Welcome to Subscribe On Youtube
119. Pascal’s Triangle II
Description
Given an integer rowIndex, return the rowIndexth (0-indexed) row of the Pascal's triangle.
In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it as shown:
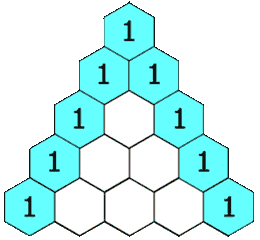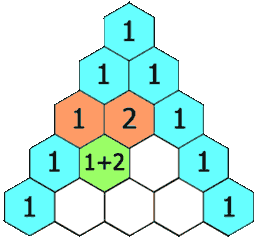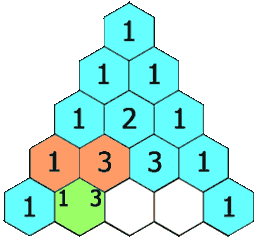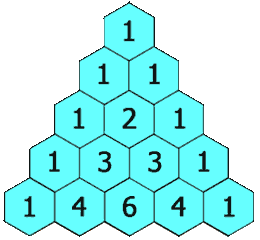
Example 1:
Input: rowIndex = 3 Output: [1,3,3,1]
Example 2:
Input: rowIndex = 0 Output: [1]
Example 3:
Input: rowIndex = 1 Output: [1,1]
Constraints:
0 <= rowIndex <= 33
Follow up: Could you optimize your algorithm to use only O(rowIndex) extra space?
Solutions
Solution 1: Recursion
We create an array $f$ of length $rowIndex + 1$, initially all elements are $1$.
Next, starting from the second row, we calculate the value of the $j$th element in the current row from back to front, $f[j] = f[j] + f[j - 1]$, where $j \in [1, i - 1]$.
Finally, return $f$.
The time complexity is $O(n^2)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ is the given number of rows.
-
class Solution { public List<Integer> getRow(int rowIndex) { List<Integer> f = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < rowIndex + 1; ++i) { f.add(1); } for (int i = 2; i < rowIndex + 1; ++i) { for (int j = i - 1; j > 0; --j) { f.set(j, f.get(j) + f.get(j - 1)); } } return f; } } -
class Solution { public: vector<int> getRow(int rowIndex) { vector<int> f(rowIndex + 1, 1); for (int i = 2; i < rowIndex + 1; ++i) { for (int j = i - 1; j; --j) { f[j] += f[j - 1]; } } return f; } }; -
class Solution: def getRow(self, rowIndex: int) -> List[int]: f = [1] * (rowIndex + 1) for i in range(2, rowIndex + 1): for j in range(i - 1, 0, -1): f[j] += f[j - 1] return f -
func getRow(rowIndex int) []int { f := make([]int, rowIndex+1) for i := range f { f[i] = 1 } for i := 2; i < rowIndex+1; i++ { for j := i - 1; j > 0; j-- { f[j] += f[j-1] } } return f } -
function getRow(rowIndex: number): number[] { const f: number[] = Array(rowIndex + 1).fill(1); for (let i = 2; i < rowIndex + 1; ++i) { for (let j = i - 1; j; --j) { f[j] += f[j - 1]; } } return f; } -
impl Solution { pub fn get_row(row_index: i32) -> Vec<i32> { let n = (row_index + 1) as usize; let mut f = vec![1; n]; for i in 2..n { for j in (1..i).rev() { f[j] += f[j - 1]; } } f } }