Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
Description
You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists list1 and list2.
Merge the two lists into one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Return the head of the merged linked list.
Example 1:
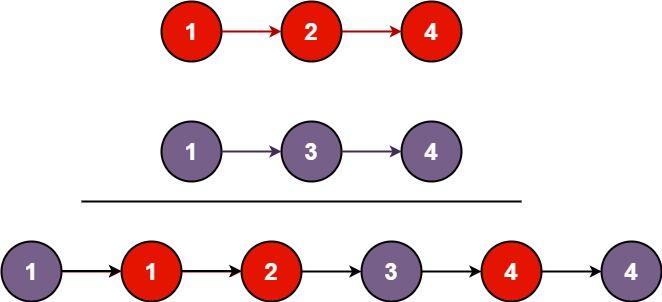
Input: list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4] Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]
Example 2:
Input: list1 = [], list2 = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: list1 = [], list2 = [0] Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in both lists is in the range
[0, 50]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100- Both
list1andlist2are sorted in non-decreasing order.
Solutions
Solution 1: Recursion
First, we judge whether the linked lists $l_1$ and $l_2$ are empty. If one of them is empty, we return the other linked list. Otherwise, we compare the head nodes of $l_1$ and $l_2$:
- If the value of the head node of $l_1$ is less than or equal to the value of the head node of $l_2$, we recursively call the function $mergeTwoLists(l_1.next, l_2)$, and connect the head node of $l_1$ with the returned linked list head node, and return the head node of $l_1$.
- Otherwise, we recursively call the function $mergeTwoLists(l_1, l_2.next)$, and connect the head node of $l_2$ with the returned linked list head node, and return the head node of $l_2$.
The time complexity is $O(m + n)$, and the space complexity is $O(m + n)$. Here, $m$ and $n$ are the lengths of the two linked lists respectively.
Solution 2: Iteration
We can also use iteration to implement the merging of two sorted linked lists.
First, we define a dummy head node $dummy$, then loop through the two linked lists, compare the head nodes of the two linked lists, add the smaller node to the end of $dummy$, until one of the linked lists is empty, then add the remaining part of the other linked list to the end of $dummy$.
Finally, return $dummy.next$.
The time complexity is $O(m + n)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the lengths of the two linked lists respectively. Ignoring the space consumption of the answer linked list, the space complexity is $O(1)$.
-
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); ListNode curr = dummy; while (list1 != null && list2 != null) { if (list1.val <= list2.val) { curr.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } else { curr.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } curr = curr.next; } curr.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1; return dummy.next; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(); ListNode* curr = dummy; while (list1 && list2) { if (list1->val <= list2->val) { curr->next = list1; list1 = list1->next; } else { curr->next = list2; list2 = list2->next; } curr = curr->next; } curr->next = list1 ? list1 : list2; return dummy->next; } }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next # without ops after while loop class Solution: def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: dummy = ListNode() current = dummy while list1 or list2: v1 = list1.val if list1 else float('inf') v2 = list2.val if list2 else float('inf') if v1 < v2: current.next = list1 list1 = list1.next else: current.next = list2 list2 = list2.next current = current.next return dummy.next ############ # Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def mergeTwoLists( self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode] ) -> Optional[ListNode]: dummy = ListNode() curr = dummy while list1 and list2: if list1.val <= list2.val: curr.next = list1 list1 = list1.next else: curr.next = list2 list2 = list2.next curr = curr.next curr.next = list1 or list2 return dummy.next """ curr.next = list1 or list2 better than: if list1: current.next = list1 if list2: current.next = list2 """ ############ # recursion class ListNode: def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): self.val = val self.next = next class Solution: def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode: if not l1: # If l1 is empty, return l2 return l2 if not l2: # If l2 is empty, return l1 return l1 if l1.val < l2.val: l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2) return l1 else: l2.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next) return l2 -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func mergeTwoLists(list1 *ListNode, list2 *ListNode) *ListNode { dummy := &ListNode{} curr := dummy for list1 != nil && list2 != nil { if list1.Val <= list2.Val { curr.Next = list1 list1 = list1.Next } else { curr.Next = list2 list2 = list2.Next } curr = curr.Next } if list1 != nil { curr.Next = list1 } else { curr.Next = list2 } return dummy.Next } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function mergeTwoLists(list1: ListNode | null, list2: ListNode | null): ListNode | null { if (list1 == null || list2 == null) { return list1 || list2; } if (list1.val < list2.val) { list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2); return list1; } else { list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next); return list2; } } -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * function ListNode(val, next) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } */ /** * @param {ListNode} list1 * @param {ListNode} list2 * @return {ListNode} */ var mergeTwoLists = function (list1, list2) { const dummy = new ListNode(); let curr = dummy; while (list1 && list2) { if (list1.val <= list2.val) { curr.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } else { curr.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } curr = curr.next; } curr.next = list1 || list2; return dummy.next; }; -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode # attr_accessor :val, :next # def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil) # @val = val # @next = _next # end # end # @param {ListNode} list1 # @param {ListNode} list2 # @return {ListNode} def merge_two_lists(list1, list2) dummy = ListNode.new() cur = dummy while list1 && list2 if list1.val <= list2.val cur.next = list1 list1 = list1.next else cur.next = list2 list2 = list2.next end cur = cur.next end cur.next = list1 || list2 dummy.next end -
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * public int val; * public ListNode next; * public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) { * this.val = val; * this.next = next; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode MergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); ListNode cur = dummy; while (list1 != null && list2 != null) { if (list1.val <= list2.val) { cur.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } else { cur.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1; return dummy.next; } } -
// Definition for singly-linked list. // #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)] // pub struct ListNode { // pub val: i32, // pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>> // } // // impl ListNode { // #[inline] // fn new(val: i32) -> Self { // ListNode { // next: None, // val // } // } // } impl Solution { pub fn merge_two_lists( list1: Option<Box<ListNode>>, list2: Option<Box<ListNode>> ) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> { match (list1, list2) { (None, None) => None, (Some(list), None) => Some(list), (None, Some(list)) => Some(list), (Some(mut list1), Some(mut list2)) => { if list1.val < list2.val { list1.next = Self::merge_two_lists(list1.next, Some(list2)); Some(list1) } else { list2.next = Self::merge_two_lists(Some(list1), list2.next); Some(list2) } } } } } -
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode { # public $val; # public $next; # public function __construct($val = 0, $next = null) # { # $this->val = $val; # $this->next = $next; # } # } class Solution { /** * @param ListNode $list1 * @param ListNode $list2 * @return ListNode */ function mergeTwoLists($list1, $list2) { $dummy = new ListNode(0); $current = $dummy; while ($list1 != null && $list2 != null) { if ($list1->val <= $list2->val) { $current->next = $list1; $list1 = $list1->next; } else { $current->next = $list2; $list2 = $list2->next; } $current = $current->next; } if ($list1 != null) { $current->next = $list1; } elseif ($list2 != null) { $current->next = $list2; } return $dummy->next; } }