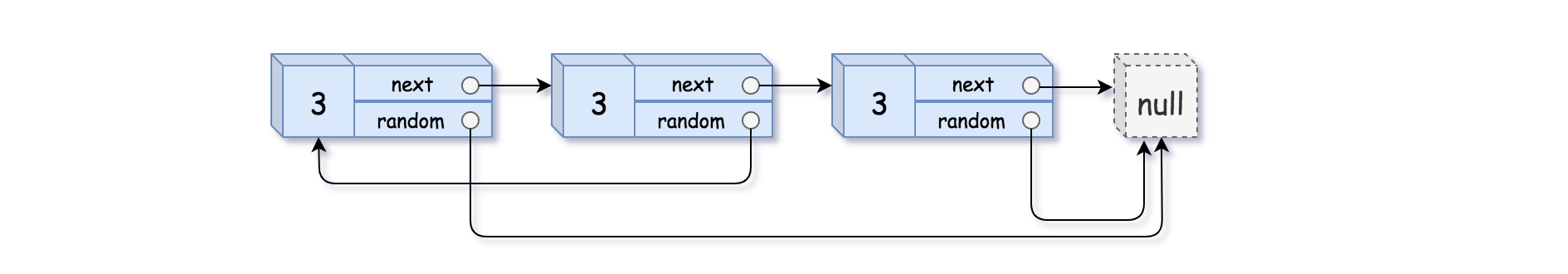
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 1000-104 <= Node.val <= 104Node.randomisnullor is pointing to some node in the linked list.
Algorithm
Three steps, with no extra space:
-
Copy a new node behind each node in the original linked list.
-
Assign values to the random pointers of new nodes in turn, and this assignment is very easy
cur->next->random = cur->random->next. -
Disconnect the linked list to get a new linked list after deep copy.
For example, for example, the original linked list is 1(2) -> 2(3) -> 3(1), and the node pointed to by its random pointer is in parentheses, so this solution is to first traverse the original linked list. Copy a same node after each node, but the random pointer of the copied node is still empty, then the original linked list becomes 1(2) -> 1(null) -> 2(3) -> 2(null ) -> 3(1) -> 3(null). Then the second traversal is to assign the correct value to the random pointer of the copy node, and the original linked list becomes 1(2) -> 1(2) -> 2(3) -> 2(3) -> 3 (1) -> 3(1), note that the assignment statement is:
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
Here cur is the node in the original linked list, cur->next is the node of the copied linked list, and cur->next->random is the random pointer of the copied linked list. cur->random is the node pointed to by the random pointer of the original linked list node. Because it points to the node of the original linked list, we have to add another next to point to the node of the copied linked list. The last traversal is to disconnect the original linked list from the copy linked list.
Code
-
public class Copy_List_with_Random_Pointer { /** * Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer. * class RandomListNode { * int label; * RandomListNode next, random; * RandomListNode(int x) { this.label = x; } * }; */ /* 1. 在原链表的每个节点后面拷贝出一个新的节点。 2. 依次给新的节点的随机指针赋值,而且这个赋值非常容易 cur->next->random = cur->random->next。 3. 断开链表可得到深度拷贝后的新链表。 */ public class Solution_noExtraMap { public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) { if (head == null) { return null; } // duplicate new node right after RandomListNode current = head; while (current != null) { RandomListNode t = new RandomListNode(current.label); t.next = current.next; current.next = t; current = t.next; } // random pointer update for duplicate new node current = head; while (current != null) { if (current.random != null) { current.next.random = current.random.next; } current = current.next.next; } // cut copied list out current = head; RandomListNode res = head.next; while (current != null) { RandomListNode t = current.next; current.next = t.next; if (t.next != null) { t.next = t.next.next; } current = current.next; } return res; } } public class Solution { // map from original node, to its copy node HashMap<RandomListNode, RandomListNode> hm = new HashMap<>(); public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) { if (head == null) { return null; } RandomListNode current = head; while (current != null) { RandomListNode currentCopy = getNodeCopy(current); RandomListNode currentNextCopy = getNodeCopy(current.next); RandomListNode currentRandomCopy = getNodeCopy(current.random); currentCopy.next = currentNextCopy; currentCopy.random = currentRandomCopy; current = current.next; } return hm.get(head); } private RandomListNode getNodeCopy (RandomListNode originalNode) { if (originalNode == null) { // @note: missed this check, last node will cause error, whose next is null return null; } if (hm.containsKey(originalNode)) { return hm.get(originalNode); } else { RandomListNode nodeCopy = new RandomListNode(originalNode.label); hm.put(originalNode, nodeCopy); return nodeCopy; } } } } ############ /* // Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } for (Node cur = head; cur != null;) { Node node = new Node(cur.val, cur.next); cur.next = node; cur = node.next; } for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next.next) { if (cur.random != null) { cur.next.random = cur.random.next; } } Node ans = head.next; for (Node cur = head; cur != null;) { Node nxt = cur.next; if (nxt != null) { cur.next = nxt.next; } cur = nxt; } return ans; } } -
