Given the root of a binary tree and a node u in the tree,
return the nearest node on the same level that is
to the right of u, or return
null if u is the rightmost node in its level.
Example 1:
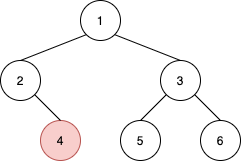
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4,5,6], u = 4 Output: 5 Explanation: The nearest node on the same level to the right of node 4 is node 5.
Example 2:
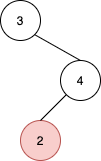
Input: root = [3,null,4,2], u = 2 Output: null Explanation: There are no nodes to the right of 2.
Example 3:
Input: root = [1], u = 1 Output: null
Example 4:
Input: root = [3,4,2,null,null,null,1], u = 4 Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- All values in the tree are distinct.
uis a node in the binary tree rooted atroot.
Difficulty:
MediumLock:
PrimeCompany:
GoogleProblem Solution
1602-Find-Nearest-Right-Node-in-Binary-TreeAll Problems:
Link to All Problems
All contents and pictures on this website come from the Internet and are updated regularly every week. They are for personal study and research only, and should not be used for commercial purposes. Thank you for your cooperation.