You have a binary tree with a small defect. There is exactly one invalid node where its right child incorrectly points to another node at the same depth but to the invalid node's right.
Given the root of the binary tree with this defect, root, return the
root of the binary tree after removing this invalid node and
every node underneath it (minus the node it incorrectly points
to).
Custom testing:
The test input is read as 3 lines:
TreeNode rootint fromNode(not available tocorrectBinaryTree)int toNode(not available tocorrectBinaryTree)
After the binary tree rooted at root is parsed, the
TreeNode with value of fromNode will have its right child
pointer pointing to the TreeNode with a value of toNode.
Then, root is passed to correctBinaryTree.
Example 1:
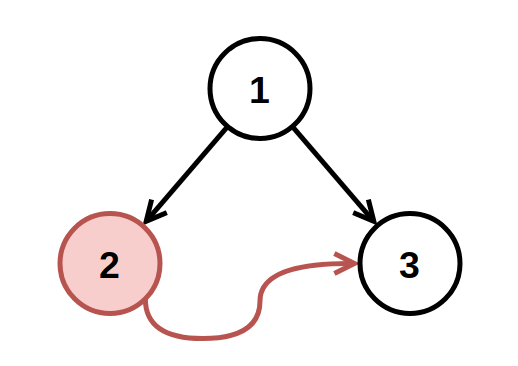
Input: root = [1,2,3], fromNode = 2, toNode = 3 Output: [1,null,3] Explanation: The node with value 2 is invalid, so remove it.
Example 2:
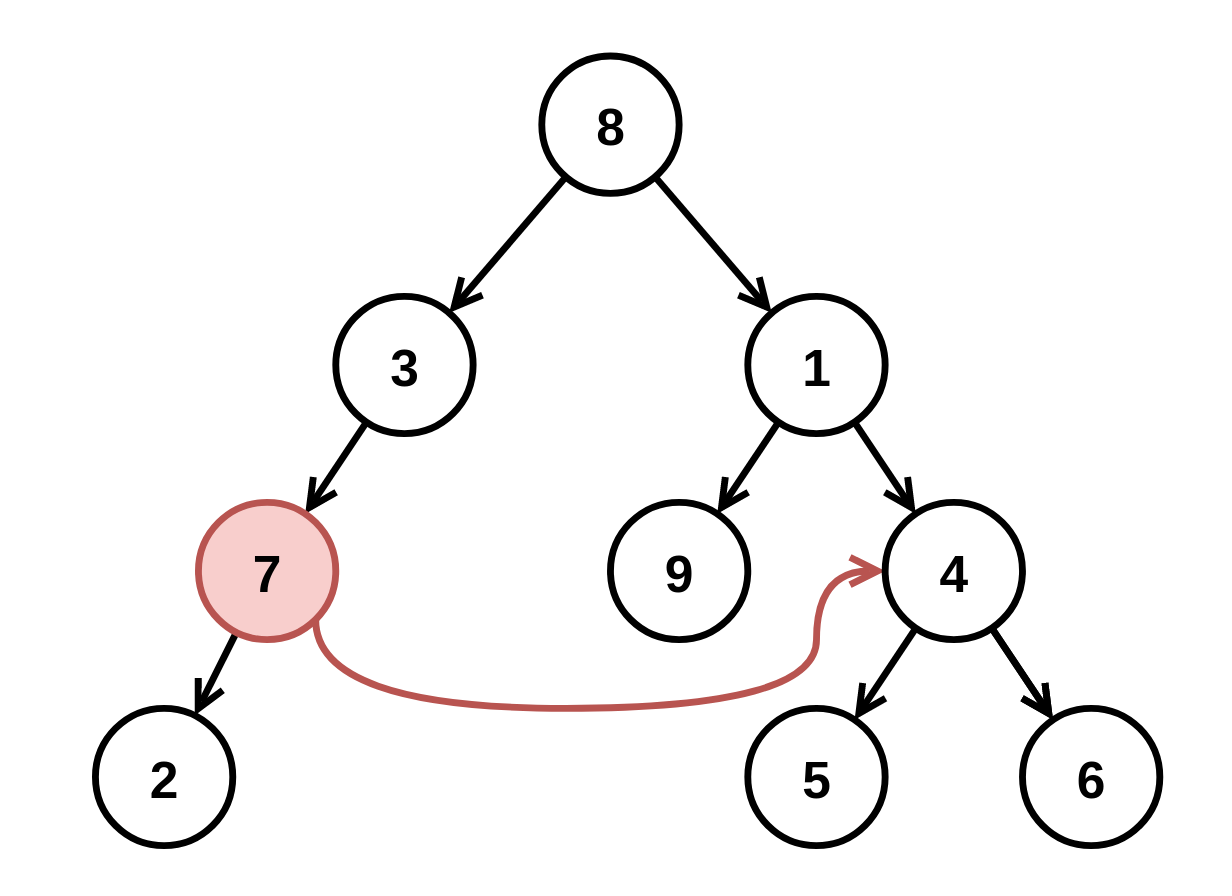
Input: root = [8,3,1,7,null,9,4,2,null,null,null,5,6], fromNode = 7, toNode = 4 Output: [8,3,1,null,null,9,4,null,null,5,6] Explanation: The node with value 7 is invalid, so remove it and the node underneath it, node 2.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[3, 104]. -109 <= Node.val <= 109- All
Node.valare unique. fromNode != toNodefromNodeandtoNodewill exist in the tree and will be on the same depth.toNodeis to the right offromNode.fromNode.rightisnullin the initial tree from the test data.