(This problem is an interactive problem.)
A binary matrix means that all elements
are 0 or 1. For each individual
row of the matrix, this row is sorted in non-decreasing order.
Given a row-sorted binary matrix binaryMatrix, return leftmost column
index(0-indexed) with at least a 1 in it. If such index doesn't
exist, return -1.
You can't access the Binary Matrix directly. You may only
access the matrix using a BinaryMatrix interface:
BinaryMatrix.get(row, col)returns the element of the matrix at index(row, col)(0-indexed).BinaryMatrix.dimensions()returns a list of 2 elements[rows, cols], which means the matrix isrows * cols.
Submissions making more than 1000 calls to BinaryMatrix.get will
be judged Wrong Answer. Also, any solutions that attempt to
circumvent the judge will result in disqualification.
For custom testing purposes you're given the binary matrix mat as
input in the following four examples. You will not have access the binary
matrix directly.
Example 1:
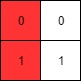
Input: mat = [[0,0],[1,1]] Output: 0
Example 2:
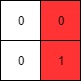
Input: mat = [[0,0],[0,1]] Output: 1
Example 3:
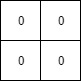
Input: mat = [[0,0],[0,0]] Output: -1
Example 4:
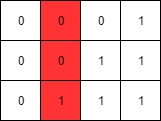
Input: mat = [[0,0,0,1],[0,0,1,1],[0,1,1,1]] Output: 1
Constraints:
rows == mat.lengthcols == mat[i].length1 <= rows, cols <= 100mat[i][j]is either0or1.mat[i]is sorted in a non-decreasing way.