Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
61. Rotate List
Description
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
Example 1:
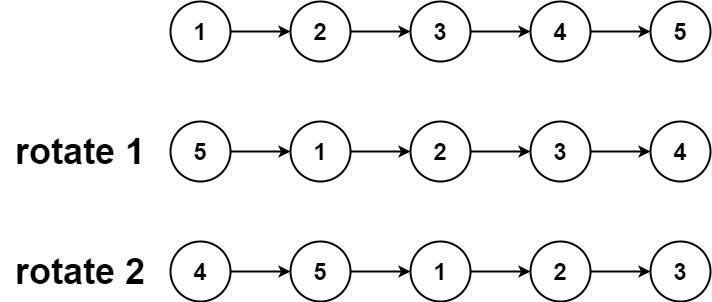
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
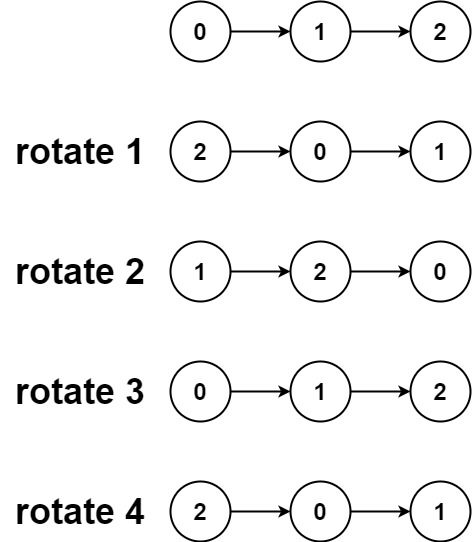
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4 Output: [2,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 500]. -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 109
Solutions
Solution 1: Fast and Slow Pointers + Link List Concatenation
First, we check whether the number of nodes in the linked list is less than $2$. If so, we directly return $head$.
Otherwise, we first count the number of nodes $n$ in the linked list, and then take the modulus of $k$ by $n$ to get the effective value of $k$.
If the effective value of $k$ is $0$, it means that the linked list does not need to be rotated, and we can directly return $head$.
Otherwise, we use fast and slow pointers, let the fast pointer move $k$ steps first, and then let the fast and slow pointers move together until the fast pointer moves to the end of the linked list. At this time, the next node of the slow pointer is the new head node of the linked list.
Finally, we concatenate the linked list.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the number of nodes in the linked list. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } ListNode cur = head; int n = 0; for (; cur != null; cur = cur.next) { n++; } k %= n; if (k == 0) { return head; } ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (k-- > 0) { fast = fast.next; } while (fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } ListNode ans = slow.next; slow.next = null; fast.next = head; return ans; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) { if (!head || !head->next) { return head; } ListNode* cur = head; int n = 0; while (cur) { ++n; cur = cur->next; } k %= n; if (k == 0) { return head; } ListNode* fast = head; ListNode* slow = head; while (k--) { fast = fast->next; } while (fast->next) { fast = fast->next; slow = slow->next; } ListNode* ans = slow->next; slow->next = nullptr; fast->next = head; return ans; } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def rotateRight(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]: if head is None or head.next is None: return head cur, n = head, 0 while cur: n += 1 cur = cur.next k %= n if k == 0: return head fast = slow = head for _ in range(k): fast = fast.next while fast.next: fast, slow = fast.next, slow.next ans = slow.next slow.next = None fast.next = head return ans -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func rotateRight(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode { if head == nil || head.Next == nil { return head } cur := head n := 0 for cur != nil { cur = cur.Next n++ } k %= n if k == 0 { return head } fast, slow := head, head for i := 0; i < k; i++ { fast = fast.Next } for fast.Next != nil { fast = fast.Next slow = slow.Next } ans := slow.Next slow.Next = nil fast.Next = head return ans } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * public int val; * public ListNode next; * public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) { * this.val = val; * this.next = next; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode RotateRight(ListNode head, int k) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } var cur = head; int n = 0; while (cur != null) { cur = cur.next; ++n; } k %= n; if (k == 0) { return head; } var fast = head; var slow = head; while (k-- > 0) { fast = fast.next; } while (fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } var ans = slow.next; slow.next = null; fast.next = head; return ans; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function rotateRight(head: ListNode | null, k: number): ListNode | null { if (!head || !head.next) { return head; } let cur = head; let n = 0; while (cur) { cur = cur.next; ++n; } k %= n; if (k === 0) { return head; } let fast = head; let slow = head; while (k--) { fast = fast.next; } while (fast.next) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } const ans = slow.next; slow.next = null; fast.next = head; return ans; } -
// Definition for singly-linked list. // #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)] // pub struct ListNode { // pub val: i32, // pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>> // } // // impl ListNode { // #[inline] // fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // ListNode { // next: None, // val // } // } // } impl Solution { pub fn rotate_right(mut head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, mut k: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> { if head.is_none() || k == 0 { return head; } let n = { let mut cur = &head; let mut res = 0; while cur.is_some() { cur = &cur.as_ref().unwrap().next; res += 1; } res }; k = k % n; if k == 0 { return head; } let mut cur = &mut head; for _ in 0..n - k - 1 { cur = &mut cur.as_mut().unwrap().next; } let mut res = cur.as_mut().unwrap().next.take(); cur = &mut res; while cur.is_some() { cur = &mut cur.as_mut().unwrap().next; } *cur = head.take(); res } }