Given the root of a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct
value.
After deleting all nodes with a value in to_delete, we are left with a
forest (a disjoint union of trees).
Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
Example 1:
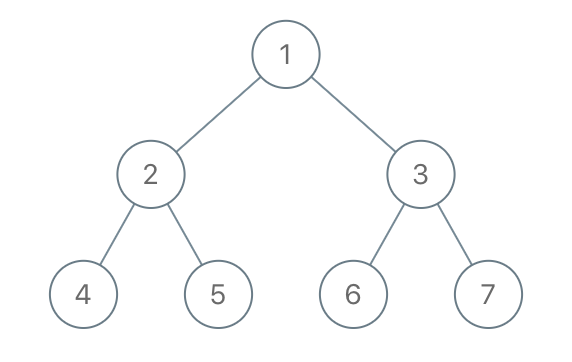
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], to_delete = [3,5] Output: [[1,2,null,4],[6],[7]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree is at most
1000. - Each node has a distinct value between
1and1000. to_delete.length <= 1000to_deletecontains distinct values between1and1000.
Difficulty:
MediumLock:
NormalCompany:
GoogleProblem Solution
1110-Delete-Nodes-And-Return-ForestAll Problems:
Link to All Problems
All contents and pictures on this website come from the Internet and are updated regularly every week. They are for personal study and research only, and should not be used for commercial purposes. Thank you for your cooperation.