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/ // Time: O(N) // Space: O(1) class Solution { public: Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { auto p = head; while (p) { auto node = p; p = p->next; auto copy = new Node(node->val); node->next = copy; copy->next = p; } p = head; while (p) { if (p->random) p->next->random = p->random->next; p = p->next->next; } p = head; Node h(0), *tail = &h; while (p) { auto node = p->next; p->next = node->next; p = p->next; tail->next = node; tail = node; } return h.next; } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer. # class RandomListNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.label = x # self.next = None # self.random = None class Solution: def copyRandomList(self, head: "Node") -> "Node": if head is None: return None cur = head while cur: # copy nodes node = Node(cur.val, cur.next) cur.next = node cur = node.next cur = head while cur: # copy random pointers if cur.random: cur.next.random = cur.random.next cur = cur.next.next ans = head.next cur = head while cur: # cut into 2 lists nxt = cur.next if nxt: cur.next = nxt.next cur = nxt return ans class Solution: # with a map def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node': if not head: return None node_map = {} # Create the copy nodes without next and random connections current = head while current: node_map[current] = Node(current.val) current = current.next # Assign next and random connections for the copy nodes current = head while current: copy_node = node_map[current] copy_node.next = node_map.get(current.next) copy_node.random = node_map.get(current.random) current = current.next return node_map[head] -
/** * Definition for a Node. * type Node struct { * Val int * Next *Node * Random *Node * } */ func copyRandomList(head *Node) *Node { if head == nil { return nil } for cur := head; cur != nil; { node := &Node{cur.Val, cur.Next, nil} cur.Next = node cur = node.Next } for cur := head; cur != nil; cur = cur.Next.Next { if cur.Random != nil { cur.Next.Random = cur.Random.Next } } ans := head.Next for cur := head; cur != nil; { nxt := cur.Next if nxt != nil { cur.Next = nxt.Next } cur = nxt } return ans } -
/** * Definition for Node. * class Node { * val: number * next: Node | null * random: Node | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: Node, random?: Node) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * this.random = (random===undefined ? null : random) * } * } */ function copyRandomList(head: Node | null): Node | null { const map = new Map<Node, Node>(); let cur = head; while (cur != null) { map.set(cur, new Node(cur.val)); cur = cur.next; } cur = head; while (cur != null) { map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next) ?? null; map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random) ?? null; cur = cur.next; } return map.get(head); } -
/** * // Definition for a Node. * function Node(val, next, random) { * this.val = val; * this.next = next; * this.random = random; * }; */ /** * @param {Node} head * @return {Node} */ var copyRandomList = function (head) { if (!head) { return null; } for (let cur = head; cur; ) { const node = new Node(cur.val, cur.next, null); cur.next = node; cur = node.next; } for (let cur = head; cur; cur = cur.next.next) { if (cur.random) { cur.next.random = cur.random.next; } } const ans = head.next; for (let cur = head; cur; ) { const nxt = cur.next; if (nxt) { cur.next = nxt.next; } cur = nxt; } return ans; }; -
/* // Definition for a Node. public class Node { public int val; public Node next; public Node random; public Node(int _val) { val = _val; next = null; random = null; } } */ public class Solution { public Node CopyRandomList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } for (Node cur = head; cur != null; ) { Node node = new Node(cur.val, cur.next); cur.next = node; cur = node.next; } for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next.next) { if (cur.random != null) { cur.next.random = cur.random.next; } } Node ans = head.next; for (Node cur = head; cur != null; ) { Node nxt = cur.next; if (nxt != null) { cur.next = nxt.next; } cur = nxt; } return ans; } }